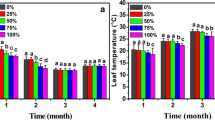
Abstract
Irradiation of sewage sludge (SS) with gamma-ray is regarded as a promising alternative and rapid method for risk mitigation of this waste in ecosystems. The effects of 13 treatments (15, 30, and 60 g kg−1 of non-irradiated SS and irradiated with doses of 5, 10, and 20 kGy gamma-ray and soil without SS and irradiation as the control treatment) was investigated on the growth, herbage yield, leaf chlorophyll index, and concentrations of macronutrients in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) root and shoot in a completely randomized design with three replications under greenhouse conditions. The results showed that application of gamma-irradiated and non-irradiated SS positively affected the concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium in basil shoot and root. The highest and lowest dry weights of root and shoot, plant height, leaf area, and leaf chlorophyll index were observed in 30 g kg−1 SS irradiated with 20 kGy absorbed dose and 60 g kg−1 non-irradiated SS, respectively. In ≤ 30 g kg−1 SS, the gamma irradiation absorbed dose did not significantly change the growth parameters, thus the use of ≤ 5 kGy absorbed dose may be suggested to stimulate positive effects on basil growth. Also, in 60 g kg−1 SS, the restrictive effects were mitigated by increasing the absorbed dose, but the use of ≥ 5 kGy absorbed dose may not cost-effective. Therefore, in order to improve nutrition and growth of basil plant, application of ≤ 30 g sewage sludge irradiated with 5 kGy absorbed dose of gamma-ray per kilogram soil can be suggested under similar conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Hossain M, Rahman S (2002) Isotope-aided studies on the effects of radiation processed sewage sludge on crop yields and bioavailability of heavy metals. Irradiated sewage sludge for application to cropland, results of a coordinated research project. (Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture), International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Asgari Lajayer B, Ghorbanpour M, Nikabadi S (2017a) Heavy metals in contaminated environment: destiny of secondary metabolite biosynthesis, oxidative status and phytoextraction in medicinal plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:377–390
Asgari Lajayer H, Savaghebi GR, Hadian J, Hatami M, Pezhmanmehr M (2017b) Comparison of copper and zinc effects on growth, micro-and macronutrients status and essential oil constituents in pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium L.). Braz J Bot 40:379–388
Asgari Lajayer B, Najafi N, Moghiseh E, Mosaferi M, Hadian J (2019) Micronutrient and heavy metal concentrations in basil plant cultivated on irradiated and non-irradiated sewage sludge- treated soil and evaluation of human health risk. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 104:141–150
Bajeli J, Tripathi S, Kumar A, Tripathi A, Upadhyay R (2016) Organic manures a convincing source for quality production of Japanese mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Ind Crop Prod 83:603–606
Brady NC, Weil RR (1999) The Nature and Properties of Soils, 12th edn. Prentice-Hall, Inc., New Jersey
Chu S, Wu D, Liang LL, Zhong F, Hu Y, Hu X, Lai C, Zeng S (2017) Municipal sewage sludge compost promotes Mangifera persiciforma tree growth with no risk of heavy metal contamination of soil. Sci Rep 7:13408
Dane JH, Topp GC (2002) Methods of soil analysis. Part 4. Physical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Dindar E, Topac EO, Baskaya HS, Kaya T (2017) Effect of wastewater sludge application on enzyme activities in soil contaminated with crude oil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 17(1):180–193
El-Motaium R (2002) Irradiated sewage sludge for increased crop production–III. Macronutrient availability. Irradiated sewage sludge for application to cropland, results of a co-ordinated research project. (Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture), International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
El-Motaium R (2006) Application of nuclear techniques in environmental studies and pollution control. Proceedings of the 2nd Environmental Physics Conference. Alexandria, Egypt, pp 169–182
El-Motaium R, El-Seoud MA (2007) Irradiated sewage sludge for production of fennel plants in sandy soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 78:133–142
Ghorbanpour M, Asgari Lajayer H, Hadian J (2016) Influence of copper and zinc on growth, metal accumulation and chemical composition of essential oils in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J Med Plant 3:132–144
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) (2002) Irradiated sewage sludge for application to cropland. Results of a coordinated research project. (Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture), International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Kchaou R, Baccar R, Bouzid J, Rejeb S (2017) The impact of sewage sludge and compost on winter triticale. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(19):18314–18319
Kumar V, Chopra A (2014) Accumulation and translocation of metals in soil and different parts of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) amended with sewage sludge. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:103–108
Limam RD, Limam I, Clérandeau C, Khouatmia M, Djebali W, Cachot J, Chouari R (2018) Assessment of the toxicity and the fertilizing power from application of gamma irradiated anaerobic sludge as fertilizer: effect on Vicia faba growth. Radiat Phys Chem 150:163–168
