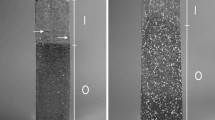
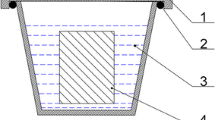
Abstract: With the development of boiler rooms using biomass, the limitation of premature wear of refractory ceramic products by chemical corrosion became a major issue to limit the premature shutdown of the installations. In this context, the French industrial technical Center for Ceramics (SFC) and its partner ICAR conducted a complete study aimed to understand the mechanisms that control the degradation of refractory bricks and identify the most adapted materials. Two mechanisms of corrosion were highlighted: corrosion by alkali vapours (on the hot face and in the core) and reactive corrosion by ashes on the refractory surface. The combination of these two phenomena leads to a progressive degradation of the microstructure on the hot face and an embrittlement of the refractory material (occurrence cracking). Among the refractory ceramic products tested, mullite bricks show the best corrosion resistance to ashes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulon, A., Filhol, A., Guichard, J. et al. Behaviour of Refractory Materials for Sustainable Use in the Energy Sector. Interceram. - Int. Ceram. Rev. 68, 16–23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42411-019-0002-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42411-019-0002-2