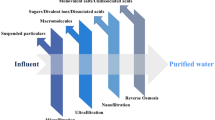
Abstract
Nanofiltration (NF) membranes have recently received growing interest in many sectors as an eco-friendly and effective separation technology. Nevertheless, biofouling resulting from the accretion and growth of bacteria over the NF membrane surface constitutes the major drawback affecting the NF membrane separation systems and prohibiting their use, especially in long term. In fact, under well-moderated growth conditions, many types of microorganisms occurring in aqueous environments (e.g., bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa) are prone to adhere onto the surface of the nanofiltration membrane, resulting in the formation of a biofilm, which in turn reduces the membrane's performance. Functionalization of NF membranes with specific materials/nanomaterials is one promising strategy to surmount this inherent problem. The objective of this review is to provide first a thorough study of the biofouling phenomenon of nanofiltration membranes by establishing the main mechanisms causing membrane biofouling and the proposed strategies for its control and monitoring. Next, recent developments in functionalizing polymer NF membranes with nanomaterials including carbonaceous materials, metal and metal oxides, proteins, enzymes, etc. as a powerful strategy for biofouling control are elucidated and discussed in detail. Further, physical and chemical fabrication methods for nanofiltration composite membranes and their practical applications are addressed as well as current issues and futures perspectives are also highlighted.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Drioli, M. Romano, Progress and new perspectives on integrated membrane operations for sustainable industrial growth. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40, 1277–1300 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0006209
S.M. Samaei, S. Gato-Trinidad, A. Altaee, The application of pressure-driven ceramic membrane technology for the treatment of industrial wastewaters – A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 200, 198–220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.02.041
A. Ali, R.A. Tufa, F. Macedonio, E. Curcio, E. Drioli, Membrane technology in renewable-energy-driven desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 1–21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.07.047
N.M. Kocherginsky, Q. Yang, L. Seelam, Recent advances in supported liquid membrane technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 53, 171–177 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.022
B. Van der Bruggen, Microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and forward osmosis. In: in: Fundam. Model. Membr. Syst. Membr. Process Perform., Elsevier Inc., pp. 25–70. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813483-2.00002-2
B. Lin, H. Tan, W. Liu, C. Gao, Q. Pan, Preparation of a novel zwitterionic striped surface thin-film composite nanofiltration membrane with excellent salt separation performance and antifouling property. RSC Adv. 10, 16168–16178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00480d
A.M. Hassan, M.A.K. Al-Sofi, A.S. Al-Amoudi, A.T.M. Jamaluddin, A.M. Farooque, A. Rowaili, A.G.I. Dalvi, N.M. Kither, G.M. Mustafa, I.A.R. Al-Tisan, A new approach to membrane and thermal seawater desalination processes using nanofiltration membranes (Part 1). Desalination 118, 35–51 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(98)00079-4
A. Bódalo, E. Gómez, A.M. Hidalgo, M. Gómez, M.D. Murcia, I. López, Nanofiltration membranes to reduce phenol concentration in wastewater. Desalination 245, 680–686 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.02.037
C. Charcosset, Membrane process in pharmaceutical and biotechnological applications. ITBM-RBM 27, 1–7 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmret.2005.10.003
K. Nath, H.K. Dave, T.M. Patel, Revisiting the recent applications of nanofiltration in food processing industries: Progress and prognosis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 73, 12–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.01.001
M.N. Chollom, S. Rathilal, Fouling and Cleaning in Osmotically Driven Membranes, Osmotically Driven Membr. Process. - Approach, Dev. Curr. Status. p. 73047 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.73047.
