Abstract
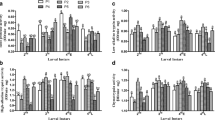
Illiberis pruni (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae) is a key polyphagous pest of pear, apple and crabapple trees. Protease secreted by insect midgut plays an indispensable role in the absorption and digestion of host plant nutrients. To understand the relationship between protease activity and different host plants, the activity of midgut proteases of I. pruni larvae were measured in this study. By detecting protease activities with enzyme specific substrates, it was found that the optimal buffers for total protease, high-alkaline trypsin, low-alkaline trypsin and chymotrypsin are Tris-HCl, glycine/NaOH, glycine/NaOH and KH2PO4/NaOH, and the optimal pH values are 11.0, 11.0, 9.0 and 9.0, respectively. The results showed that protease activity was different across different developmental stages of I. pruni larvae, and that host plant species express the most significant differences on midgut proteases of 4th instar larvae. The protease activities of I. pruni larvae feeding on host plant species with different characteristics are significantly distinct. It was observed that when I. pruni larvae ingest Pyrus bretschneideri, the activity of the protease was highest. In contrast, when ingesting Malus pumila and Chaenomeles cathayensis, the activity of the proteases were found to be lowest. When 5th instar I. pruni larvae ingest C. cathayensis, the activity of total proteases and high-alkalinity were higher in the fruit feeding than in the leaves feeding. In practical orchard applications, we can reduce damage to fruit trees by redistributing the cultivation structure of fruit forest structure by optimally cultivating various host species to limit minimize pest outbreaks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azidah, A. A., & Sofian-Azirun, M. (2006). Life history of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on various host plants. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 96, 613–618.
Baghery, F., Fathipour, Y., & Naseri, B. (2014). Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities in Helicoverpa armigera (Lep.: Noctuidae) larvae fed on five host plants. Journal of Crop Protection, 3, 191–198.
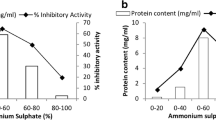
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Brito, L. O., Lopes, A. R., Parrac, J. R. P., Terrab, W. R., & Silva, M. C. (2001). Adaptation of tobacco budworm Heliothis virescens to proteinase inhibitors may be mediated by the synthesis of new proteinases. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B-Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 128, 365–375.
Cates, R. G. (1980). Feeding patterns of monophagous, oligophagous, and polyphagous insect herbivores: the effect of resource abundance and plant chemistry. Oecologia, 46, 22–31.
Da, L. T., Zhu, Y. L., Song, L. W., Hu, G. X., & Wang, S. (2015). The effect of different alfalfa varieties on the midgut protease activity of pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24, 80–87.
Damle, M. S., Gir, A. P., Sainani, M. N., & Gupta, V. S. (2005). Higher accumulation of proteinase inhibitors in flowers than leaves and fruits as a possible basis for differential feeding preference of Helicoverpa armigera on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill, Cv. Dhanashree). Phytochemistry, 66, 2659–2667.
Efetov, K. A., Tarmann, G. M., Toshova, T. B., & Subchev, M. A. (2015). Enantiomers of 2-butyl 7Z-dodecenoate are sex attractants for males of Adscita mannii (Lederer, 1853), A. geryon (Hübner, 1813), and Jordanita notata (Zeller, 1847) (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae, Procridinae) in Italy. Nota Lepidopterologica, 38, 161–169.
Gaylor, M. J., & Ali, A. (1992). Effects of temperature and larval diet on development of the beet armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 21, 780–786.
Geng, H. (2005). General principles of insect nutritional ecology. Trakya University Journal of Sciences, 7, 53–57.
Golla, K. G., Rajasekhar, P., Akbar, S. M. D., & Sharma, H. C. (2018). Proteolytic activity in the midgut of Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) larvae fed on wild relatives of chickpea, Cicer arietinum Journal of Economic Entomology, 111, 2409–2415.
Gou, Y. P., Liu, Q., & Liu, C. Z. (2015). Effects of host plants on the growth, development and fecundity of Bradysia difformis Plant Protection, 41, 29–32.
