Abstract
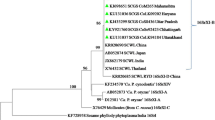
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is a widely cultivated and commercially important vegetable crop widely grown in India. Profuse shoot proliferation symptoms were observed in potato plants of two varieties, Kufri Khyati and Kufri Surya at the Research plots of All India Co-ordinated Research Project on Potato, Orissa University of Agriculture and Technology, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India during February, 2017. The symptomatic plants were tested for phytoplasma etiology. Nested and semi-nested PCR assays primed by primer pairs P1/P7 and 3Far/3Rev for 16S rRNA gene and secAF1/R3 for secA gene amplified DNA fragments of 1.3 kb (3Far/3Rev) and 840 bp (secAF1/R3), respectively from all the symptomatic potato samples but not from any asymptomatic plants. The 16S rDNA sequences of potato tuber (Acc. no. KY815100, Kufri Khyati; MG566064, Kufri Surya) and shoot phytoplasma strains (Acc. no. KY815099, Kufri Khyati; MG566063, Kufri Surya) shared 100% nucleotide sequence identity with 16S rDNA sequence of identified phytoplasma strains belonging to 16SrVI-D subgroup associated with Lens culinaris witches’ broom (Acc. no. KY439869), brinjal little leaf (Acc. no. KX284698) and Brassica oleracea var. capitata witches’ broom (Acc. no. KX671553) in pair wise sequence comparison. Sequence comparison of 840 bp of secA gene of potato phytoplasma strains from tuber of variety, Kufri Khyati (Acc. no. KY815101) and variety Kufri Surya (Acc. no. MG566065) showed 99% sequence identity to secA gene sequences of brinjal little leaf phytoplasma strains (Acc. no. KX610808, KX894792, KY064175), which belonged to 16SrVI-D subgroup. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA and secA gene sequences, and virtual RFLP analysis of 16S rDNA sequences of potato shoot proliferation phytoplasma strain confirmed their clustering and grouping with strains of clover proliferation subgroup D. Our results confirmed potato as a new host of 16SrVI-D subgroup of phytoplasmas in the world. The 16SrVI-D strain is wide spread in India and cause significant yield losses and hence poses serious socio-economic threat to commercially grown potato crops.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens U, Seemuller E (1992) Detection of DNA of plant pathogenic mycoplasma like organisms by a polymerase chain reaction which amplifies a sequence of the 16S rRNA gene. J Phytopathol 82:828–832
Anonymous (2017). Annual Report (2016–17), Department of Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and farmer welfare, Govt. of India, Krishi Bhavan, New Delhi, India, p 194
Arocha Y, Singh A, Pandey M, Tripathi AN, Chandra B, Shukla SK, Singh Y, Kumar A, Srivastava RK, Zaidi NW, Arif M, Narwal S, Tewari AK, Gupta MK, Nath PD, Rabindran R, Khirbat SK, Byadgi AS, Singh G, Boa E (2008) New plant hosts for group 16SrII, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia’ in India. Plant Pathol 17:36
Bertaccini A, Duduk B, Paltrinieri S, Contaldo N (2014) Phytoplasmas and phytoplasma diseases: a severe threat to agriculture. Am J Plant Sci 5:1763–1788
Caicedo J, Crizón M, Pozo A, Cevallos A, Simbaña L, Rivera L, Arahana V (2015) First report of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia’ (16SrII) associated with potato purple top in San Gabriel-Carchi, Ecuador. New Dis Rep 32:20
Dehghan H, Salehi M, Khanchezar A, Afshar H (2014) Biological and molecular characterization of a phytoplasma associated with greenhouse cucumber phyllody in Fars province. Iran J Plant Pathol 50:393–401
Delic N, Contaldo B, Lolic Đ, Moravcˇe D, Bertaccini A (2016) First report of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in pepper and celery in Bosnia and Herzegovina. J Plant Pathol 98:171–185
Deng S, Hiruki C (1991) Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and nonculturable Mollicutes. J Microbiol Methods 14:53–61
Ember I, Acs Z, Munyaneza JE, Crosslin JM, Kölber M (2011) Survey and molecular detection of phytoplasmas associated with potato in Romania and southern Russia. Eur J Plant Pathol 130:367–377
Garg ID, Khurana SMP, Singh RA (1989) Degeneration of mollicutes with high temperature associated symptom remission of marginal flavescence infected potato plants. Int J Trop Plant Dis 7:161–166
Ghanekar AM, Manohar SK, Reddy SV, Nene YL (1988) Association of a mycoplasmas-like organism with chickpea phyllody. Indian Phytopath 41:462–464
Ghosh DK, Das AK, Shyam Singh, Singh SJ, Ahlawat YS (1999) Occurrence of witches’- Broom, a new phytoplasma disease of acid lime (Citrus aurantifolia) in India. New Dis Rep 83:302
Girsova N, Bottner KD, Mozhaeva KA, Kastalyeva TB, Owens RA, Lee IM (2008) Diverse phytoplasmas associated with potato stolbur and other related potato diseases in Russia. Eur J Plant Pathol 145:139–153
Hodgetts BN, Mumford R, Harrison N, Dickinson M (2008) Phytoplasma phylogenetics based on analysis of secA and 23S rRNA gene sequences for improved resolution on candidate species of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1826–1837
Holeva MC, Glynos PE, Karafla CD, Koutsioumari EM (2014) First report of Candidatus Phytoplasma solani associated with potato plants in Greece. Dis Notes 98:1739
Hosseini Esmailzadeh Salehi SA, Mirchenari M, Tarizeh SM, Gholampoor H (2015) First report of a 16SrVI group related phytoplasma associated with cucumber phyllody in a greenhouse in Iran. New Dis Rep 32:5
