Abstract
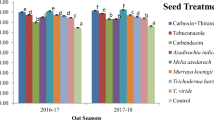
Foot and stem rot (FSR) and Phoma leaf spot caused by Phytophthora parasitica var. sabdariffae and Phoma sabdariffae are the two major diseases, affecting the roselle cultivation across India and worldwide. The efficacy of different group of fungicides like, Acetamida-Dithiocarbamate, Methoxyacrylates, Trifloxystrobin and Tebuconazole, Phenyl amide and Copper compound were assessed under field conditions against FSR and Phoma leaf spot. Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT) was used to determine significant difference (p < 0.05) between the treatments. Seed treatment with cymoxanil 8% + mancozeb 64% WP @ 3 g kg−1 seed + prophylactic foliar spraying of cymoxanil 8% + mancozeb 64% WP @ 0.3% at 30 and 45 days of crop age showed lowest disease incidence (3.66 and 2.93%) against FSR and Phoma leaf spot disease as compared to the untreated control (9.73 and 7.66%) and exhibited higher plant height (350 cm), high basal diameter (17.51 cm), highest benefit–cost ratio (2.1), more incremental benefit–cost ratio (15.6) and highest fibre yield (26.53 q/ha) over untreated control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand YR, Begum S, Dangmei R, Nath PS (2013) Evaluation of trifloxystrobin 25% + tebuconazole 50% (Nativo 75 WG) against Exserohilum turcicum causing leaf blight disease of maize. J Crop Weed 9:198–200
Bartlett DW, Clough JM, Godwin JR, Hall AA, Hamer M, Parr-Dobrzanski B (2002) The strobilurin fungicides. Pest Manag Sci 58:649–662
Chewonarin T, Kinouchi T, Kataoka K, Arimochi H, Kuwahara T, Vinitketkumnuen U, Ohnishi Y (1999) Effects of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn.), a Thai medicinal plant, on the mutagenicity of various known mutagens in Salmonella typhimurium and on formation of aberrant crypt foci induced by the colon carcinogens azoxymethane and 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol 37:591–601
De RK, Mandal RK (2007a) Effect of seed treatment with fungicides on foot and stem rot disease caused by Phytophthora parasitica var. sabdariffae in Hibiscus sabdariffa. J Interacademicia 11:161–165
De RK, Mandal RK (2007b) Epidemiology of foot and stem rot and collar rot diseases of HS and HC mesta. In: Presented in “National symposium on microbial diversity and plant health” held between November 28 and 29, BCKV, Kalyani, p 30
Devlash R (2012) Chemical management of Phytophthora blight of colocasia in mid hills of Himachal Pradesh. Indian Phytopathol 65:307–309
Dhar P (2013) Autonomic Responses in High Altitude and Adaptogenic Efficacy of Phytococktail from Trans-Himalayan Plants. PhD thesis, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, India
Duke JA (1986) Isthmian ethnobotanical dictionary. Scientific Publisher, Jodhpur
Eslaminejad Touba, Zakaria Maziah (2011) Morphological characteristics and pathogenicity of fungi associated with Roselle (Hibiscus Sabdariffa) diseases in Penang, Malaysia. Microb Pathog 51:325–337
Farih A, Tsao PH, Menge JA (1981) In vitro effects of metalaxyl on growth, sporulation, and germination of Phytophthora parasitica and P. citrophthora. Plant Dis 65:651–654
Ghosh T (1983) “Handbook on jute”. FAO, plant production and protection paper, 51, p 219
Gisi U (1996) Synergistic action of fungicides in mixtures. Phytopathology 86:1273–1279
Grayson BT, Batten DM, Walter D (1995) Adjuvant effects on the therapeutic control of potato late blight by dimethomorph wettable powder formulations. Pest Manag Sci 46:355–359
Gullino ML, Minuto A, Gilardi G, Garibaldi A (2002) Efficacy of azoxystrobin and other strobilurins against Fusarium wilts of Carnation, Cyclaman and Paris daisy. Crop Prot 21:57–61
Gupta SK, Jarial K (2014) Efficacy of some fungicides against downy mildew of cucumber. Int J Farm Sci 4:72–75
Kannan GS, Ganesh S (2003) Efficacy of azoxystrobin (Amistar 25 SC) against foliar diseases in grapevine. Pestology 27:15–17
Lawton BP (2004) Hibiscus: hardy and tropical plants for the garden. Timber Press Inc, Portland
Mahadevan N, Shivali A, Kamboj P (2009) Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn.—an overview. Nat Prod Radiance 8:77–83
