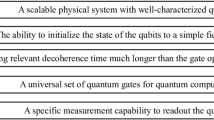
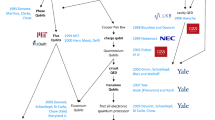
Abstract
Quantum state tomography (QST) is a fundamental technique in quantum information processing (QIP) for reconstructing unknown quantum states. However, the conventional QST methods are limited by the number of measurements required, which makes them impractical for large-scale quantum systems. To overcome this challenge, we propose the integration of quantum machine learning (QML) techniques to enhance the efficiency of QST. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive investigation into various approaches for QST, encompassing both classical and quantum methodologies. We also implement different QML approaches for QST and demonstrate their effectiveness on various simulated and experimental quantum systems, including multi-qubit networks. Our results show that our QML-based QST approach can achieve high fidelity (\(98 \%\)) with significantly fewer measurements than conventional methods, making it a promising tool for practical QIP applications.























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets and numerical details necessary to replicate this work are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Acharya A, Kypraios T, Guţă M (2019) A comparative study of estimation methods in quantum tomography. J Phys A Math Theor 52(23):234001
Ahmed S, Muñoz CS, Nori F, Kockum AF (2021) Quantum state tomography with conditional generative adversarial networks. Phys Rev Lett 127(14):140502
Altepeter JB, Jeffrey ER, Kwiat PG (2005) Photonic state tomography. Adv At Mol Opt Phys 52:105–159
Cha P, Ginsparg P, Wu F, Carrasquilla J, McMahon PL, Kim E-A (2021) Attention-based quantum tomography. Mach Learn Sci Technol 3(1):01LT01
Choi M-D (1975) Completely positive linear maps on complex matrices. Linear Algebra Appl 10(3):285–290
Gao J, Qiao LF, Jiao ZQ, Ma YC, Hu CQ, Ren RJ, Jin XM (2018) Experimental machine learning of quantum states. Phys Rev Lett 120(24):240501
Gonçalves DS, Gomes-Ruggiero MA, Lavor C, Farías OJ, Ribeiro PH (2011) Local solutions of maximum likelihood estimation in quantum state tomography. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1103.3682
Gonçalves DS, Azevedo CLN, Lavor C, Gomes-Ruggiero MA (2018) Bayesian inference for quantum state tomography. J Appl Stat 45(10):1846–1871
Greenberger DM, Horne MA, Zeilinger A (2007) Going beyond Bell’s theorem. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/0712.0921
Hai VT, Ho LB (2023) Universal compilation for quantum state tomography. 13(3750):1–12
He C, Li J, Liu W, Peng J, Wang ZJ (2022) A low-complexity quantum principal component analysis algorithm. IEEE Trans Quantum Eng 3:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TQE.2021.3140152
Hsieh HY, Ning J, Chen YR, Wu HC, Chen HL, Wu CM, Lee RK (2022) Direct parameter estimations from machine learning-enhanced quantum state tomography. Symmetry 14(5):874
IBM Quantum (2024). https://quantum-computing.ibm.com/
James DFV, Kwiat PG, Munro WJ, White AG (2001) Measurement of qubits. Phys Rev A 64(5):052312
Jianqing F, Liao Y, Liu H (2015) An overview on the estimation of large covariance and precision matrices, arXiv:https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.02995
Kopczyk D (2018) Quantum machine learning for data scientists. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.10068
Koutný D, Motka L, Hradil Z, Řeháček J, Sánchez-Soto LL (2022) Neural-network quantum state tomography. Phys Rev A 106(1):012409
Kurmapu MK (2020) Machine learning assisted quantum state tomography. M.S. thesis, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada. https://prism.ucalgary.ca/items/ce19b9c3-34cb-4166-b5ba-f4582502eb38
Li Z, Chai Z, Guo Y, Ji W, Wang M, Shi F, Wang Y, Lloyd S, Du J (2021) Resonant quantum principal component analysis. Sci Adv 7(34). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abg2589
Lin L (2022) Lecture notes on quantum algorithms for scientific computation. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.08309
Lin J, Bao W-S, Zhang S, Li T, Wang X (2019) An improved quantum principal component analysis algorithm based on the quantum singular threshold method. Phys Letts A 383(24):2862–2868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2019.06.026
Liu Y, Wang D, Xue S, Huang A, Fu X, Qiang X, Xu P, Huang H, Deng M, Guo C, Yang X, Wu J (2020) Variational quantum circuits for quantum state tomography. Phys Rev A 101(5):052316