Magnavacca C (2002) Evaluation of irradiated sewage sludge as an industrial crop fertilizer using nuclear techniques. Irradiated sewage sludge for application to cropland, results of a co-ordinated research project. (Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture), International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Mahmoudi S, Najafi N, Reyhanitabar A (2015a) Effect of soil moisture and sewage-sludge compost on some soil chemical properties and alfalfa forage macronutrients concentrations in greenhouse conditions. J Sci Technol Greenh Cult 6(22):37–55 (in Persian with English abstract)
Mahmoudi S, Najafi N, Reyhanitabar A (2015b) Effects of soil moisture and sewage sludge compost on leaf chlorophyll index and some growth traits of alfalfa in greenhouse conditions. J Sci Technol Greenh Cult 5(20):207–220. (in Persian with English abstract)
Marschner H (1995) Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd edn. Academic, London
Mohamed B, Mounia K, Aziz A, Ahmed H, Rachid B, Lotfi A (2018) Sewage sludge used as organic manure in Moroccan sunflower culture: effects on certain soil properties, growth and yield components. Sci Total Environ 627:681–688
Najafi N, Mardomi S, Oustan S (2012a) The effect of waterlogging, sewage sludge and manure on selected macronutrients and sodium uptake in sunflower plant in a loamy sand soil. J Water Soil 26(3):619–636 (in Persian with English abstract)
Najafi N, Mardomi S, Oustan S (2012b) Changes in DTPA extractable copper, iron, manganese and zinc after waterlogging and application of sewage sludge and animal manure in two different soils. Iran J Soil Water Res 43(1):9–22 (in Persian with English abstract)
Page A, Miller R, Keeney D (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Pagliari PH, Kaiser DE, Rosen CJ, Lamb JA (2017) The nature of phosphorus in soils. Extension specialists in nutrient management. University of Minnesota Extension, Falcon Heights
Pandya GA, Prakash L, Devasia P, Modi VV (1988) Effect of gamma-irradiated sludge on the growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L. var. GR-3). Environ Pollut 51:63–73
Pandya GA, Sachidanand S, Modi VV (1989) Potential of recycling gamma-irradiated sewage sludge for use as a fertilizer: a study on chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Environ Pollut 56:101–111
Pascual I, Antolín MC, García C, Polo A, Sánchez-Díaz M (2007) Effect of water deficit on microbial characteristics in soil amended with sewage sludge or inorganic fertilizer under laboratory conditions. Bioresour Technol 98(1):29–37
Peters J, Combs S, Hoskins B, Jarman J, Kovar J, Watson M, Wolf A, Wolf N (2003) Recommended methods of manure analysis. University of Wisconsin Cooperative Extension Publishing, Madison
Prakash A, Adholeya A (2004) Effect of different organic manures/composts on the herbage and essential oil yield of Cymbopogon winterianus and their influence on the native AM population in a marginal alfisol. Bioresour Technol 92:311–319
Prinzenberg AE, Barbier H, Salt DE, Stich B, Reymond M (2010) Relationships between growth, growth response to nutrient supply, and ion content using a recombinant inbred line population in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:1361–1371
Rathod PH, Patel JC, Shah MR, Jhala AJ (2009) Recycling gamma irradiated sewage sludge as fertilizer: a case study using onion (Alium cepa). Appl Soil Ecol 41:223–233
Rathod PH, Patel JC, Jhala AJ (2011) Potential of gamma irradiated sewage sludge as fertilizer in radish: evaluating heavy-metal accumulation in sandy loam soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 42:263–282
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Schreck E, Xiong T, Niazi NK (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1993) 503 standards for the use or disposal of sewage sludge, Fed. Regis, 58, 9387
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2003) Control of pathogens and vector attraction in sewage sludge. EPA 815-R-06e002 Revised edition. US EPA, Washington, DC
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2010) Method 1680: fecal coliforms in sewage sludge (biosolids) by multiple-tube fermentation using lauryl tryptose broth (Ltb) and Ec medium. US EPA, Washington, DC
Westerman RL (1990) Soil testing and plant analysis. 3rd edn. Book Series No. 3, SSSA, Madison
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105(7):1073–1080
Zheljazkov VD, Craker LE, Xing B, Nielsen NE, Wilcox A (2008) Aromatic plant production on metal contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 395(2):51–62
Zhou L, Xu Y, Jiang T, Zheng S, Wu H (2002) Characterization of irradiated sewage sludge and its effects on soil fertility, crop yields and nutrient bioavailability. Irradiated sewage sludge for application to cropland, Results of a co-ordinated research project. (Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture), International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Zoghlami RI, Hamdi H, Boudabbous K, Hechmi S, Khelil MN, Jedidi N (2018) Seasonal toxicity variation in light-textured soil amended with urban sewage sludge: interaction effect on cadmium, nickel, and phytotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3608–3615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asgari Lajayer, B., Najafi, N., Moghiseh, E. et al. Effects of Gamma Irradiated and Non-Irradiated Sewage Sludge on Growth Characteristics, Leaf Chlorophyll Index, and Macronutrients Concentrations in Basil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19, 580–591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00057-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00057-4