Abstract
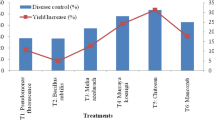
Pyrenophora avenae Ito & Kurib. is an important fungal pathogen of leaf blight (HLB) causing significant fodder and grain yield losses in oat. The effect of fungicides (carboxin + thiram, tebuconazole, carbendazim, mancozeb and propiconazole), plant extracts (Melia azedarach, Murraya koenigii and Azadirachta indica) and biocontrol agents (Trichoderma harzianum and T. viride) was evaluated in 2016–17 and 2017–18 for HLB management in oats. The seed infection was almost double in 2017–18 (19.6%) as compared to 2016–17 (8.8%). Greater mean reduction in disease severity was provided by propiconazole spray (54.28%) followed by tebuconazole (46.22%). Foliar spray of propiconazole provided 23.47 and 26.75% increase in green fodder yield in 2016–17 and 2017–18 respectively as compared to control. Foliar applications increased grain yield by a factor of 13–50% in 2016–17 and 3–44% in 2017–18 and seed treatments increased grain yield by 12–39%. Aqueous extract of M. azedarach and A. indica significantly reduced the leaf blight severity by 57.85 and 52.78% respectively with increase in green fodder yield, grain yield and thousand kernel weight. Therefore, seed treatment and foliar application of fungicides or aqueous plant extracts were equally effective against leaf blight and showed increase in green fodder and grain yields.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, R. V. (1971). Influence of chemical fungicide treatment of oat seed on seedling emergence, seed yield, and kernel weight. Canadian Plant Disease Survey, 51, 71–75.
Clifford, B.C. (1995). Diseases, pests and disorders of oats/R.W. Welch (ed.). The oat crop. Production and utilization. – Northern Ireland, UK, 1995, p.252–278.
Cummings, J. A., Bergstrom, G. C., Richtmyer, R. J., III, & Hahn, R. R. (2015). Evaluation of foliar fungicides and a biological control product for control of Fusarium head blight and foliar diseases of winter wheat in New York, 2014. Plant Disease Management Reports, 9, CF026.
Das, M. K., Rajaram, S., Mundt, C. C., & Kronstad, W. E. (1992). Inheritance of slow rusting resistance to leaf rust in wheat. Crop Science, 32, 1452–1456.
Dubin, H. J., Arun, B., Begum, S. N., Bhatta, M., Dhari, R., Goel, L. B., Joshi, A. K., Khanna, B. N., Malaker, P. K., Pokhrel, D. R., Rahman, M. M., Saha, N. K., Shaheed, M. A., Sharma, R. C., Singh, A. K., Singh, R. M., Singh, R. V., Vargas, M., & Verma, P. C. (1998). Results of the South Asia regional Helminthosporium leaf blight and yield experiment, 1993-94. In E. Duveiller, H. J. Dubin, J. Reeves, & A. McNab (Eds.), Helminthosporium blights of wheat: Spot blotch and tan spot (pp. 182–187). Mexico D.F.: CIMMYT.
Duveiller, E., Kandel, Y. R., Sharma, R. C., & Shrestha, S. M. (2005). Epidemiology of foliar blights (spot blotch and tan spot) of wheat in the plains bordering the Himalayas. Phytopathology, 95, 248–256.
Ellis, M.B. (1971). Dematiaceous Hyphomycetes. Kew, Commonwealth Mycological Institute, 608 pp.
Giri, G. K., Gade, R. M., & Patil, C. U. (2001). Seed borne Bipolaris sorokiniana in wheat and its chemical control. Journal of Soils and Crops, 11, 109–112.
Gough, F. J., & Mc Daniel, M. E. (1974). Occurrence of oat leaf blotch in Texas in 1973. Plant Disease Report, 58, 80–81.
Hao, W., Ren, L., Ran, W., & Shen, Q. (2010). Allelopathic effects of root exudates from water melon and rice plants on Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. niveum. Plant and Soil, 336, 485–497.
