Abstract
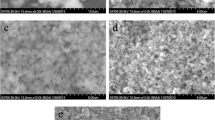
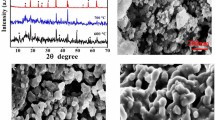
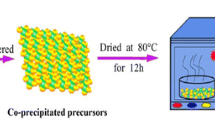
A simple two-step method for preparing nanostructured Li4Ti5O12 (LTO), a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), is reported. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results reveal that the structure of the synthesised LTO is cubic spinel type characterised by a space group Fd3m. The shape of the final powder obtained is faceted polyhedral. The average particle diameter is 68 nm. The LTO exhibits good rate capability when assembled into half cells and tested in the 1.0 to 2.5 V range. The half-cell delivers a specific capacity of 149.1, 145.5, 141.3, 139.0, 136.0, and 131.9 mAh g−1 at 0.1C, 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, 2C, and 5C, respectively. In addition, it exhibits a reversible discharge capacity of 96.8 mAh g−1 at a 2C rate whilst maintaining a Coulombic efficiency of 99.9% after 100 cycles. The overall resistance of the LTO/Li cells at 25 °C is only 35.5 Ω, suggesting a low impedance of the LTO/Li interfaces.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Energy Information Administration, U.S. energy-related carbon dioxide emissions, 2019, (2019). www.eia.gov (accessed September 2, 2021).
A.G. Chmielewski, Environmental effects of fossil fuel combustion, Interact. Energy Environ. 4, 56–74 (2009)
R. Pichs Madruga, K. Seyboth, P. Eickemeier, P. Matschoss, G. Hansen, S. Kadner, S. Schlömer, T. Zwickel, C. Von Stechow, Renewable energy sources and climate change mitigation, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, (2011). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139151153.
X. Cao, S. Chen, G. Wang, Porous carbon particles derived from natural peanut shells as lithium ion battery anode and its electrochemical properties. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 819–826 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-014-4153-z
B. Zhao, R. Ran, M. Liu, Z. Shao, A comprehensive review of Li4Ti5O12-based electrodes for lithium-ion batteries: the latest advancements and future perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Reports. 98, 1–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSER.2015.10.001
Z. Yang, J. Zhang, M.C.W. Kintner-Meyer, X. Lu, D. Choi, J.P. Lemmon, J. Liu, Electrochemical energy storage for green grid. Chem. Rev. 111, 3577–3613 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/CR100290V
J.-Z. Guo, Z.-Y. Gu, X.-X. Zhao, M.-Y. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Yang, W.-H. Li, X.-L. Wu, Flexible Na/K-ion full batteries from the renewable cotton cloth–derived stable, low-cost, and binder-free anode and cathode. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1902056 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/AENM.201902056
X. Ma, X. Wu, Y. Liu, W. Wu, Z. Pan, P.K. Shen, Toward a high-energy-density cathode with enhanced temperature adaptability for sodium-ion batteries: a case study of Na3MnZr(PO4)3microspheres with embedded dual-carbon networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13, 21390–21400 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.1C03642
S. Park, J.N. Chotard, D. Carlier, I. Moog, M. Courty, M. Duttine, F. Fauth, A. Iadecola, L. Croguennec, C. Masquelier, Crystal structures and local environments of NASICON-type Na3FeV(PO4)3and Na4FeV(PO4)3positive electrode materials for Na-Ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 33, 5355–5367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.CHEMMATER.1C01457
H. Gao, I.D. Seymour, S. Xin, L. Xue, G. Henkelman, J.B. Goodenough, Na3MnZr(PO4)3: a high-voltage cathode for sodium batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 18192–18199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/JACS.8B11388
P.S. Veluri, S. Mitra, High-rate capable full-cell lithium-ion battery based on a conversion anode and an intercalation cathode. ChemElectroChem 4, 686–691 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/CELC.201600681
F. Zhang, F. Yi, T. Meng, A. Gao, D. Shu, H. Chen, H. Cheng, X. Zhou, In situ supramolecular self-assembly assisted synthesis of Li4Ti5O12–carbon-reduced graphene oxide microspheres for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 916–924 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.8B04522
X. Xia, Y. Zhang, D. Chao, C. Guan, Y. Zhang, L. Li, X. Ge, I.M. Bacho, J. Tu, H.J. Fan, Solution synthesis of metal oxides for electrochemical energy storage applications. Nanoscale 6, 5008–5048 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR00024B
L. Zeng, R. Liu, L. Han, F. Luo, X. Chen, J. Wang, Q. Qian, Q. Chen, M. Wei, Preparation of a Si/SiO2–ordered-mesoporous-carbon nanocomposite as an anode for high-performance lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. Chem. - A Eur. J. 24, 4841–4848 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/CHEM.201704780
J. Wang, S. Xie, L. Li, Z. Li, A.M. Asiri, H.M. Marwani, X. Han, H. Wang, Electrospinning synthesis of porous NiCoO2 nanofibers as high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/PPSC.201900109.
