Abstract
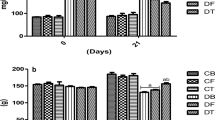
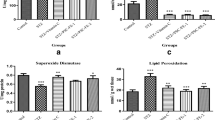
Chrysophyllum albidum (C. albidum) is an indigenous fruit, found predominantly in African countries. The fleshy pulp of the fruit is widely consumed by the populace and used in folklore for diabetes management. The present study was carried out to assess the effects of dietary supplementation of Chrysophyllum albidum fruit pulp powder (CAPP) on biochemical parameters in a type 2 diabetes rat model, induced by a combination of high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin (35 mg kg −1) for 14 days. Diabetic rats were placed on dietary regimen containing 5–10% Chrysophyllum albidum fruit pulp powder (CAPP) supplemented diet. The results revealed that there was no significant (P > 0.05) difference in the average feed intake and weight changes between the rat groups. Furthermore, supplementation with CAPP gradually reduced blood glucose level in diabetic rat compared to control diabetic rats without CAPP supplementation. Moreover, reduced activities of α-amylase and α-glucosidase were observed in CAPP and metformin-treated rat groups when compared to control diabetic rats without CAPP supplementation. In addition, CAPP showed significantly (P < 0.05) elevated levels of antioxidant status (reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione-S-transferase) while significantly (P < 0.05) reduced malondialdehyde level. Histologically, a pale stained cellular architecture in pancreas depicting an atrophy and decreased size of islet of Langerhans were observed in control diabetic rats without CAPP supplementation while CAPP and metformin-treated rat groups showed a preserved cellular morphology with increased size of islet of Langerhans. The results suggest that the C. albidum fruit pulp diet may attenuate hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in the type 2 diabetic condition and therefore provides pharmacological basis for the folkloric use of this fruit as a therapy for the management of oxidative stress induced pathologies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo AH, Aliyu R, Gatsing D, Garba IH (2006) The effects of ethanolic leaf extract of Chrysophyllumalbidum on biochemical and haematologicalparameters of albino Wistar rats. Afr J Biotechnol 9:2145–2150
Adefegha SA, Oboh G, Adefegha OM, Boligond AA, Athayded ML (2014) Antihyperglycemic, hypolipidemic, hepatoprotective and antioxidative effects of dietary clove (Szyzgium aromaticum) bud powder in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin induced diabetes rat model. J Sci Food Agric. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6617
Ademiluyi AO, Oboh G, Boligon AA, Athayde ML (2014) Effect of fermented soybean condiment supplemented diet on α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Funct Foods 9:1–9
Adisakwattana S, Lerdsuwankij O, Poputtachai U, Minipun A, Suparpprom C (2011) Inhibitory activity of cinnamon bark species and their combination effect with acarbose against intestinal α-glucosidase and pancreatic α-amylase. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 66:143–148
Akubugwo IE, Ugbogu AE (2007) Physicochemical studies on oils from five selected Nigerian plant seeds. Pak J Nutr 6:75–78
Almeida DAT, Braga CP, Novelli ELB, Fernandes A (2012) Evaluation of lipid profile and oxidative stress in STZ-induced rats treated with antioxidant vitamin. Braz Arch Biol Technol 55(4):527–536
Al-Shiekh AAM, Al-Shati AA, Sarhan MAA (2014) Effect of white tea extract on antioxidant and resilient. Exp Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/6103
Apostolidis E, Kwon YI, Shetty K (2007) Inhibitory potential of herb, fruit, and fungal-enriched cheese against key enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 4:46–54
Asru KS (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47:389–394
Bischoff H (1994) Pharmacology of alpha-glucosidase inhibition. Eur J Clin Invest 24:3–10
Cheng DM, Kuhn P, Poulev A, Rojo LE, Lila MA, Raskin I (2012) In vivo and in vitro antidiabetic effects of aqueous cinnamon extract and cinnamon polyphenol-enhanced food matrix. Food Chem 135:2994–3002
Diao BZ, Jin WR, Yu XJ (2014) Protective effect of polysaccharides from Inonotus obliquus on streptozotocin-induced diabetic symptoms and their potential mechanisms in rats. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/841496
Florence AB, Adiaha AH (2015) Storage effects and the postharvest quality of African star apple fruits (Chrysophyllumafricanum) under ambient conditions. Afr J Food Sci Technol 6(1):35–40
Friedman MA, Fleming LE, Fernandez M, Bienfang P, Schrank K, Dickey R (2008) Ciguatera fish poisoning: treatment, prevention and management. Mar Drugs 6:456–479
