Abstract
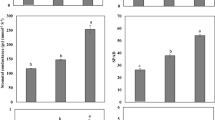
Soil heavy metal pollution exists worldwide and strongly affects the crop yield. The passivating agents have been demonstrated to reduce the heavy metal content in plants and relieve the heavy metal stress to plants. This study aimed to compare the alleviation effects of four passivating agents on maize growth under heavy metal pollution. We conducted a comparison experiment in the greenhouse and set up five treatments such as H (heavy metals), HB (heavy metals and 2% biochar), HW (heavy metals and 2% garden waste), HL (heavy metals and 2% lime), and HD (heavy metals and 2% diatomite) and measured the growth index and photosynthetic parameters of maize to compare the passivation effects. Our results showed that the addition of garden waste exhibited the greatest effects on increasing soil NH4+, NO3−, and available P content. The garden waste, lime, and biochar application all increased the transpiration rate (Tr), net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), photochemical quenching (qP), and electron transfer rate (ETR) of maize. Moreover, the garden waste stimulated the plant height, single biomass, and root length of maize. Our study demonstrates that biochar, garden waste, and lime all enhance the photosynthesis and growth of maize and mitigate the heavy metal stress of maize. Therefore, the addition of passivating agents may play an important role in relieving heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils. The study is also potentially beneficial for the remediation of heavy metal–polluted agricultural soils, soil ecological health, and food security.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas A, Azeem M, Naveed M, Latif A, Bashir S, Ali A, Bilal M, Ali L (2020) Synergistic use of biochar and acidified manure for improving growth of maize in chromium contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediat 22:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1644286
Akhtar T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Naeem A, Nawaz R, Ali S, Murtaza G, Maqsood MA, Azhar M, Khalid H, Rizwan M (2017) Photosynthesis and growth response of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids exposed to cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:5521–5529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8246-0
Ali E, Maodzeka A, Hussain N, Shamsi IH, Jiang L (2015) The alleviation of cadmium toxicity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by the application of salicylic acid. Plant Growth Regul 75:641–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9966-0
Ayoub F-N, Cristina B, Rebeca G, Angeles CM, Alejandra S (2021) Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging as a tool to evaluate calyx senescence during the ripening of persimmon fruit treated with gibberellic acid. Postharvest Biol Tec 179:111582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2021.111582
Baruah SG, Ahmed I, Das B, Ingtipi B, Boruah H, Gupta SK, Nema AK, Chabukdhara M (2021) Heavy metal (loid)s contamination and health risk assessment of soil-rice system in rural and peri-urban areas of lower Brahmaputra valley, northeast India. Chemosphere 266:129150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129150
Bashir MA, Naveed M, Ahmad Z, Gao B, Núñez-Delgado A (2020) Combined application of biochar and sulfur regulated growth, physiological, antioxidant responses and Cr removal capacity of maize (Zea mays L.) in tannery polluted soils. J Environ Manage 259:110051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110051
Björkman O, Demmig B (1987) Photon yield of O2 evolution and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics at 77 K among vascular plants of diverse origins. Planta 170:489–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402983
Boriskov D, Efremova S, Komarova N, Tikhomirova E, Bodrov A (2021) Applicability of the modified diatomite for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metals. E3S Web of Conferences 247:01052. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202124701052
Bossolani JW, Crusciol CAC, Momesso L, Portugal JR, Moretti LG, Garcia A, de Cássia da Fonseca M, Rodrigues VA, Calonego JC, dos Reis AR (2022) Surface liming triggers improvements in subsoil fertility and root distribution to boost maize crop physiology, yield and revenue. Plant Soil 477:319–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05432-2
Carpenter RL, Jiang B-H (2013) Roles of EGFR, PI3K, AKT, and mTOR in heavy metal-induced cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Tar 13:337–372. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009611313030004
Cayuela ML, Mondini C, SM MA, Roig A (2008) Chemical properties and hydrolytic enzyme activities for the characterisation of two-phase olive mill wastes composting. Bioresource Technol 99:4255–4262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.057
Chandra R, Kang H (2016) Mixed heavy metal stress on photosynthesis, transpiration rate, and chlorophyll content in poplar hybrids. For Sci Technol 12:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2015.1044024