J. Zhang, Y.X. Yin, Y. You, Y. Yan, Y.G. Guo, A high-capacity tellurium@carbon anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Technol. 2, 757–762 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/ENTE.201402069
Y. Huyan, J. Wang, J. Chen, Q. Zhang, B. Zhang, Magnetic tubular carbon nanofibers as anode electrodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Energy Res. 43, 8242–8256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ER.4821
A. Manthiram, A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry, (n.d.). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15355-0.
D. Kong, W. Ren, Y. Luo, Y. Yang, C. Cheng, Scalable synthesis of graphene-wrapped Li4Ti5O12 dandelion-like microspheres for lithium-ion batteries with excellent rate capability and long-cycle life. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2, 20221–20230 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA04711G
N. Nitta, F. Wu, J.T. Lee, G. Yushin, Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater. Today. 18, 252–264 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATTOD.2014.10.040
J.-M. Tarascon, M. Armand, Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries, Nat. 2001 4146861. 414 (2001) 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644.
J. Asenbauer, T. Eisenmann, M. Kuenzel, A. Kazzazi, Z. Chen, D. Bresser, The success story of graphite as a lithium-ion anode material – fundamentals, remaining challenges, and recent developments including silicon (oxide) composites, Sustain. Energy Fuels. 4, 5387–5416 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SE00175A
J. Kim, S.M. NithyaJeghan, G. Lee, Superior fast-charging capability of graphite anode via facile surface treatment for lithium-ion batteries. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 305, 110325 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2020.110325
A. Tomaszewska, Z. Chu, X. Feng, S. O’Kane, X. Liu, J. Chen, C. Ji, E. Endler, R. Li, L. Liu, Y. Li, S. Zheng, S. Vetterlein, M. Gao, J. Du, M. Parkes, M. Ouyang, M. Marinescu, G. Offer, B. Wu, Lithium-ion battery fast charging: a review. ETransportation. 1, 100011 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETRAN.2019.100011
J.-M. Tarascon, M. Armand, Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414, 359–367 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644
T. Ohzuku, A. Ueda, N. Yamamoto, Zero-strain insertion material of Li [Li1 / 3Ti5 / 3 ] O 4 for rechargeable lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 1431–1435 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2048592
S. Scharner, W. Weppner, P. Schmid-Beurmann, Evidence of two-phase formation upon lithium insertion into the Li1.33Ti1.67 O 4 spinel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 146, 857–861 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1391692
Y.B. He, M. Liu, Z.D. Huang, B. Zhang, Y. Yu, B. Li, F. Kang, J.K. Kim, Effect of solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film on cyclic performance of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for Li ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 239, 269–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.03.141
Y. Sun, L. Zhao, H. Pan, X. Lu, L. Gu, Y.-S. Hu, H. Li, M. Armand, Y. Ikuhara, L. Chen, X. Huang, Direct atomic-scale confirmation of three-phase storage mechanism in Li4Ti5O12 anodes for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 1870 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2878
Q. Zhang, C. Zhang, B. Li, S. Kang, X. Li, Y. Wang, Preparation and electrochemical properties of Ca-doped Li 4Ti5O12 as anode materials in lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta. 98, 146–152 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.03.006
M. Ji, Y. Xu, Z. Zhao, H. Zhang, D. Liu, C. Zhao, X. Qian, C. Zhao, Preparation and electrochemical performance of La3+ and F - co-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 263, 296–303 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.04.051
Z. Zhao, Y. Xu, M. Ji, H. Zhang, Synthesis and electrochemical performance of F-doped Li4Ti 5O12for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta. 109, 645–650 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.164
C.W. Chang-Jian, B.C. Ho, C.K. Chung, J.A. Chou, C.L. Chung, J.H. Huang, J.H. Huang, Y.S. Hsiao, Doping and surface modification enhance the applicability of Li4Ti5O12 microspheres as high-rate anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 44, 23063–23072 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.09.110
Q. Zhang, M.G. Verde, J.K. Seo, X. Li, Y.S. Meng, Structural and electrochemical properties of Gd-doped Li4Ti5O12 as anode material with improved rate capability for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 280, 355–362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.124
Z. Pu, Q. Lan, Y. Li, S. Liu, D. Yu, X.J. Lv, Preparation of W-doped hierarchical porous Li4Ti5O12/brookite nanocomposites for high rate lithium ion batteries at − 20 °C. J. Power Sources. 437, 226890 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226890
W. Wang, H. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Hu, Q. Tian, S. Jiao, Ru-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode materials for high rate lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 228, 244–249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.11.092
Z. Liu, L. Sun, W. Yang, J. Yang, S. Han, D. Chen, Y. Liu, X. Liu, The synergic effects of Na and K co-doping on the crystal structure and electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for lithium ion battery. Solid State Sci. 44, 39–44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2015.04.002