Ivanović Z, Nenad T, Svetlana Ž, Erika PD, Nenad D, Jelena J, Milana M (2011) First report of stolbur phytoplasma infecting celery in Serbia. Bulletin Insectol 64:S239–S240
Jones P, Arocha Y, Antesana O, Montellano E, Franco P (2005) ‘Brotes grandes’ (big bud) of potato: a new disease associated with a 16SrI-B subgroup phytoplasma in Bolivia. Plant Pathol 54:234
Kaur S, Mukerji KG (2004) Potato diseases and their management. In: Mukerji K (ed) Disease management of fruits and vegetables. Springer, Germany, p 233–280
Khan MS, Raj SK (2006) First report of molecular detection of an aster yellows phytoplasma (‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’) isolate infecting chilli (Capsicum annuum) in India. Plant Pathol 155:822
Khasa E, Taloh A, Prabha T, Rao GP (2016) Molecular characterization of phytoplasmas of ‘Clover proliferation’ group associated with three ornamental plant species in India. 3 Biotech 6:237
Khurana SMP, Singh S, Singh V, Dhingra MK (1977) Diagnosis of viral and mycoplasmal diseases of potatoes and their control. Indian Farming Dig 10:141–144
Kumar S, Singh V, Lakhanpaul S (2012) Molecular characterization and phylogeny of phytoplasma associated with bunchy top disease in its new host Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) in India reveal a novel lineage within the 16SrI group. Eur J Plant Pathol 133:371–378
Kumar M, Madhupriya, Rao GP (2017) Molecular characterization, vector identification and sources of phytoplasmas associated with brinjal little leaf disease in India. 3 Biotech 7:7
Lee IM, Gundersen RD, Davis RE, Bartoszyk IM (1998) Revised classification scheme of phytoplasmas based on RFLP analysis of 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:1153–1169
Lee IM, Davis RE, Gundersen-Rindal DE (2000) Phytoplasma: phytopathogenic mollicutes. Ann Rev Microbiol 54:221–255
Manimekalai R, Soumya VP, Sathish KR, Selvarajan R, Krishna Reddy M, Sasikala Thomas GV, Rajeev M, Baranwal VK (2010) Molecular detection of 16Sr XI group phytoplasma associated with root (wilt) disease of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) in India. Plant Dis 94:636
Jovic J, Ibolya E, Milana M, Tatjana C, Oliver K, Slobodan K, Zoltan ACS, Maria K, Ivo T (2011) Molecular detection of potato stolbur phytoplasma in Serbia. Bull Insectol 64(Supplement):S83–S84
Mejia JF, Contaldo N, Paltrinieri S, Pardo JM, Rios CA, Alvarez A, Bertaccini A (2011) Molecular detection and identification of group 16SrV and 16SrXII phytoplasmas associated with potatoes in Colombia. Bull Insectol 64:S97–S98
Radonjić S, Hrnčić S (2016) First Report of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Associated with Potato Stolbur disease in Montenegro. Disease Notes 100:1775
Rao GP, Kumar M (2017) World status of phytoplasma diseases associated with eggplant. Crop Prot 96:22–29
Rao GP, Thorat V, Madhupriya, Manimekalai R, Tiwari AK, Yadav A (2017) A century progress of research on phytoplasma diseases in India. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 6:1–38
Salehi M, Izadpanah K, Nejat N, Siampour M (2007) Partial characterization of phytoplasmas associated with lettuce and wild lettuce phyllodies in Iran. Plant Pathol 56:669–676
Santos-Cervantes ME, Chavez- Medina JA, Acosta-Pardini J, Flores-Zamora GL, Méndez-Lozano J, Leyva-López NE (2010) Genetic diversity and geographical distribution of phytoplasmas associated with potato purple top disease in Mexico. Plant Dis 94:388–395
Schneider B, Seemueller E, Smart CD, Kirkpatrick BC (1995) Phylogenetic classification of plant pathogenic mycoplasma-like organisms or phytoplasmas. In: Razin S, Tully JG (eds) Molecular and diagnostic procedures in mycoplasmology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 369–380
Sichani FV, Bahar M, Zirak L (2014) Characterization of phytoplasmas related to aster yellows group infecting annual plants in Iran, based on the studies of 16S rRNA and rp genes. J Plant Prot Res 54:1–8
Singh N, Upadhaya PP, Madhupriya, Rao GP (2012) ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma trifolii’ associated with little leaf and witches’ broom disease of Datura stramonium L. in India. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2:69–71
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725
Tiwari AK, Iqbal A, Khan MS, Chun SC, Madhupriya (2013) Molecular identification of ‘Ca. P. asteris’ associated with little leaf disease of potato in India. J Plant Pathol 95:659–668
Tran-Nguyen L, Blanche KR, Egan B, Gibb KS (2000) Diversity of phytoplasma in northern Australian sugarcane and other grasses. Plant Pathol 49:666–679
Verdin E, Salar P, Danet JL, Choueiri E, Jreijiri F, El-Zammar S, Gèlie B, Bové J, Garnier M (2003) ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma phoeniceum’, a new phytoplasma associated with an emerging lethal disease of almond trees in Lebanon and Iran. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:833–838
Zhang J, Hogenhout SA, Nault LR, Hoy CW, Miller SA (2004) Molecular and symptom analyses of phytoplasma strains from lettuce reveal a diverse population. Phytopathology 94:842–849
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, G.P., Mishra, A., Mishra, M.K. et al. Identification and characterization of Candidatus Phytoplasma trifolii (16SrVI-D) inducing shoot proliferation disease of potato in India. Indian Phytopathology 71, 75–81 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0011-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0011-5