A.I. Schäfer, N. Andritsos, J. Anastasios, E.M. V Hoek, R. Schneider,Fouling in Nanofiltration, in: Nanofiltration - Princ. Appl. 169–239 (2004)
E.A. Bell, R.W. Holloway, T.Y. Cath, Evaluation of forward osmosis membrane performance and fouling during long-term osmotic membrane bioreactor study. J. Memb. Sci. 517, 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.06.014
S. Jiang, Y. Li, B.P. Ladewig, A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 595, 567–583 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.235
M.A. Al Mamun, S. Bhattacharjee, D. Pernitsky, M. Sadrzadeh, Colloidal fouling of nanofiltration membranes: Development of a standard operating procedure, Membranes (Basel). 7, 4 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010004
N. Ogawa, K. Kimura, Y. Watanabe, Membrane fouling in nanofiltration/reverse osmosis membranes coupled with a membrane bioreactor used for municipal wastewater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 18, 292–296 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2010.1795
R. Komlenic, Rethinking the causes of membrane biofouling. Filtr. Sep. 47, 26–28 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-1882(10)70211-1
V. Kochkodan, N. Hilal, A comprehensive review on surface modified polymer membranes for biofouling mitigation. Desalination 356, 187–207 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.09.015
T. Nguyen, F.A. Roddick, L. Fan, Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes (Basel). 2, 804–840 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2040804
A. Al-Amoudi, R.W. Lovitt, Fouling strategies and the cleaning system of NF membranes and factors affecting cleaning efficiency. J. Memb. Sci. 303, 4–28 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.06.002
J. Mansouri, S. Harrisson, V. Chen, Strategies for controlling biofouling in membrane filtration systems: Challenges and opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 4567–4586 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/b926440j
S. Bucs, N. Farhat, J.C. Kruithof, C. Picioreanu, M.C.M. van Loosdrecht, J.S. Vrouwenvelder, Review on strategies for biofouling mitigation in spiral wound membrane systems. Desalination 434, 189–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.01.023
D. Pichardo-Romero, Z.P. Garcia-Arce, A. Zavala-Ramírez, R. Castro-Muñoz, Current advances in biofouling mitigation in membranes for water treatment: An overview. Processes. 8, 1–22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020182
H. Lin, Y. Ding, Polymeric membranes: Chemistry, physics, and applications. J. Polym. Sci. 58, 2433–2434 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.20200622
S.P. Kaldis, G. Skodras, P. Grammelis, G.P. Sakellaropoulos, Application of polymer membrane technology in coal combustion processes. Chem. Eng. Commun. 194, 322–333 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/15397730600830021
S. Waqas, M.R. Bilad, Z.B. Man, C. Klaysom, J. Jaafar, A.L. Khan, An integrated rotating biological contactor and membrane separation process for domestic wastewater treatment. Alexandria Eng. J. 59, 4257–4265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.07.029
M.K. Selatile, S.S. Ray, V. Ojijo, R. Sadiku, Recent developments in polymeric electrospun nanofibrous membranes for seawater desalination. RSC Adv. 8, 37915–37938 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA07489E
D.M. Warsinger, S. Chakraborty, E.W. Tow, M.H. Plumlee, C. Bellona, S. Loutatidou, L. Karimi, A.M. Mikelonis, A. Achilli, A. Ghassemi, L.P. Padhye, S.A. Snyder, S. Curcio, C.D. Vecitis, H.A. Arafat, J.H. Lienhard, A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 209–237 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.01.004
M.A. Abdel-Fatah, Nanofiltration systems and applications in wastewater treatment: Review article. Ain Shams Eng. J. 9, 3077–3092 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2018.08.001
K. Nath, H.K. Dave, T.M. Patel, Revisiting the recent applications of nanofiltration in food processing industries: Progress and prognosis, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 73, 12–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.01.001.