Goldstein BJ (2007) Clinical translation of ‘a diabetes outcome progression trial’: adopt appropriate combination oral therapies in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 92:1226–1228
Gruenwald J, Freder J, Armbruester N (2010) Cinnamon and health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50:822–834
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jacoby WB (1974) Glutathione-S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercaptoric acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hayes JD, Pulford DJ (1995) The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 30:445–600
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillete JR (1974) Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4 bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11:151–169
Kim SH, Jo SH, Kwon YI, Hwang JK (2011) Effects of onion (Allium cepa L.) extract administration on intestinal α-glucosidases activities andspikes in postprandial blood glucose levels in rats model. Int J Mol Sci 12:3757–3769
Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Kim YC, Shetty K (2007) Health benefits of traditional corn, beans and pumpkin: in vitro studies for hyperglycemia and hypertension management. J Med Food 10:266–275
Lawerence RA, Burk RF (1961) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat’s liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958
Lorenzi M (2007) The polyol pathway as a mechanism for diabetic retinopathy: attractive, elusive and resilient. Exp Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/61038
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The generation of superoxide radical during the antioxidant of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem 247:6960–6962
Oboh G, Akinyemi AJ, Ademiluyi AO, Adefegha SA (2010) Inhibitory effects of aqueous extract of two varieties of ginger on some key enzymes linked to type-2 diabetes in vitro. J Food Nutr Res 49:14–20
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Okoli BJ, Okere OS (2010) Antimicrobial activity of the phytochemical constituents of Chrysophyllum albidum Plant. J Res Nat Dev 8(1):1035–1037
Olorunnisola DS, Amao IS, Ehigie DO, Ajayi ZAF (2008) Anti-hyperglycaemic and hypolipidemic effect of ethanolic extract of Chrysophyllum albidum seed cotyledon in alloxan induced-diabetic rats. Res J Appl Sci 3:123–127
Onyeka CA, Nwakanma A, Bakare A, Okoko I, Ofoego U, Wali C, Abengowe F (2013) Hypoglycemic, antioxidants and hypertoprotective activities of ethanolic root bark extract of chrysophyllum albidum in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Bangladesh J Med Sci 3(2):123–127
Oyenihi AB, Ayeleso AO, Mukwevho E, Masola B (2015) Antioxidant strategies in the management of diabetic neuropathy. Bio Med Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/515042 (Article ID 515042)
Ranilla LG, Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Shetty K (2010) Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and in vitro inhibitory potential against key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and hypertension of commonly used medicinal plants, herbs and spices in Latin America. Bioresour Technol 101:4676–4689
Saravanan G, Ponmurugan P (2013) S-allylcysteine improves streptozotocin-induced alterations of blood glucose, liver cytochrome P450 2E1, plasma antioxidant system, and adipocytes hormones in diabetic rats. Int J Endocrinol Metab 11(4):10927
Sellamuthu PS, Arulselvan P, Kamalraj S, Fakurazi S, Kandasamy M (2013) Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ISRN Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/750109 (Article ID 750109)
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type-2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res 52:313–320
Tormo MA, Gil-Exojo I, Romero de Tejada A, Campillo JE (2006) White beanamylaseinhibitor administered orally reduces glycaemia in type-2 diabetic rats. Br J Nutr 96:539–544
Ullah A, Khan A, Khan I (2016) Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress: a concise review. Saudi Pharm J 24(5):547–553
Wild SG, Roglic A, Green R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes estimated for the year 2000 and projection for 2030. Diabetic Care 27:1047–1054
Worthington V (1993) Alpha amylase. In: Worthington K, Worthington V (eds) Worthington EnzymeManual. Worthington Biochemical Corp, Freehold, pp 36–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyetayo, F.L., Akomolafe, S.F. & Odeniyi, I.A. Effects of dietary supplementation of Chrysophyllum albidum fruit pulp powder on some biochemical parameters in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Vegetos 32, 190–199 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00022-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00022-7