Chen Y, Xie T, Liang Q, Liu M, Zhao M, Wang M, Wang G (2016) Effectiveness of lime and peat applications on cadmium availability in a paddy soil under various moisture regimes. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:7757–7766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5930-4
Cho HH, Wepasnick K, Smith BA, Bangash FK, Fairbrother DH, Ball WP (2010) Sorption of aqueous Zn[II] and Cd[II] by multiwall carbon nanotubes: the relative roles of oxygen-containing functional groups and graphenic carbon. Langmuir 26:967–981. https://doi.org/10.1021/la902440u
Cui N, Qu L, Wu G (2022) Heavy metal accumulation characteristics and physiological response of Sabina chinensis and Platycladus orientalis to atmospheric pollution. J Environ Sci 112:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.05.013
Do Carmo LI, Bursztyn Fuentes AL, de los Ríos A, Fabrizio de Iorio A, Rendina AE (2021) Effects of green waste compost addition to dredged sediments of the Matanza-Riachuelo River (Argentina) on heavy metal extractability and bioaccumulation in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Water Air Soil Poll 232:200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05161-9
Edelstein M, Ben Hur M (2018) Heavy metals and metalloids: sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci Hortic 234:431–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.12.039
Fang X, Li Y, Nie J, Wang C, Huang K, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, She H, Liu X, Ruan R (2018) Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and grain yield in common buckwheat ( Fagopyrum esculentum M.). Field Crop Res 219:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.02.001
Flores-Cano JV, Leyva-Ramos R, Padilla-Ortega E, Mendoza-Barron J (2013) Adsorption of heavy metals on diatomite: mechanism and effect of operating variables. Adsorp Sci Technol 31:275–291. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.31.2-3.275
Ghorbani M, Konvalina P, Neugschwandtner RW, Kopecký M, Amirahmadi E, Moudrý J, Menšík L (2022) Preliminary findings on cadmium bioaccumulation and photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) using biochar made from C3- and C4-originated straw. Plants 11:1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111424
Gouma V, Tziasiou C, Pournara AD, Giokas DL (2022) A novel approach to sorbent-based remediation of soil impacted by organic micropollutants and heavy metals using granular biochar amendment and magnetic separation. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107316
Guo X (2012) Effect of lime and superphosphate on maize production and heavy metals uptake by low-accumulating maize. J Environ Eng 6:1374–1380
Guo XF, Wei ZB, Wu QT, Qiu JR, Zhou JL (2011) Cadmium and zinc accumulation in maize grain as affected by cultivars and chemical fixation amendments. Pedosphere 21:650–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(11)60167-7
Haider F, Farooq M, Naveed M, Alam S, Ain N, Salim M, Liqun C, Mustafa A (2022) Influence of biochar and microorganism co-application on stabilization of cadmium (Cd) and improved maize growth in Cd-contaminated soil. Front Plant Sci 13:983830. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.983830
Hao DC, Zhou JQ, Wang C, Han J (2017) Plant bionic remediation and phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil. Biotechnol Bull 33:66–71
He Y, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Wang S, Liu SL, He HB, Zhu HH, Xu C (2017) A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotox Environ Safe 136:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.005
Hermle S, Vollenweider P, Günthardt-Goerg MS, McQuattie CJ, Matyssek R (2007) Leaf responsiveness of Populus tremula and Salix viminalis to soil contaminated with heavy metals and acidic rainwater. Tree Physiol 27:1517–1531. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/27.11.1517
Huang M, Zhu Y, Li Z, Huang B, Luo N, Liu C, Zeng G (2016) Compost as a soil amendment to remediate heavy metal-contaminated agricultural soil: mechanisms, efficacy, problems, and strategies. Water Air Soil Poll 227:359.351-359.318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3068-8
Huo K, Shangguan X, Xia Y, Shen Z, Chen C (2020) Excess copper inhibits the growth of rice seedlings by decreasing uptake of nitrate. Ecotox Environ Safe 190:110105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110105
Irfan M, Mudassir M, Khan MJ, Dawar KM, Muhammad D, Mian IA, Ali W, Fahad S, Saud S, Hayat Z, Nawaz T, Khan SA, Alam S, Ali B, Banout J, Ahmed S, Mubeen S, Danish S, Datta R et al (2021) Heavy metals immobilization and improvement in maize (Zea mays L.) growth amended with biochar and compost. Sci Rep 11:18416. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97525-8
Jain R, Verma R, Singh A, Chandra A, Solomon S (2015) Influence of selenium on metallothionein gene expression and physiological characteristics of sugarcane plants. Plant Growth Regul 77:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0042-1