Lloyd S, Mohseni M, Rebentrost P (2014) Quantum principal component analysis. Nat Phys 10(9):631–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3029
Lohani S, Kirby BT, Brodsky M, Danaci O, Glasser RT (2020) Machine learning assisted quantum state estimation. Mach Learn Sci Technol 1(3):035007
Lum DJ, Weinstein YS (2022) Bayesian quantum state tomography with python’s PyMC. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10655
Ma H, Dong D, Petersen IR (2021) On how neural networks enhance quantum state tomography with limited resources. In: 2021 60th IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC), IEEE pp 4146–4151
Mondal S, Dutta AK (2023) A modified least squares-based tomography with density matrix perturbation and linear entropy consideration along with performance analysis. New J Phys 25(8):083051
Nielsen MA, Chuang IL (2011) Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
O’Donnell R, Wright J (2016) Efficient quantum tomography. Proceedings of the Forty-Eighth Annual ACM symposium on theory of computing, pp 899–912. https://doi.org/10.1145/2897518.2897544
Opatrny T, Welsch DG, Vogel W (1997) Least-square inversion for density-matrix reconstruction. Phys Rev A 56(3):1788–1799
Paris M, Řeháček J (2004) Quantum state estimation. Springer, New York, USA
Preskill J (2018) Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2:79–99
Qi B, Hou Z, Wang Y, Dong D, Zhong HS, Li L, Guo GC (2017) Adaptive quantum state tomography via linear regression estimation: theory and two-qubit experiment. npj Quantum Inf 3(1):19
Qiskit Contributors (2023) Qiskit: an open-source framework for quantum computing. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2573505
Quek Y, Fort S, Ng HK (2021) Adaptive quantum state tomography with neural networks. Nature npj Quantum Inf 7(105):1–6
Ramadhani S, Rehman JU, Shin H (2021) Quantum error mitigation for quantum state tomography. IEEE Access 9:107955–10796
Řeháček K, Hradil Z, Ježek M (2001) Iterative algorithm for reconstruction of quantum states. Phys Rev A 63(4):040303
Rippe L, Julsgaard B, Walther A, Ying Y, Kröll S (2008) Experimental quantum-state tomography of a solid-state qubit. Phys Rev A 77(2):022307
Schmale T, Reh M, Gärttner M (2022) Efficient quantum state tomography with convolutional neural networks. Nature npj Quantum Inf 8(115):1–8
Schuld M, Bergholm V, Gogolin C, Izaac J, Killoran N (2019) Evaluating analytic gradients on quantum hardware. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.11184
Sen P, Bhatia AS, Bhangu KS, Elbeltagi A (2022) Variational quantum classifiers through the lens of the hessian. Plos One 17(1):e0262346
Surawy-Stepney T, Kahn J, Kueng R, Guţă M (2022) Projected least-squares quantum process tomography. Quantum 6:844
Tang E (2021) Quantum principal component analysis only achieves an exponential speedup because of its state preparation assumptions. Phys Rev Lett 127(6):060503. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.060503
Teo YS (2015) Introduction to quantum-state estimation. World Scientific, Singapore
Thew RT, Nemoto K, White AG, Munro WJ (2002) Qudit quantum-state tomography. Phys Rev A 66(1):012303
Torlai G, Mazzola G, Carrasquilla J, Troyer M, Melko RG (2018) Many-body quantum state tomography with neural networks. arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.05334
Uhlmann A (1976) The “transition probability ’ ’ in the state space of a \(*\)-Algebra. Rep Math Phys 9(2):273–279
Vogel K, Risken H (1989) Determination of quasiprobability distributions in terms of probability distributions for the rotated quadrature phase. Phys Rev A 40(5):2847–2849
Wiebe N, Braun D, Lloyd S (2012) Quantum algorithm for data fitting. Phys Rev Lett 109(5):050505
Wootters WK, Zurek WH (1982) A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299(5886):802–803
Xin T, Lu S, Cao N, Anikeeva G, Lu D, Li J, Zeng B (2019) Local-measurement-based quantum state tomography via neural networks. npj Quantum Inf 5(1):109
Xu Q, Xu S (2018) Neural network state estimation for full quantum state tomography. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.06654
Zuo Y, Cao C, Cao N, Lai X, Zeng B, Du S (2022) Optical neural network quantum state tomography. Adv Photonics 4(2):026004–026004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equal contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Innan, N., Siddiqui, O.I., Arora, S. et al. Quantum state tomography using quantum machine learning. Quantum Mach. Intell. 6, 28 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42484-024-00162-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42484-024-00162-3