Harlapur, S. I., Kulkarni, M. S., Wali, M. C., & Kulkarni, S. (2007). Evaluation of plant extracts, bio-agents and fungicides against Exserohilum turcicum (pass.) Leonard and Suggs. Causing turcicum leaf blight of maize. Karnataka Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 20, 541–544.
Kakraliya, S. S., Zacharia, S., Bajiya, M. R., & Sheshma, M. (2017). Management of leaf blight of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with bio-agents, neem leaf extract and fungicides. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 6, 296–303.
Khamari, B., & Beura, S. K. (2014). Efficacy of biocontrol agents against maydis leaf blight of maize. Journal of Plant Protection and Environment, 11, 95–97.
Khanzada, K. A., Rajput, M. A., Shah, G. S., Lodhi, A. M., & Mehboob, F. (2002). Effect of seed dressing fungicides for the control of seed borne mycoflora of wheat. Asian Journal of Plant Sciences, 1, 441–444.
Korbas, M., & Kubiak, K. (2000). Ochronić ziarno siewne. Top Agrar Polska, 1, 44–45.
Kumar, S., Rani, A., & Jha, M. M. (2009). Evaluation of plant extracts for management of maydis leaf blight of maize. Annals of Plant Protection Sciences, 17, 130–132.
Malaker, P. K., & Mian, I. H. (2009). Effect of seed treatment and foliar spray with fungicides controlling black point disease of wheat. Bangladesh Journal of Agricultural Research, 34, 425–434.
Malik, V. K., Singh, D. P., & Panwar, M. S. (2008). Management of spot blotch of wheat (Triticum aestivum) caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana using foliar sprays of botanicals and fungicides. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 78, 646–648.
Malik, V. K., Manjeet, S., Hooda, K. S., Yadav, N. K., & Chauhan, P. K. (2018). Efficacy of newer molecules, bioagents and botanicals against maydis leaf blight and banded leaf and sheath blight of maize. Plant Pathology Journal, 34, 121–125.
Mathre, D. E., Johnston, R. H., & Grey, W. E. (2001). Small grain cereal seed treatment. Online. Plant Health Instructor, 118.
Mehta, Y. R. (1993). Spot blotch. In S. B. Mathur & B. M. Cunfer (Eds.), Seedborne disease and seed health testing of wheat (pp. 105–112). Copenhagen: Jordhurgsforlaget.
Motovilin, A. A. (2000). The response of oat cultivars to fungicide application against leaf blight. Zashchita I Karantin Rastenii, 10, 30 (in Russian).
Nasir, A., Singh, V. K., & Singh, A. (2012). Management of maydis leaf blight using fungicides and phytoextracts in maize. Maize Journal, 1, 106–109.
Neergaard, P. (1977). Seed pathology. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Pathan, M. A., Jiskani, M. M., & Wagan, K. H. (2003). Effect of seed-borne fungi on seed quality components of different wheat varieties and their response to fungicide seed treatment. Mycopath, 1, 119–123.
Perello, A. E., Monaco, C. I., Moreno, M. V., Cordo, C. A., & Simon, M. R. (2006). The effect of Trichoderma harzianum and T. koningii on the control of tan spot (Pyrenophora tritici-repentis) and leaf blotch (Mycosphaerella graminicola) of wheat under field conditions in Argentina. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 16, 803–813.
Pille, S., & Mati, K. (2011). Timing of fungicide application for profitable disease management in oat (Avena sativa L.). Žemdirbystė Agriculture, 98, 167–174.
Platz, G.J., Meldrum, S.I. Webb, N.A. (1999). Chemical control of seed borne diseases of barley. In: Proceedings of 9th Australian Barley Technical Symposium, ABTS, Melbourne, vol. 2, pp. 1–2.
