Abstract
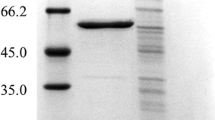
Recently, there has been a growing interest in exploring the potential of insect proteases for industrial applications, owing to their versatile biochemical properties. The primary focus is on overexpressing a distinct 37 kDa pupal gut serine protease, termed PGSP, from Bombyx mori, using Escherichia coli (E. coli) as a heterologous system for the proteomic characterization and future industrial applications. The study involves amplifying the 987-base pair PGSP gene and incorporating it into the pET-30a ( +) expression vector, subsequently introduced into E. coli JM109. The fidelity of ligation is verified through restriction digestion, gene-specific PCR, and sequencing. The ensuing recombinant construct is transferred to E. coli BL21 (DE3), induced with IPTG to enable overexpression. Experimental results with varying IPTG concentrations (0.5–1.5 mM) confirm successful overexpression of recombinant PGSP within E. coli cells. SDS-PAGE reveals an overaccumulated protein band at approximately 42 kDa, present in both soluble and insoluble fractions. However, most of the PGSP is found to be insoluble, so we solubilize it using a denaturing buffer containing urea and then purify it using Ni–NTA agarose resin. Analysis of the purified recombinant PGSP via 2D-PAGE yields a distinct isoelectric point (pI) of 6.4. Notably, the observed molecular weight (Mw) discrepancy (42 kDa) from the expected 37 kDa is attributed to additional tags. In-gel solution and liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry confirm the protein as Bombyx mori p37k protease. The recombinant full-length PGSP, when overexpressed, exhibits a lack of protease activity due to its zymogenic state. This highlights the need for further research to identify the zymogen processing enzyme responsible for activating the protease, a subject that will be investigated in future studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Change history
08 February 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42485-024-00130-2
References
Akbar SM, Sharma HC (2017) Alkaline serine proteases from Helicoverpa armigera: potential candidates for industrial applications. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.21367
Anwar A, Saleemuddin M (2000) Alkaline protease from Spilosoma obliqua: potential applications in bio-formulations. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:85. https://doi.org/10.1042/ba19990078
Arunprasanna V, Kannan M, Anbalagan S, Krishnan M (2017) Comparative proteomic analysis of larva and adult heads of silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). J Entomology 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3923/je.2017.1.12
Bakli M, Pascalau R, Smuleac L (2020) Rare codon analysis in rickettsia affecting recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Adv Res Life Sci 4:30–35. https://doi.org/10.2478/arls-2020-0015
Bhatwa A, Wang W, Hassan YI, Abraham N, Li XZ, Zhou T (2021) Challenges associated with the formation of recombinant protein inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli and strategies to address them for industrial applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.630551
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Dinglasan RR, Devenport M, Florens L, Johnson JR, McHugh CA, Donnelly-Doman M, Carucci DJ, Yates JR, Jacobs-Lorena M (2009) The Anopheles gambiae adult midgut peritrophic matrix proteome. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.10.010
Duckert P, Brunak S, Blom N (2004) Prediction of proprotein convertase cleavage sites. Protein Eng Des Sel 17:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzh013
Hamed MBB, Attias J (1987) Isolation and partial characterization of two alkaline proteases of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella (L.). Insect Biochem 17:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1790(87)90032-1
Hivrale VK, Chougule NP, Chhabda PJ, Giri AP, Kachole MS (2005) Unraveling biochemical properties of cockroach (Periplaneta americana) proteinases with a gel X-ray film contact print method. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 141:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2005.02.015
Hou Y, Yang L, Xu S, Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Li Y, Gong J, Xia Q (2021) Trypsin-type serine protease p37k hydrolyzes CPAP3-type cuticle proteins in the molting fluid of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2021.103610
Kaji K, Tomino S, Asano T (2009) A serine protease in the midgut of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: protein sequencing, identification of cDNA, demonstration of its synthesis as zymogen form and activation during midgut remodeling. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.12.001
Kannan M, Suryaaathmanathan V, Saravanakumar M, Jaleel A, Romanelli D, Tettamanti G, Krishnan M (2016) Proteomic analysis of the silkworm midgut during larval–pupal transition. ISJ 13:191–204