Mahapatra BS, Mitra S, Ramasubramanian T, Sinha MK (2009) Research on jute (Corchorus olitorius and C. capsularis) and kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus and H. sabdariffa): present status and future perspective. Indian J Agric Sci 79:951–967
Majumdar M, Mandal N (1994) Source of resistance in roselle to foot and stem rot caused by Phytophthora parasitica and effect of soil amendment on the disease incidence and fibre yield. Indian Agric 38:219–223
McClintock NC, Tahir IME (2004) Hibiscus sabdariffa L. In: Grubben GJH, Denton OA (eds) Vegetables/legumes. PROTA, Wageningen
Morton JF (1987) Roselle. Fruits of Warm climates. Florida Flair Books, Miami, pp 281–286
Mukherjee N, Basak M (1973) Chemotherapeutic control of foot and stem rot of roselle (Hibiscus sabdarifa altissima) caused by Phytophthora parasitica var. sabdariffae. Indian Phytopathol 26:576–577
Nithyameenakshi S, Jeyaramraja PR, Manian S (2006) Investigations on phytotoxicity of two new fungicides azoxystrobin and difenoconazole. Am J Plant Physiol 1:89–98
Pal DC, Jain SK (1998) Tribal medicine. Naya Prakash, Calcutta
Patil VA, Mehta BP, Deshmukh AJ (2010) Field evaluation of different fungicides against phoma leaf spot disease of Indian bean. Int J Pharm Biosci 2:1–5
Pethybridge SJ, Hay FS, Wilson CR, Groom T (2005) Development of a fungicide based management strategy for foliar disease caused by Phoma ligulicola in Tasmanian pyrethrum fields. Plant Dis 89:1114–1120
Pranamika S, Saikia MK (2013) Management of Late blight of potato through chemicals. J Agric Vet Sci 2:23–26
Prom LK, Isakeit T (2003) Laboratory, greenhouse and field assessment of fourteen fungicides for activity against Claviceps africana, causal agent of sorghum ergot. Plant Dis 87:252–258
Quezon (2005) Roselle: the dawn of a sunrise industry. http://www.quezon.org/roselle
Radisek S, Leskosek GJ and Javornik B (2011). Management of cercospora and phoma leaf spot on hops in Slovenia. In: International Hop Growers` Convention I.H.G.C. Proceedings of the Scientific Commission Lublin, Poland 19–23 June, 2011, pp 104–108
Rao PU (1996) Nutrient composition and biological evaluation of mesta (Hibiscus sabdariffa) seeds. Plant Food Human Nutr 49:27–34
Rolfs PH (1929) Subtropical vegetable-gardening. The Macmillan Company, New York, p 360
Samoucha Y, Cohen Y (1989) Field control of potato late blight by synergistic fungicidal mixtures. Plant Dis 73:751–753
Sendhilvel V, Raguchander T, Nakkeran S, Amutha G, Marimuthu T (2004) Bio efficacy of azoxystrobin against downy mildew of Grapevine. Pestology 18:44–51
Sharma P, Saikia MK (2013) Management of late blight of potato through chemicals. J Agric Vet Sci 2:23–26
Siddique NA, Aktar MS, Swapon NH (2016) Comparative efficacy of different fungicides against late blight diseases of potato incited by Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary and its Management. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 7:364. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7471
Thind TS, Mohan Chander, Prem R, Arora JK (2002) Activity of strobilurin fungicides against some phytopathogenic fungi. J Mycol Plant Pathol 32:425–426
Thind TS, Goswami S, Thind SK, Mohan C (2009) Resistance in Phytophthora parasitica against metalaxyl in citrus orchards. Indian Phytopathol 62(4):536–538
Tindal HD (1986) Vegetable in the tropics Macmillan. Edn. Ltd, Hampshire, pp 267–268
Wang WQ, Zhang XF, Zhang WJ, David M (2002) Resistance to fungicides, mating types and fitness of Phytophthora infestans. Acta Phytopathol Sin 32:278–283 (In Chinese)
Zhu GN, Huang FX, Qin BX, Liu ZM, Cai JH (2008) Studies on the isolation and culture of Phytophthora infestans and the methods for purification with zoospore. China Veg 6:41–42 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Director, ICAR-Central Research Institute for Jute and Allied Fibres, Barrackpore, Kolkata, and All India Network programme for providing the support to undertake the investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meena, P.N., Satpathy, S. Evaluation of fungicides against foot and stem rot and Phoma leaf spot of roselle and their impact on fibre yield. Indian Phytopathology 71, 563–569 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0094-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0094-z