Pszczółkowska, A., Fordoński, G., Olszewski, J., Okorski, A., & Płodzień, K. (2010). The effect of fungicide seed treatment on the productivity and health of husked oat grain. Polish Journal of Natural Science, 25, 332–340.
Rahman, S. N. M., Maniruzzaman, S. M., Nusrat, S., & Abdul, K. (2015). In vitro evaluation of botanical extract, bioagents and fungicides against purple blotch diseases of bunch onion in Bangladesh. Advances in Zoology and Botony, 3, 179–183.
Rinez, A., Daami-Remadi, M., Ladhari, A., Omezzine, F., Rinez, I., & Haouala, R. (2013). Antifungal activity of Datura metel L. organic and aqueous extracts on some pathogenic and antagonistic fungi. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 7, 1605–1612.
Roopa, R. S., Yadahalli, I. C. B., & Kavyashree, M. C. (2014). Evaluation of natural plant extracts, antagonists and fungicides against early blight caused by Alternaria solani in vitro. The Bioscan, 9, 1309–1312.
Sharma-Poudyal, D., Duveiller, E., & Sharma, R. C. (2005). Effects of seed treatment and foliar fungicides on Helminthosporium leaf blight and on performance of wheat in warmer growing conditions. Journal of Phytopathology, 153, 401–408.
Sharma-Poudyal, D., Sharma, R. C., & Duveiller, E. (2016). Control of Helminthosporium leaf blight of spring wheat using seed treatments and single foliar spray in indo-Gangetic Plains of Nepal. Crop Protection, 88, 161–166.
Shrestha, K. K., Timla, R. D., Mahato, B. N., & Bim, H. B. (1998). Disease incidence and yield loss due to foliar blight of wheat in Nepal. In: Helminthosporium blights of wheat. Indian Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology, 23, 112–116.
Soovali, P. (2011). Integrated plant disease management in spring barley and oat production. Ph.D. dissertation. Tartu: Estonian University of Life Sciences, Kreutzwaldi.
Subedi, S. (2015). A review on important maize diseases and their management in Nepal. Journal of Maize Research and Development, 1, 28–52.
Surekha, C. H., Neelapu, N. R. R., Siva, P. B., & Sankar Ganesh, P. (2014). Induction of defense enzymes and phenolic content by Trichoderma viride in Vigna mungo infested with Fusarium oxysporum and Alternaria alternata. International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research, 4, 31–40.
Viedma, D. L., & Kohli, M. M. (1998). Spot blotch and tan spot of wheat in Paraguay. In E. Duveiller, H. J. Dubin, J. Reeves, & A. McNab (Eds.), Proc. Int. workshop Helminthosporium diseases of wheat: Spot blotch and tan spot. 9–14 February 1997 (pp. 126–133). Mexico, DF: CIMMYT, El Batan.
Waxman, K. D., Bergstrom, G. C., Richtmyer, R. J., III, & Hahn, R. R. (2010). Evaluation of integrated methods for management of Fusarium head blight and foliar diseases of winter wheat in New York, 2009. Plant Disease Management Reports, 4, CF016.
Waxman, K. D., Bergstrom, G. C., Richtmyer, R. J., III, & Hahn, R. R. (2011). Evaluation of foliar fungicides for control of foliar diseases and Fusarium head blight of winter wheat in New York, 2010. Plant Disease Management Reports, 5, CF018.
Waxman, K. D., Bergstrom, G. C., Richtmyer, R. J., III, & Hahn, R. R. (2012). Evaluation of foliar fungicides for control of Fusarium head blight of winter wheat in New York, 2011. Plant Disease Management Reports, 6, CF009.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the Head of the Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, PAU, Ludhiana for providing financial assistance, all laboratory and other facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atri, A., Tiwana, U.S. Effect of seed treatment and foliar spray on leaf blight of fodder oat in Punjab. Phytoparasitica 47, 723–731 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-019-00758-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-019-00758-7