M. Shokri Doodeji, M. Zerafat, A review on the applications of nanofiltration in virus removal and pharmaceutical industries. Glob J. Nanomedicine. 3, 125–127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.19080/GJN.2018.03.555624
P. Wu, M. Imai, Novel biopolymer composite membrane involved with selective mass transfer and excellent water permeability, in: Adv. Desalin. 2012: pp. 57–81
C. Conidi, R. Castro-Muñoz, A. Cassano, Nanofiltration in beverage industry. Nanotechnol. Beverage Ind. (2020) 525–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-819941-1.00018-3
F.G. Donnan, Theory of membrane equilibria and membrane potentials in the presence of non-dialysing electrolytes. A contribution to physical-chemical physiology. J. Memb. Sci. 100, 45–55 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-7388(94)00297-C
P. Marchetti, M.F. Jimenez Solomon, G. Szekely, A.G. Livingston, Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: A critical review. Chem. Rev. 114, 10735–10806 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500006j
B.A. Abdelkader, M.A. Antar, Z. Khan, Nanofiltration as a pretreatment step in seawater desalination: A Review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 4413–4432 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3096-3
H.D.M. Sombekke, D.K. Voorhoeve, P. Hiemstra, Environmental impact assessment of groundwater treatment with nanofiltration. Desalination 113, 293–296 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(97)00144-6
A.W. Mohammad, N. Hilal, H. Al-Zoubib, N.A. Darwish, N. Ali, Modelling the effects of nanofiltration membrane properties on system cost assessment for desalination applications. Desalination 206, 215–225 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.02.068
M. Paul, S.D. Jons, Chemistry and fabrication of polymeric nanofiltration membranes: A review. Polymer (Guildf). 103, 417–456 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.07.085
C. Zhao, J. Xue, F. Ran, S. Sun, Modification of polyethersulfone membranes - A review of methods. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 76–150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.07.002
Y. Liu, G.Q. Chen, X. Yang, H. Deng, Preparation of layer-by-layer nanofiltration membranes by dynamic deposition and crosslinking. Membranes (Basel). 9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9020020
F.M. Roli, H.W. Yussof, S.M. Saufi, M.N.A. Seman, A.W. Mohammad, Synthesis of nanofiltration membrane developed from triethanolamine (TEOA) and trimesoyl chloride (TMC) for separation of xylose from glucose. Chem. Eng. Trans. 56, 1507–1512 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1756252
M.A. Rasool, C. Van Goethem, I.F.J. Vankelecom, Green preparation process using methyl lactate for cellulose-acetate-based nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 232, 115903 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115903
I. Ounifi, C. Ursino, S. Santoro, J. Chekir, A. Hafiane, A. Figoli, E. Ferjani, Cellulose acetate nanofiltration membranes for cadmium remediation. J Membr Sci Res 6, 226–234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.22079/JMSR.2020.120669.1336
J.H. Choi, K. Fukushi, K. Yamamoto, A submerged nanofiltration membrane bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment: the performance of cellulose acetate nanofiltration membranes for long-term operation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 52, 470–477 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.05.027
N. Ghaemi, S.S. Madaeni, A. Alizadeh, P. Daraei, A.A. Zinatizadeh, F. Rahimpour, Separation of nitrophenols using cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane: Influence of surfactant additives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 85, 147–156 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.10.003
J. Su, Q. Yang, J.F. Teo, T.S. Chung, Cellulose acetate nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for forward osmosis processes. J. Memb. Sci. 355, 36–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.03.003
H. Wang, T. Yu, C. Zhao, Q. Du, Improvement of hydrophilicity and blood compatibility on polyethersulfone membrane by adding polyvinylpyrrolidone. Fibers Polym. 10, 1–5 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-009-0001-4
R. Du, J. Zhao, Positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane prepared by Poly ( N , N -dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate )/ Polysulfone, (2003)
M. Homayoonfal, A. Akbari, M. Reza, Preparation of polysulfone nano fi ltration membranes by UV-assisted grafting polymerization for water softening. DES. 263, 217–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.062