Han, X. N., Wang, X. Q., Zhao, L. P., & Liu, C. Z. (2012). Effects of host plants on the growth, development and fecundity of Acyrthosiphon pisum Plant Protection, 38, 40–43.
Hemati, S. A., Naseri, B., Nouri, G. G., Rafiee, D. H., & Golizadeh, A. (2012). Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities and feeding responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants. Journal of Economic Entomology, 105, 1439–1446.
Hivrale, V. K., Lomate, P. R., Basaiyye, S. S., & Kalve, N. D. (2012). Compensatory proteolytic responses to dietary proteinase inhibitors from Albizia lebbeck seeds in the Helicoverpa armigera larvae. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 7, 259–266.
Hwang, S. Y., Liu, C. H., & Shen, T. C. (2008). Effects of plant nutrient availability and host plant species on the performance of two Pieris butterflies (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Biochemical Systematics & Ecology, 36, 505–513.
Johnston, K. A., Lee, M. J., Gatehouse, J. A., & Anste, J. H. (1991). The partial purification and characterisation of serine protease activity in midgut of larval. Helicoverpa armigera Insect Biochemistry, 21, 389–397.
Kipgen, A., & Aggarwal, K. K. (2014). Gut protease profiles of different instars of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 34, 172–178.
Kotkar, M. H., Sarate, P. J., Tamhane, V. A., Gupta, V. S., & Giri, A. P. (2009). Responses of midgut amylases of Helicoverpa armigera to feeding on various host plants. Journal of Insect Physiology, 55, 663–670.
Li, D. M., Li, J., & Li, L. C. (1997). Studies on sex pheromone of pear leaf borer, Illiberis pruni Dyar III fine structure of the sex pheromone glands. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 12, 112–116.
Li, Y. S., Luo, W. C., & Zhao, S. H. (1996). Effects of food plants on the activity of carboxylesterase of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Journal of Shandong Agricultural University, 27, 147–151.
Li, Z. G., Han, S. C., Guo, M. F., Li, L. Y., Peng, T. X., & Liu, W. H. (2005). Effects of feeding on different food plants on nutritional utilization and midgut enzyme activities in Actinote anteas (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 48, 674–678.
Liu, H. X., Xu, S., Dou, S. L., Wang, R., & Jing, Y. X. (2021). Field trials of synthetic sex attractants of Illiberis pruni in China. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 169, 640–645.
Lomate, P. R., & Hivrale, V. K. (2011). Differential responses of midgut soluble aminopeptidases of Helicoverpa armigera to feeding on various host and non-host plant diets. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 5, 359–368.
Namin, F. R., Naseri, B., & Razmjou, J. (2014). Nutritional performance and activity of some digestive enzymes of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, in response to seven tested bean cultivars. Journal of Insect Science, 14, 93.
Naseri, B., Fathipour, Y., Moharramipour, S., Hosseininaveh, V., & Gatehouse, A. M. (2010). Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities of Helicoverpa armigera in response to feeding on different soybean cultivars. Pest Management Science, 66, 1316–1323.
Naseri, B., Kouhi, D., Razmjou, J., & Golizadeh, A. (2014). Digestive enzymatic activity and nutritional responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae fed various tomato cultivars. Journal of Economic Entomology, 107, 1655–1661.
Navaei, B. R., Kazzazi, M., Saber, M., & Vatanparast, M. (2018). Differential inhibition of Helicoverpa armigera (Lep.: Noctuidae) gut digestive trypsin by extracted and purified inhibitor of Datura metel (Solanales: Solanaceae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 111, 178–186.
Ottea, J. A., & Plapp, F. W. (1980). Induction of Glutathione S-Aryl transferase by phenobarbital in the house fly. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 15, 10–13.
Pauchet, Y., Wilkinson, P., Vogel, H., Nelson, D. R., Reynolds, S. E., & Heckel, D. G. (2010). Pyrosequencing the Manduca sexta larval midgut transcriptome: messages for digestion, detoxification and defence. Insect Molecular Biology, 19, 61–75.