Kannan M, Ramya T, Anbalagan S, Suriya J, Krishnan M (2017) Proteomic analysis of pupal gut serine protease of Silkworm, Bombyx mori: partial purification and biochemical characterization. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 12:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.10.001
Kannan M, Mubarakali D, Thiyonila B, Krishnan M, Padmanaban B, Shantkriti S (2019) Insect gut as a bioresource for potential enzymes—an unexploited area for industrial biotechnology. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.01.048
Khan AR, James MNG (1998) Molecular mechanisms for the conversion of zymogens to active proteolytic enzymes. Protein Sci 7:815–836
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2015) SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D257–D260. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku949
Lv D, Liu X, Dong Y, Yan Z, Zhang X, Ren J, Wang P, Li Y (2022) Larval midgut protease activity of Illiberis pruni (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae) feeding on multiple characteristic hosts. Phytoparasitica 50:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-022-01019-w
Mótyán J, Tóth F, Tőzsér J (2013) Research applications of proteolytic enzymes in molecular biology. Biomolecules 3:923–942. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3040923
Page-McCaw A, Ewald AJ, Werb Z (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:221–233
Patankar AG, Giri AP, Harsulkar AM, Sainani MN, Deshpande VV, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2001) Complexity in specificities and expression of Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases explains polyphagous nature of the insect pest. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:453–464
Petersen TN, Brunak S, Von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Petrescu AJ, Milac AL, Petrescu SM, Dwek RA, Wormald MR (2004) Statistical analysis of the protein environment of N-glycosylation sites: implications for occupancy, structure, and folding. Glycobiology 14:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwh008
Reddy Patakottu BK, Vedire VR, Reddy CR (2023) Robust production of active Ulp1 (SUMO protease) from inclusion bodies. Protein Expr Purif 211:106328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2023.106328
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sanatan PT, Lomate PR, Giri AP, Hivrale VK (2013) Characterization of a chemostable serine alkaline protease from Periplaneta americana. BMC Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2091-14-32
Srinivasan A, Giri AP, Gupta VS (2006) Structural and functional diversities in lepidopteran serine proteases. Cell Mol Biol Lett 11:132–154. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11658-006-0012-8
Srivastava V, Mishra S, Chaudhuri TK (2019) Enhanced production of recombinant serratiopeptidase in Escherichia coli and its characterization as a potential biosimilar to native biotherapeutic counterpart. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1267-x
Venancio TM, Cristofoletti PT, Ferreira C, Verjovski-Almeida S, Terra WR (2009) The Aedes aegypti larval transcriptome: a comparative perspective with emphasis on trypsins and the domain structure of peritrophins. Insect Mol Biol 18:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.2008.00845.x
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL (2012) Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinf 13:1–11
Funding
We would like to express our gratitude to the Board of Research in Nuclear Science, Mumbai; the Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi; and the University Grant Commission-BSR-ONE TIME GRANT for providing financial support. We also extend our thanks to Bharathidasan University for providing the necessary infrastructure facilities. The funding agencies played no role in the preparation or decision to publish the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MKa performed the experiments, prepared the original draft, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. NK assisted in the cloning experiments. VA and NRK assisted in protein purification. MKr: conceptualism, funding acquisition, reviewed and corrected the final version of the manuscript. All authors have thoroughly read and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest that could have influenced the work reported in this research work.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Legends of Figs. 4, 5, 6 and 7 contained errors which have been corrected.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kannan, M., Kayalvizhi, N., Arunprasanna, V. et al. Heterologous expression, purification, and proteomic characterization of a 37 kDa pupal gut serine protease from Bombyx mori in Escherichia coli. J Proteins Proteom 15, 43–52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42485-023-00126-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42485-023-00126-4