R. Derakhsheshpoor, M. Homayoonfal, A. Akbari, M.R. Mehrnia, Amoxicillin separation from pharmaceutical wastewater by high permeability polysulfone nanofiltration membrane. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 11, 1–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-11-9
E. Saljoughi, S.M. Mousavi, Preparation and characterization of novel polysulfone nanofiltration membranes for removal of cadmium from contaminated water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 90, 22–30 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.02.008
S.H. Chen, D.J. Chang, R.M. Liou, C.S. Hsu, S.S. Lin, Preparation and separation properties of polyamide nanofiltration membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 83, 1112–1118 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.2282
C. Labbez, P. Fievet, A. Szymczyk, A. Vidonne, A. Foissy, J. Pagetti, Retention of mineral salts by a polyamide nanofiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 30, 47–55 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00107-7
A. Akbari, J.C. Remigy, P. Aptel, Treatment of textile dye effluent using a polyamide-based nanofiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. Process. 41, 601–609 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0255-2701(01)00181-7
Y. Liang, Y. Zhu, C. Liu, K.R. Lee, W.S. Hung, Z. Wang, Y. Li, M. Elimelech, J. Jin, S. Lin, Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometre pores for sub-1 Å precision separation. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15771-2
S. Mehdipour, V. Vatanpour, H.R. Kariminia, Influence of ion interaction on lead removal by a polyamide nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 362, 84–92 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.01.030
C. Wei, Q. Cheng, L. Lin, Z. He, K. Huang, S. Ma, L. Chen, One-step fabrication of recyclable polyimide nanofiltration membranes with high selectivity and performance stability by a phase inversion-based process. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 11104–11115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2369-2
A.M. Hidalgo, G. León, M. Gómez, M.D. Murcia, M.D. Bernal, S. Ortega, Polyamide nanofiltration membranes to remove aniline in aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom) 35, 1175–1181 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.864338
D. Shi, Y. Kong, J. Yu, Y. Wang, J. Yang, Separation performance of polyimide nanofiltration membranes for concentrating spiramycin extract. Desalination 191, 309–317 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.09.015
I. Soroko, Y. Bhole, A.G. Livingston, Environmentally friendly route for the preparation of solvent resistant polyimide nanofiltration membranes. Green Chem. 13, 162–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0gc00155d
Y. Kong, D. Shi, H. Yu, Y. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Zhang, Separation performance of polyimide nanofiltration membranes for solvent recovery from dewaxed lube oil filtrates. Desalination 191, 254–261 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.09.014
C.C. Lin, W.F. Lien, Y.Z. Wang, H.W. Shiu, C.H. Lee, Preparation and performance of sulfonated polyimide/Nafion multilayer membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources. 200, 1–7 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.10.001
T. He, M. Frank, M.H.V. Mulder, M. Wessling, Preparation and characterization of nanofiltration membranes by coating polyethersulfone hollow fibers with sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK). J. Memb. Sci. 307, 62–72 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.09.016
R.H. Tullis, R.P. Duffin, M. Zech, J.L. Ambrus, Affinity hemodialysis for antiviral therapy. I. Removal of HIV-1 from cell culture supernatants, plasma, and blood. Ther. Apher. 6, 213–220 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-0968.2002.00407.x
Y. Li, H. Zhang, X. Li, H. Zhang, W. Wei, Porous poly (ether sulfone) membranes with tunable morphology: Fabrication and their application for vanadium flow battery. J. Power Sources. 233, 202–208 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.088
W.P. Zhu, S.P. Sun, J. Gao, F.J. Fu, T.S. Chung, Dual-layer polybenzimidazole/polyethersulfone (PBI/PES) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metals removal from wastewater. J. Memb. Sci. 456, 117–127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.01.001
M.N.A. Seman, M. Khayet, N. Hilal, Nanofiltration thin-film composite polyester polyethersulfone-based membranes prepared by interfacial polymerization. J. Memb. Sci. 348, 109–116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.10.047
