Abstract
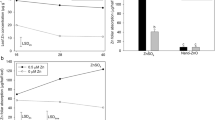
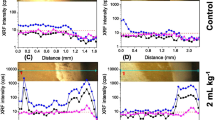
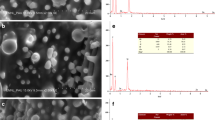
Due to a zinc-deficient diet, about 800,000 children die each year worldwide. This aspect is amended by exploiting foliar fertilization, a useful alternative to improve crop yield and nutritional quality of food crops. The aim of this study was then to investigate the leaf uptake and transport of zinc by soybean (Glycine max (L) Merrill). Plant leaves were treated with Zn phosphite and Zn ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) commercial formulations. X-ray spectroscopy (XRF and XANES) was exploited to trace nutrient movement in the petiolule and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to evaluate the influence of leaf surface treatments. No radiation damage, in terms of elemental redistribution, was observed during the XRF and XANES measurements. As an alternative to radioisotopes, XRF allowed to detect the movement of Zn from both sources in the plant petiolule. Both fertilizers disintegrated leaf epicuticular wax crystals, yet accumulation of sediments in the vicinity of stomata was noted only for Zn phosphite. Absorption and redistribution of Zn were higher for plants that received Zn phosphite. Zinc supplied as Zn phosphite was transported in a form different from that of the pristine Zn phosphite, whereas Zn supplied as Zn EDTA was transported in its chelated form.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data are available in the ESI zip file.
References
Avellan A, Yun J, Zhang YL, Spielman-Sun E, Unrine JM, Thieme J, Li JR, Lombi E, Bland G, Lowry GV (2019) Nanoparticle size and coating chemistry control foliar uptake pathways, translocation, and leaf-to-rhizosphere transport in wheat. ACS Nano 13:5291–5305. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b09781
Aytaç S, Çirak C, Ozçelik H (2007) Foliar zinc application on yield and quality characters of soybean. Asian J Chem 19(3):2410–2418
Bala R, Kalia A, Dhaliwal SS (2019) Evaluation of efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles as remedial zinc nanofertilizer for rice. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00040-z
Brennan RF (1996) Effectiveness of different sources of manganese foliar sprays in alleviating manganese deficiency of Lupinus angustifolius L grown on manganese deficient soils in western Australia. J Plant Nutr 19:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169609365123
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marschner P (ed) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 191–248
Burkhardt J (2010) Hygroscopic particles on leaves: nutrients or desiccants? Ecol Monogr 80:369–399. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1988.1
Burkhardt J, Zinsmeister D, Grantz DA, Vidic S, Sutton MA, Hunsche M (2018) Pariyar S (2018) Camouflaged as degraded wax: hygroscopic aerosols contribute to leaf desiccation, tree mortality, and forest decline. Environ Res Lett 13:085001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aad346
Cakmak I, Kutman UB (2018) Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur J Soil Sci 69:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12437
Cakmak I, Kalayci M, Kaya Y, Torun AA, Aydin N, Wang Y, Arisoy Z, Erdem H, Yazici A, Gokmen O, Ozturk L, Horst WJ (2010) Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. J Agric Food Chem 58:9092–9102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101197h
Caulfield LE, Black RE (2004) Zinc deficiency. In: Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers AA, Murray CJL (eds) Comparative quantification of health risks: global and regional burden of disease attribution to selected major risk factors. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 257–279
Doolette CL, Read TL, Li C, Scheckel KG, Donner E, Kopittke PM, Schjoerring JK, Lombi E (2018) Foliar application of zinc sulphate and zinc EDTA to wheat leaves: differences in mobility, distribution, and speciation. J Exp Bot 69:4469–4481. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery236
Du YM, Kopittke PM, Noller BN, James SA, Harris HH, Xu ZP, Li P, Mulligan DR, Huang LB (2015) In situ analysis of foliar zinc absorption and short-distance movement in fresh and hydrated leaves of tomato and citrus using synchrotron-based X-ray fluorescence microscopy. Ann Bot-London 115:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu212
Edwards HH, Bonde MR (2011) Penetration and establishment of Phakopsora pachyrhizi in soybean leaves as observed by transmission electron microscopy. Phytopathology 101(7):894–900. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-09-10-0248
