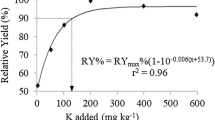
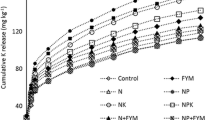
Abstract
The objective of this study was to obtain sufficient estimates of quantity-intensity (Q/I) parameters using a single-point method, and to evaluate the role of cation exchange capacity (CEC) and Gapon selectivity coefficient (KG) as parameters that improve prediction model’s estimation accuracy or explain its limitations under conditions of K deficiency. Regression models were applied on raw data derived from previews Q/I experiments conducted on 20 soils of northern Greece at initial and K-depleted treatment states. Relationships between soil K adsorbed or released (ΔΚ), or K activity ratios at each K addition (ARK) and respective values at equilibria (-ΔΚ0, AReK) were tested to find the best fitting models. CEC was included in regression models to improve their performance, while KG parameter was assessed for initial and K-depleted soils. The study showed that Q/I parameters were well predicted with the single-point method for a wide range of K saturation ratios, by applying 0.01 M CaCl2 and 10 mg L−1 K addition. Furthermore, CEC significantly improved model’s estimation accuracy. Under the ΔG breakpoint of − 14.67 kJ mol−1, specific adsorption sites of the soil inner-sphere region weaken the single-point prediction efficacy, as was clearly indicated by the KG formation under conditions of K depletion. The study suggests that the proposed method is applicable for estimating Q/I parameters for soils covering a wide range of K activity ratios. Moreover, CEC and KG parameters constitute useful tools in improving prediction model’s estimation accuracy, or explaining their limitations under conditions of K deficiency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow NJ (2000) Towards a single-point method for measuring phosphate sorption by soils. Aust J Soil Res 38:1099–1113
Beckett PHT (1964a) Studies on soil potassium: I. Confirmation of the ratio law: measurement of potassium potential. J Soil Sci 15:1–8
Beckett PHT (1964b) Studies on soil potassium: II. The “immediate” Q/I relations of labile potassium in the soil. J Soil Sci 15:9–23
Bilias F, Barbayiannis N (2018) Contribution of non-exchangeable potassium on its quantity-intensity relationships under K-depleted soils. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:1988–2004
Bilias F, Barbayiannis N (2019a) Potassium availability: an approach using thermodynamic parameters derived from quantity-intensity relationships. Geoderma 338:355–364
Bilias F, Barbayiannis N (2019b) Potassium fixing clay minerals as parameters that define K availability of K-deficient soil assessed with a modified Mitscherlich equation model. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:830–840
Das D, Dwivedi BS, Datta SP, Datta SC, Meena MC, Agarwal BK, Shahi DK, Singh M, Chakraborty D, Jaggi S (2019) Potassium supplying capacity of a red soil from eastern India after forty-two years of continuous cropping and fertilization. Geoderma 341:76–92
Evangelou VP, Wang J, Phillips RE (1994) New developments and perspectives on soil potassium quantity/intensity relationships. Adv Agron 52:173–227
Halvin JL, Tisdale SL, Nelson WL, Beaton JD (2014) Soil fertility and fertilizers: an introduction to nutrient management, 8th edn. Pearson education, New Jersey
Hernández-Pérez OI, Valdez-Aguilar LA, Alia-Tejacal I, Cartmill AD, Cartmill DL (2020) Tomato fruit yield, quality, and nutrient status in response to potassium: calcium balance and electrical conductivity in the nutrient solution. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00133-9
Islam A, Sirajul Karimb AJM, Solaiman ARM, Shafiqul Islam M, Abu Saleque M (2017) Eight-year long potassium fertilization effects on quantity/intensity relationship of soil potassium under double rice cropping. Soil Till Res 169:99–117
Jalali M, Arian TM, Ranjbar F (2020) Selectivity coefficients of K, Na, Ca, and Mg in binary exchange systems in some calcareous soils. Environ Monit Assess 192:80
Jiang N, Hu B, Wang X, Meng Y, Chen B, Zhou Z (2019) Effects of crop residue incorporation and inorganic potassium fertilization on soil potassium supply power. Arch Agron Soil Sci 65:1223–1236
Panda R, Patra SK (2018) Quantity-intensity relations of potassium in representative coastal soils of eastern India. Geoderma 332:198–206
Schneider A (1997) Release and fixation of potassium by a loamy soil as affected by initial water content and potassium status of soil samples. Eur J Soil Sci 48:263–271
Sposito G (2008) The chemistry of soils, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Suttanukool P, Darunsontaya T, Jindaluang W (2019) A study on the quantity/intensity relationships of potassium of sugarcane growing soils, Eastern Thailand. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 50:153–163
Wang J, Farrell RE, Scott AD (1988) Potentiometric determination of potassium Q/I relationships. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:657–662
Wang J, Farrell RE, Scott AD (1990) Comparison of ion-selective electrode methods for determining potassium Q/I relationships. Can J Soil Sci 70:693–704
Wang J, Harrell DL, Bell PF (2004) Potassium buffering characteristics of three soils low in exchangeable potassium. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:654–661
Woodruff CM (1955a) Ionic equilibria between clay and dilute salt solutions. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 19:36–40
Woodruff CM (1955b) The energies of replacement of calcium by potassium in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 19:167–171
Zhu D, Lu J, Cong R, Ren T, Zhang W, Li X (2019) Potassium management effects on quantity/intensity relationship of soil potassium under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1663830
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilias, F., Barbayiannis, N. Towards a Single-Point Approach for Estimating Potassium Quantity-Intensity Parameters in Soils at Different K Saturation Ratios. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 1679–1685 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00238-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00238-6