A. Moarefian, H.A. Golestani, H. Bahmanpour, Removal of amoxicillin from wastewater by self-made Polyethersulfone membrane using nanofiltration. Environ. Heal. 12, 1–10 (2014)
D. Karisma, G. Febrianto, D. Mangindaan, Removal of dyes from textile wastewater by using nanofiltration polyetherimide membrane. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 109, 0–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/109/1/012012
I.C. Kim, K.H. Lee, Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) 200 on the formation of a polyetherimide asymmetric membrane and its performance in aqueous solvent mixture permeation. J. Memb. Sci. 230, 183–188 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2003.11.002
B. Seifert, G. Mihanetzis, T. Groth, W. Albrecht, K. Richau, Y. Missirlis, D. Paul, G. Von Sengbusch, Polyetherimide: A new membrane-forming polymer for biomedical applications. Artif. Organs. 26, 189–199 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1594.2002.06876.x
A. El-Gendi, E. Favre, D. Roizard, Asymmetric polyetherimide membranes (PEI) for nanofiltration treatment. Eur. Polym. J. 105, 204–216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.06.001
G. Febrianto, D. Karisma, D. Mangindaan, Polyetherimide nanofiltration membranes modified by interfacial polymerization for treatment of textile dyes wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 622, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/622/1/012019
M.M.A. Almijbilee, X. Wu, A. Zhou, X. Zheng, X. Cao, W. Li, Polyetheramide organic solvent nanofiltration membrane prepared via an interfacial assembly and polymerization procedure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 234, 116033 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116033
Y. Qi, L. Zhu, C. Gao, J. Shen, A novel nanofiltration membrane with simultaneously enhanced antifouling and antibacterial properties. RSC Adv. 9, 6107–6117 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra09875a
A. Simon, W.E. Price, L.D. Nghiem, Changes in surface properties and separation efficiency of a nanofiltration membrane after repeated fouling and chemical cleaning cycles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 113, 42–50 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.04.011
E. Nagy, Nanofiltration, basic equations mass transport through a membrane layer. 249–266 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-416025-5.00010-7
H. Yacubowicz, J. Yacubowicz, Nanofiltration: Properties and uses. Filtr. Sep. 42, 16–21 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-1882(05)70617-0
L. Braeken, B. Bettens, K. Boussu, P. Van der Meeren, J. Cocquyt, J. Vermant, B. Van der Bruggen, Transport mechanisms of dissolved organic compounds in aqueous solution during nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 279, 311–319 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.024
A.G. Fane, C.Y. Tang, R. Wang, Membrane technology for water: Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, and Reverse Osmosis. Treatise Water Sci. 4, 301–335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53199-5.00091-9
Z. Berk, Z. Berk, Chapter 10 – Membrane processes. Food Process Eng. Technol. 233–257 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-373660-4.00010-7
J.M.M. Peeters, M.H.V. Mulder, H. Strathmann, Streaming potential measurements as a characterization method for nanofiltration membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 150, 247–259 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00828-0
A.R.D. Verliefde, E.R. Cornelissen, S.G.J. Heijman, J.Q.J.C. Verberk, G.L. Amy, B. Van Der Bruggen, J.C. Van Dijk, The role of electrostatic interactions on the rejection of organic solutes in aqueous solutions with nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 322, 52–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.05.022
H. Lin, M. Zhang, F. Wang, F. Meng, B.Q. Liao, H. Hong, J. Chen, W. Gao, A critical review of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in membrane bioreactors: Characteristics, roles in membrane fouling and control strategies. J. Memb. Sci. 460, 110–125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.02.034
Q. She, R. Wang, A.G. Fane, C.Y. Tang, Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 499, 201–233 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.10.040
M. Badruzzaman, S. Aramco, Pretreatment for seawater reverse osmosis: Existing plant performance and selection guidance. (2018). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.31363.14889
W.L. Ang, D. Nordin, A.W. Mohammad, A. Benamor, N. Hilal, Effect of membrane performance including fouling on cost optimization in brackish water desalination process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 117, 401–413 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.10.041