Jasiewicz C, Antonkiewicz J (2002) Heavy metal contents in maize cultivated in soils contaminated with these metals. Chemia i Inżynieria Ekologiczna 9:373–377
Ji Y, Xie X, Wang G (2018) Effects of the heavy metal cadmium on photosynthetic activity and the xanthophyll cycle in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Oceanol Limnol 36:2194–2201
Ke S, Cheng XY, Zhang N, Hu HG, Yan Q, Hou LL, Sun X, Chen ZN (2015) Cadmium contamination of rice from various polluted areas of China and its potential risks to human health. Environ Monit Assess 187:408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4638-8
Khatiwada B, Hasan MT, Sun A, Kamath KS, Mirzaei M, Sunna A, Nevalainen H (2020) Probing the role of the chloroplasts in heavy metal tolerance and accumulation in Euglena gracilis. Microorganisms 8:115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010115
Kong S, Tang J, Ouyang F, Chen M (2021) Research on the treatment of heavy metal pollution in urban soil based on biochar technology. Environ Technol Inno 23:101670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101670
Li J (2009) Production, breeding and process of maize in China. In: Bennetzen JL, Hake SC (eds) Handbook of maize: its biology. Springer New York, New York, NY, pp 563–576
Li D, Liu G, Li X, Li R, Wang J, Zhao Y (2022) Heavy metal (loid)s pollution of agricultural soils and health risk assessment of consuming soybean and wheat in a typical non-ferrous metal mine area in Northeast China. Sustainability 14:2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052953
Liang XH, Cao TH (2010) Effects of heavy metal growth, development and yield of maize. J Maize Sci 18:86–88. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1142.2010.40491
Liu K, Lv J, He W, Zhang H, Cao Y, Dai Y (2015) Major factors influencing cadmium uptake from the soil into wheat plants. Ecotox Environ Safe 113:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.005
Majeda AMK, Al-Degs YS, Mcminn W (2004) Remediation of wastewater containing heavy metals using raw and modified diatomite. Chem Eng 99:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2003.11.029
Manara A, Fasani E, Molesini B, DalCorso G, Pennisi F, Pandolfini T, Furini A (2020) The tomato metallocarboxypeptidase inhibitor I, which interacts with a heavy metal-associated isoprenylated protein, is implicated in plant response to cadmium. Molecules 25:700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030700
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth T (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Nguyen XC (2015) The effects of heavy metals, phosphate, lime and sawdust on plant growth and heavy metal accumulation by lettuce. J Agr Biol Sci 10:241–246
Pant H, Singh VLR (2020) Lead toxicity in plants and phytoremediation potential of aromatic plants for lead contaminated soils. J Med Aroma Plant Sci 42:205–219 https://doi.org/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350373274
Pospíilová J, Schulze ED, Caldwell MM (1995) Ecophysiology of photosynthesis. Biol Plantarum 37:560–560
Qin G, Niu Z, Yu J, Li Z, Ma J-Y, Xiang P (2021) Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 267:129205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129205
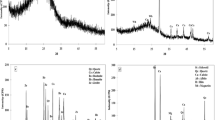
Qu F, Fan CW, Liu GH, Chen XY, Qin S (2019) Effects of different passivating agents on the effective state of heavy metals in typical yellow soil in Guizhou. Journal of Southern Agriculture 50:1967–1972. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2019.09.11
Rabinowitch I, Ylj J (1935) Chemistry of photosynthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 3:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1101/SQB.1935.003.01.020
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Abbas Z, Hannan F (2017) Use of maize (Zea mays L.) for phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Geochem Hlth 39:259–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9826-0
Schulz H (2012) Effects of biochar compared to organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil quality and plant growth in a greenhouse experiment. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 175:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201100143
Sorkhi F, Fateh M (2014) Effect of density on grain yield, biological yield and harvest index on corn hybrids of SC301 and SC320. Int J Biosciences 5:21–26. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/5.6.21-8
Sui F, Zuo J, Chen D, Li L, Pan G, Crowley DE (2018) Biochar effects on uptake of cadmium and lead by wheat in relation to annual precipitation: a 3-year field study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:3368–3377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0652-4
Tong W, Hamid Y, Hussain B, Usman M, Sher A, Liu L, Yang X (2020) The effect of single and composite additives on Cd and Pb mobility, speciation and accumulation in late rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown on contaminated soil. Appl Ecol Env Res 18:4207–4221. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1803_42074221
