Abstract
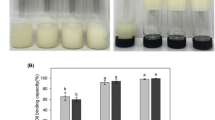
High ammonia (HA) natural rubber latex (NRL) is generally very sensitive at lower temperature and will form big rubber lumps after the freezing and thawing processes. The growth of ice crystals in an aqueous medium during freezing causes the rubber particles to move closer together and thus disrupts the protein cloud surrounding the latex particles. The broken protein cloud causes rubber particles to coalesce and form big lumps after the thawing process. However, this phenomenon did not occur when potassium oleate (PO) was incorporated into the HA NRL medium. PO acted as a colloid stabiliser by means of adsorbance at the rubber latex surface, thus preventing the coalescence of rubber particles from occurring. This study investigated the effect of PO loading (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 phr) on the colloid stability of HA NRL after being subjected to both freezing and thawing. These latex mixtures were frozen by cooling it at − 4 °C for 24 h and thawed by allowing them to stand at room temperature for 1 h followed by heating at 40 °C for another hour. The results obtained showed that the PO improved the colloid stability of HA NRL in terms of morphological properties, viscosity, and mechanical stability time values. Particle-size distribution of latex mixtures, however, did not vary even after freezing.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cockbain EG, Gregory J (1969) Freeze-resistant natural rubber latex concentrate. J Rubber Res Ins Malaya 22(5):409–422
Walker HW (1947) Stability of synthetic rubber dispersion. II Coagulation of neoprene latices by freezing. J Phys Colloid Chem 15:451
Talalay L (1963) Agglomeration and reinforcement of synthetic latexes by freezing. Rubber Chem Technol 36(3):581–596
De Vries O, Beumee-Neuwland N (1928) Coagulation phenomena in Havea Latex VIII rubber obtained by freezing the latex. Arch Rubber Cult Ned Indie 12:683
Ritchie AH (1966) Kepong Plantations Ltd., British Patent No. 1,053,156
Blackley DC (1997) Polymer latices: science and technology, fundamental principles, vol 1, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Blackley DC (1997) Polymer latices: science and technology, applications of Latices, vol 3, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Manjula Dilkushi Silva K, Walpalage S (2009) Effects of added ammonium laurate soap on natural rubber latex. J Rubber Res 12(2):59–70
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the financial support. This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (F/RGS) no 203.PTEKIND.6711524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siti nuraya, A.S., Baharin, A. & Azura, A.R. Effect of potassium oleate (PO) on the colloid stability of high ammonia (HA) natural rubber latex (NRL) after the freezing and thawing processes. J Rubber Res 22, 13–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42464-019-00002-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42464-019-00002-1