W. Li, M. Chen, J. Jiang, R. Wu, F. Wang, W. Liu, G. Peng, M. Qu, Structural and electrochemical characteristics of SiO2 modified Li4Ti5O12 as anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 637, 476–482 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.049
J. Kim, K.E. Lee, K.H. Kim, S. Wi, S. Lee, S. Nam, C. Kim, S.O. Kim, B. Park, Single-layer graphene-wrapped Li4Ti5O12 anode with superior lithium storage capability. Carbon N. Y. 114, 275–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.12.022
W.K. Pang, V.K. Peterson, N. Sharma, J.-J. Shiu, S. Wu, Lithium migration in Li4Ti5O12 studied using in situ neutron powder diffraction. Chem. Mater. 26, 2318–2326 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm5002779
L. Wang, Y. Zhang, M.E. Scofield, S. Yue, C. McBean, A.C. Marschilok, K.J. Takeuchi, E.S. Takeuchi, S.S. Wong, Enhanced performance of “flower-like” Li4Ti5O12 motifs as anode materials for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. Chemsuschem 8, 3304–3313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201500639
B. VikramBabu, K. VijayaBabu, G. TewodrosAregai, L. Seeta Devi, B. MadhaviLatha, M. SushmaReddi, K. Samatha, V. Veeraiah, Structural and electrical properties of Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Results Phys. 9, 284–289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.02.050
M. Zukalová, M. Fabián, M. Klusáčková, M. Klementová, B. PitňaLásková, Z. Danková, M. Senna, L. Kavan, Li insertion into Li4Ti5O12 spinel prepared by low temperature solid state route: charge capability vs surface area. Electrochim. Acta. 265, 480–487 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.01.171
C.P. Sandhya, B. John, C. Gouri, Lithium titanate as anode material for lithium-ion cells: a review, Ionics 2014 205. 20 (2014) 601–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11581-014-1113-4.
Y.-J. Hao, Q.-Y. Lai, J.-Z. Lu, H.-L. Wang, Y.-D. Chen, X.-Y. Ji, Synthesis and characterisation of spinel Li4Ti5O12 anode material by oxalic acid-assisted sol–gel method. J. Power Sources. 2, 1358–1364 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2005.09.063
Y. Hao, Q. Lai, Z. Xu, X. Liu, X. Ji, Synthesis by TEA sol-gel method and electrochemical properties of Li 4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion battery. Solid State Ionics 176, 1201–1206 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SSI.2005.02.010
H.-Y. Wu, M.-H. Hon, C.-Y. Kuan, I.-C. Leu, Hydrothermal synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 5, 35224–35229 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01351H
S.-H. Yu, A. Pucci, T. Herntrich, M.-G. Willinger, S.-H. Baek, Y.-E. Sung, N. Pinna, Surfactant-free nonaqueous synthesis of lithium titanium oxide (LTO) nanostructures for lithium ion battery applications. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 806–810 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM03064C
R. Wang, X. Cao, D. Zhao, L. Zhu, L. Xie, J. Liu, Y. Liu, Wet-chemistry synthesis of Li 4 Ti 5 O 12 as anode materials rendering high-rate Li-ion storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 44, 4211–4223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5020
S. Scharner, W. Weppner, P. Schmid‐Beurmann, Evidence of two‐phase formation upon lithium insertion into the Li1.33Ti1.67 O 4 spinel, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 (1999) 857–861. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1391692/XML.
C. Schöttle, D.E. Doronkin, R. Popescu, D. Gerthsen, J.-D. Grunwaldt, C. Feldmann, Ti 0 nanoparticles via lithium-naphthalenide-driven reduction. Chem. Commun. 52, 6316–6319 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC01957A
C. Huang, S.X. Zhao, H. Peng, Y.H. Lin, C.W. Nan, G.Z. Cao, Hierarchical porous Li4Ti5O12-TiO2 composite anode materials with pseudocapacitive effect for high-rate and low-temperature applications. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6, 14339–14351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta03172j
L. Noerochim, W. Caesarendra, A. Habib, Suwarno Widyastuti, Y.L. Ni’mah, A. Subhan, B. Prihandoko, B. Kosasih, Role of TiO2 phase composition tuned by LiOH on the electrochemical performance of dual-phase Li4Ti5O12-TiO2 microrod as an anode for lithium-ion battery. Energies. 13, 5251 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205251
Y. Wang, H. Liu, K. Wang, H. Eiji, Y. Wang, H. Zhou, Synthesis and electrochemical performance of nano-sized Li4Ti5O12 with double surface modification of Ti(III) and carbon. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 6789 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b908025b
W. Chen, H. Jiang, Y. Hu, Y. Dai, C. Li, Mesoporous single crystals Li 4 Ti 5 O 12 grown on rGO as high-rate anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 50, 8856–8859 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC02886D
Z. Zhang, G. Li, H. Peng, K. Chen, Hierarchical hollow microspheres assembled from N-doped carbon coated Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets with enhanced lithium storage properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 15429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13860g
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Royal Society Te Apārangi through the Marsden Fund (Grant number UOA1816). Martin Ryan of Callaghan Innovation, New Zealand, is acknowledged for his assistance in the structural characterisation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, K.D., Song, X., Lim, K. et al. Wet-chemical synthesis of spinel Li4Ti5O12 as a negative electrode. emergent mater. 6, 1151–1158 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-022-00424-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-022-00424-5