Srinivasan, A., Giri, A. P., & Gupta, V. S. (2006). Structural and functional diversities in lepidopteran serine proteases. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 11, 132–154.
Subchev, M., Efetov, K. A., Toshova, T. B., Parshkova, E., Tóth, M., & Francke, W. (2010). New Sex Attractants for Species of the Zygaenid Subfamily Procridinae (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae). Entomologia Generalis, 32, 243–250.
Subchev, M., Koshio, C., Toshova, T., Efetov, K., & Francke, W. (2013). (2R)-butyl (7Z)-Dodecenoate, a main sex pheromone component of Illiberis (Primilliberis) pruni Dyar (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae: Procridinae)? Acta Zoologica Bulgarica, 65, 391–396.
Telang, M. A., Giri, A. P., Sainani, M. N., & Gupta, V. S. (2005). Characterization of two midgut proteinases of Helicoverpa armigera and their interaction with proteinase inhibitors. Journal of Insect Physiology, 51, 513–522.
Valencia, A., Arboleda, J. W., Lopez, A., & Grossi, M. F. (2008). Digestive alpha-amylases from Tecia solanivora larvae (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): response to pH, temperature and plant amylase inhibitors. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 98, 575–579.
Wang, C. Z., & Qin, J. D. (1996). Partial characterization of protease activity in the midgut of Helicoverpa armigera larvae. Journal of Plant Protection, 39, 7–14.
Wang, G. H., Zhao, Q. J., Xu, F. D., Zou, Y. X., Wang, H. G., & Wang, H. X. (2016). Influence of three kinds of plant leaves on Prodenia litura Nutrient effect and intestinal enzyme activity. Journal of Guizhou Agricultural Science, 44, 77–80.
Wang, Q. Q., Wang, L., Li, K. B., Cao, Y. J., Yin, J., & Xiao, C. (2015). Influences of different host plants on the nutrition and digesive enzymes of Loxostege sticticalis Plant Protection, 41, 46–51.
Wei, H., Zhao, S. X., Hu, J. F., Zhan, Z. X., & Wu, W. (2006). Influence of hosts on the resistance recession and esterase activity of Plutella xylostella field population. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 35, 138–142.
Xu, W., Fu, X. X., Feng, X. Y., & Li, Y. (2012). Effects of different host plants on development and total midgut protease activities of Lymantria dispar larvae. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 40, 121–122.
Zhang, N., Guo, J. Y., Wan, F. H., & Wu, G. (2009). Effects of three kinds of host plants on development and some digestive enzyme activities of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 36, 146–150.
Zhao, A. P., Li, Y., Leng, C. M., Wang, P., & Li, Y. P. (2018). Inhibitory effect of protease inhibitors on larval midgut protease activities and the performance of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Frontiers in Physiology, 9, 1963.
Zhao, A. P., Sun, C., Zhan, E. L., Wu, J. X., & Li, Y. P. (2016). Effects of protease inhibitors on the activities of midgut proteases of larval Grapholitha molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 59, 1069–1078.
Zhao, A. P., Yuan, X. Q., Hu, D., Leng, C. M., Li, Y., & Li, Y. P. (2019). The effect of host plant on the development and larval midgut protease activity of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Phytoparasitica, 47, 475–483.
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for valuable comments on the manuscript. Financial assistance was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871971, 31772503), and the Key Science and Technology Project of Shaanxi Province (2020zdzx03-03-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lv DB and Liu XY participated in the design of the study, performed the experiments and data analysis, generated the Figures and Tables, and helped draft the manuscript; Dong YL, Yan ZZ, Zhang X and Ren JY helped Lv DB to perform the experiments; Li YP and Wang P conceived the study, designed the study, coordinated the study and drafted the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicting interests with regard to the work as carried out and reported in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 144 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, D., Liu, X., Dong, Y. et al. Larval midgut protease activity of Illiberis pruni (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae) feeding on multiple characteristic hosts. Phytoparasitica 50, 1033–1042 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-022-01019-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-022-01019-w