Eichert T, Fernández V (2012) Uptake and release of elements by leaves and other aerial plant. In: Marschner P (ed) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 71–84
Eichert T, Goldbach HE (2008) Equivalent pore radii of hydrophilic foliar uptake routes in stomatous and astomatous leaf surfaces - further evidence for a stomatal pathway. Physiol Plant 132:491–502. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.01023.x
Eichert T, Kurtz A, Steiner U, Goldbach HE (2008) Size exclusion limits and lateral heterogeneity of the stomatal foliar uptake pathway for aqueous solutes and water-suspended nanoparticles. Physiol Plant 134:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01135.x
Fernandez V, Brown PH (2013) From plant surface to plant metabolism: the uncertain fate of foliar-applied nutrients. Front Plant Sci 4:289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00289
Fernandez V, Stiropoulos T, Brown PH (2013) Foliar fertilization: scientific principles and field pratices. International Fertilizer Industry Association. ISBN 979-10-92366-00-6
Fernandez V, Bahamonde HA, Peguero-Pina JJ, Gil-Pelegrin E, Sancho-Knapik D, Gil L, Goldbach HE, Eichert T (2017) Physico-chemical properties of plant cuticles and their functional and ecological significance. J Exp Bot 68:5293–5306. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx302
Ferrandon M, Chamel AR (1988) Cuticular retention, foliar absorption and translocation of Fe, Mn and Zn supplied in organic and inorganic form. J Plant Nutr 11:247–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168809363800
Gangloff WJ, Westfall DG, Peterson GA, Mortvedt JJ (2002) Relative availability coefficients of organic and inorganic Zn fertilizers. J Plant Nutr 25:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1081/pln-100108834
Ghasal PC, Shivay YS, Pooniya V, Choudhary M, Verma RK (2017) Zinc accounting for different varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum) under different source and methods of application. Indian J Agric Sci 87:1111–1116
Goodwin SM, Jenks M (2005) Plant cuticle function as a barrier to water loss. In: Jenks M, Hasegawa PM (eds) Plant abiotic stress. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 14–36
Gozzo F, Faoro F (2013) Systemic acquired resistance (50 years after discovery): moving from the lab to the field. J Agric Food Chem 61:12473–12491. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404156x
Guilherme LRG, Corguinha APB, Souza GA, Sacco M, Menezes MD (2015) Zinc availability in Brazillian agroecosystems. Proceedings of the 4th International Zinc Symposium: Improving Crop Production and Human Health, São Paulo, Brazil, p 59–49
Kayan N, Gulmezoglu N, Kaya MD (2015) The optimum foliar zinc source and level for improving Zn content in seed of chickpea. Legume Res 38:826–831. https://doi.org/10.18805/lr.v38i6.6731
Kinaci E, Gulmezoglu N (2007) Grain yield and yield components of triticale upon application of different foliar fertilizers. Interciencia 32:624–628
Li C, Wang P, Menzies NW, Lombi E, Kopittke PM (2017) Effects of changes in leaf properties mediated by methyl jasmonate (MeJA) on foliar absorption of Zn, Mn and Fe, Ann. Botany 120(3):405–415. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx063
Li C, Wang P, Lombi E, Cheng M, Tang C, Howard DL, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2018) Absorption of foliar-applied Zn fertilizers by trichomes in soybean and tomato, J experimental Botany69(10). Issue 10(27):2717–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery085
Lombi E, Scheckel KG, Kempson IM (2011b) In situ analysis of metal(loid)s in plants: state of the art and artefacts. Environ Exp Bot 72:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.04.005
McDonald AE, Grant BR, Plaxton WC (2001) Phosphite (phosphorous acid): its relevance in the environment and agriculture and influence on plant phosphate starvation response. J Plant Nutr 24:1505–1519
Montalvo D, Degryse F, Silva RC, Baird R, Mclaughlin (2016) Chapter five - agronomic effectiveness of zinc sources as micronutrient fertilizers. Adv Agron 139:215–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2016.05.004
Neinhuis C, Koch K, Barthlott W (2001) Movement and regeneration of epicuticular waxes through plant cuticles. Planta 213(3):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250100530
Peryea FJ (2006) Phytoavailability of zinc in postbloom zinc sprays applied to ‘Golden Delicious’ apple trees. HortTechnology 16:60–65. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH.16.1.0060