Tóth G, Hermann T, Szatmári G, Pásztor L (2016) Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci Total Environ 565:1054–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.115
Türkdoğan MK, Kilicel F, Kara K, Tuncer I, Uygan I (2003) Heavy metals in soil, vegetables and fruits in the endemic upper gastrointestinal cancer region of Turkey. Environ Toxicol Phar 13:175–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1382-6689(02)00156-4
Ullah R, Ullah W, Shah F, Saleem A, Zia-Ur-Rahman A, SAA K, Wu ZH (2020) Evaluation of different maize varieties for yield and yield contributing traits. Int J Biosciences 16:150–161. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/16.1.150-161
Unuabonah EI, Adebowale KO, Olu-Owolabi BI, Yang LZ, Kong LX (2008) Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions onto sodium tetraborate-modified Kaolinite clay: equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Hydrometallurgy 93:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.02.009
Wang Y, Qiu Q, Shaoshan LI, Xin G (2014) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on heavy metal uptake of maize under Cd and Cu combined pollution conditions. Science and Technology Review 32:15–20. https://doi.org/10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.21.001
Wang S, Chen D, Yuxi LI, Junping XU, Jiang Y, Sheng B (2018) Humic composition of mixed materials affected by the ratio of turf grass clippings and fallen leaves frompopulus alba 'berolinensis' l.& hosta plantaginea aschers. Northern Horticulture 42:78–83. https://doi.org/10.11937/bfyy.20172590
Wang Q, Js L, Poon CS (2019) Recycling of incinerated sewage sludge ash as an adsorbent for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions. J Environ Manage 247:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.115
Waqas M, Khan AL, Kang SM, Kim YH, Lee IJ (2014) Phytohormone-producing fungal endophytes and hardwood-derived biochar interact to ameliorate heavy metal stress in soybeans. Biol Fert Soils 50:1155–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0937-4
Wei L, Huang Y, Huang L, Huang Q, Liu Z (2021) Combined biochar and soda residues increases maize yields and decreases grain Cd/Pb in a highly Cd/Pb-polluted acid Udults soil. Agr Ecosyst Environ 306:107198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107198
Winter TR, Borkowski L, Zeier J, Rostás M (2012) Heavy metal stress can prime for herbivore-induced plant volatile emission. Plant Cell Environ 35:1287–1298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02489.x
Xu Y (2017) Stabilization of heavy metal-contaminated sediment with a chelator and humic acid mixture. Water Air Soil Poll 228:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3198-z
Ye S, Wang L, Liu T (2022) Study of solidification and stabilization of heavy metals by passivators in heavy metal-contaminated soil. Open Chem 20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2021-0101
Yu Z, Phanpadith P, Zhang S, Yu D, Kang Y (2017) Biochar-morel promotes wheat saline resistance by increasing root/shoot ratio. Fresen Environ Bull 25:7667–7673 https://doi.org/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326403938
Zhang S, Wen J, Hu Y, Fang Y, Zhang H, Xing L, Wang Y, Zeng G (2018) Humic substances from green waste compost: an effective washing agent for heavy metal (Cd, Ni) removal from contaminated sediments. J Hazard Mater 366:210–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.103
Zhang G, Ba Q, Chen S, Liu F, Li G (2020) Exogenous application of glycine betaine alleviates cadmium toxicity in super black waxy maize by improving photosynthesis, the antioxidant system and glutathione-ascorbic acid cycle metabolites. Cereal Res Commun 48:449–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-020-00062-9
Zhang Q, Zou D, Zeng X, Li L, Wang A, Liu F, Wang H, Zeng Q, Xiao Z (2021) Effect of the direct use of biomass in agricultural soil on heavy metals _ activation or immobilization? Environ Pollut 272:115989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115989
Zhao JR, Wang RH (2013) Development process, problem and countermeasure of maize production in China. J Agr Sci Tech-Iran 15:1–6
Zhou J, Yu Y-W, Jiang Y, Yang Y-H, Zhang C (2019) Effect of biochar on available heavy metals during sewage sludge composting and land application of compost. Huanjing Kexue 40:987–993. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201804184
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 31800443, 32160288, 32272818), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) program (grant number: 2019QZKK0308), the Thousand Young Talents Program of Yunnan Province, the Double Top University Plan Fund of Yunnan University (grant number: C176220100044), and the 2021 Low-carbon Development Guidance Project of Yunnan Province, China (No. 135). We appreciated the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, G., Tang, J., Huang, J. et al. Passivating Agents Relieved Cu and Cd Pollution on Maize Growth. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 2030–2038 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01159-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01159-w