Phattarakul N, Rerkasem B, Li LJ, Wu LH, Zou CQ, Ram H, Sohu VS, Kang BS, Surek H, Kalayci M, Yazici A, Zhang FS, Cakmak I (2012) Biofortification of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries. Plant Soil 361:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1211-x
Ristic Z, Jenks MA (2002) Leaf cuticle and water loss in maize lines differing in dehydration avoidance. J Plant Physiol 159:645–651
Rogiers SY, Whitelaw-Weckert M, Radovanonic-Tesic M, Greer LA, White RG, Steel CC (2005) Effects of spray adjuvants on grape (Vitis vinifera) berry microflora, epicuticular wax and susceptibility to infection by Botrytis cinerea. Aust Plant Pathol 34:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP05031
Santos LR, Silva BRS, Pedron T, Batista BL, Lobato KS (2020) 24-Epibrassinolide improves root anatomy and antioxidant enzymes in soybean plants subjected to zinc stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:105–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00105-z
Scheckel KG, Lombi E, Rock SA, McLaughlin MJ (2004) In vivo synchrotron study of thallium speciation and compartmentation in lberis intermedia. Environ Sci Technol 38:5095–5100. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049569g
Schlegel TK, Schönherr J, Schreiber L (2006) Rates of foliar penetration of chelated Fe (III): role of light, stomata, species, and leaf age. J Agric Food Chem 54(18):6809–6813
Silva MLDS, Vitti GC, Trevizam AR (2014) Heavy metal toxicity in rice and soybean plants cultivated in contaminated soil. Rev Ceres 61:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-737X2014000200013
Singh P, Shukla AK, Behera SK, Pk T (2019) Zinc application enhances superoxide dismutase and carbonic anhydrase activities in zinc-efficient and zinc-inefficient wheat genotypes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00038-7
Slaton NA, Norman RJ, Wilson CE (2005) Effect of zinc source and application time on zinc uptake and grain yield of flood-irrigated rice. Agron J 97:272–278. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2005.0272
Smith E, Kempson I, Juhasz AL, Weber J, Skinner WM, Grafe M (2009) Localization and speciation of arsenic and trace elements in rice tissues. Chemosphere 76:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.03.010
Wei YY, Shohag MJI, Yang XE (2012) Biofortification and bioavailability of rice grain zinc as affected by different forms of foliar zinc fertilization. Plos One:7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045428
Zou CQ, Zhang YQ, Rashid A, Ram H, Savasli E, Arisoy RZ, Ortiz-Monasterio I, Simunji S, Wang ZH, Sohu V, Hassan M, Kaya Y, Onder O, Lungu O, Mujahid MY, Joshi AK, Zelenskiy Y, Zhang FS, Cakmak I (2012) Biofortification of wheat with zinc through zinc fertilization in seven countries. Plant Soil 361:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1369-2
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Brazilian Synchrotron Light Source (LNLS) for providing beamtime at XRF beamline (proposals 20180650 & 20180167), to Dr. C.A. Perez for his assistance during beamtime, and to E.W. Kitajima (ESALQ-USP) for providing electron microscopy facilities. We also thank Prof. E.A.G. Zagatto for his invaluable contribution during the writing of the manuscript.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) under the grants 2015/19121-8, 2015/05942-0, and 2018/13401-7. Partial support by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brasil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001 is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. H. F. Gomes and B. A. Machado carried out plant growth, fertilizer application, and the XRF and XANES measurements. J. P. R. Marques was responsible for obtaining the SEM images. Data interpretation and discussion were carried out by M. H. F. Gomes, J. P. R. Marques, R. Otto, T. Eichert, and H. W. P. Carvalho. M. H. F. Gomes wrote the first manuscript draft which was reviewed and edited by the other authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5956 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomes, M.H.F., de Almeida Machado, B., Marques, J.P.R. et al. Foliar Application of Zn Phosphite and Zn EDTA in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill): In Vivo Investigations of Transport, Chemical Speciation, and Leaf Surface Changes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 2731–2739 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00338-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00338-3