L.F. Greenlee, D.F. Lawler, B.D. Freeman, B. Marrot, P. Moulin, Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 43, 2317–2348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.010
K.V. (Klaus-V. Peinemann, P. Nunes, S.P. (Suzana P. Nunes, Membrane technology: Volume 4: Membranes for Water Treatment. 4, (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527631407
C.Y. Tang, T.H. Chong, A.G. Fane, Colloidal interactions and fouling of NF and RO membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 164, 126–143 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2010.10.007
S. Li, J. Luo, X. Hang, S. Zhao, Y. Wan, Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by nanofiltration membranes : Rejection and fouling mechanisms. J. Memb. Sci. 582, 264–273 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.04.008
P. Xu, C. Bellona, J.E. Drewes, Fouling of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes during municipal wastewater reclamation: Membrane autopsy results from pilot-scale investigations. J. Memb. Sci. 353, 111–121 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.02.037
L. Weinrich, M. LeChevallier, C.N. Haas, Contribution of assimilable organic carbon to biological fouling in seawater reverse osmosis membrane treatment. Water Res. 101, 203–213 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.075
J.N. Hakizimana, B. Gourich, C. Vial, P. Drogui, A. Oumani, J. Naja, L. Hilali, Assessment of hardness, microorganism and organic matter removal from seawater by electrocoagulation as a pretreatment of desalination by reverse osmosis. Desalination 393, 90–101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.12.025
S. Tul Muntha, A. Kausar, M. Siddiq, Advances in Polymeric Nanofiltration Membrane: A Review. Polym. - Plast. Technol. Eng. 56, 841–856 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2016.1233562
W. Ye, N.J. Bernstein, J. Lin, J. Jordens, S. Zhao, C.Y. Tang, B. Van der Bruggen, Theoretical and experimental study of organic fouling of loose nanofiltration membrane. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 93, 509–518 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.029
K. Chon, J. Cho, Fouling behavior of dissolved organic matter in nanofiltration membranes from a pilot-scale drinking water treatment plant: An autopsy study, Elsevier B.V. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.057
M.A. Sari, S. Chellam, Relative Contributions of Organic and Inorganic Fouling during Nanofiltration of Inland Brackish Surface Wate. J. Memb. Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.10.005
W. Stumm, Aquatic colloids as chemical reactants: surface structure and reactivity, ELSEVIER SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTD, 1993. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-1-85861-038-2.50004-8
I. Buffle, G.G. Leppard, Characterization of aquatic colloids and macromolecules. 1. Structure and behavior of colloidal material. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 2169–2175 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1021/es00009a004
K. Boussu, A. Belpaire, A. Volodin, C. Van Haesendonck, P. Van der Meeren, C. Vandecasteele, B. Van der Bruggen, Influence of membrane and colloid characteristics on fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 289, 220–230 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.12.001
H.C. Flemming, Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 14, 382–391 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-1777(96)00140-9
S. Anand, D. Singh, M. Avadhanula, S. Marka, Development and control of bacterial biofilms on dairy processing membranes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 13, 18–33 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12048
H.F. Ridgway, A. Kelly, C. Justice, B.H. Olson, Microbial fouling of reverse-osmosis membranes used in advanced wastewater treatment technology: Chemical, bacteriological, and ultrastructural analyses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45, 1066–1084 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.45.3.1066-1084.1983
Y. Baek, J. Yu, S.H. Kim, S. Lee, J. Yoon, Effect of surface properties of reverse osmosis membranes on biofouling occurrence under filtration conditions. J. Memb. Sci. 382, 91–99 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.07.049
M. Herzberg, M. Elimelech, Biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Role of biofilm-enhanced osmotic pressure. J. Memb. Sci. 295, 11–20 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.02.024
C.V. Manalo, M. Ohno, T. Okuda, S. Nakai, W. Nishijima, Rapid novel test for the determination of biofouling potential on reverse osmosis membranes. Water Sci. Technol. 73, 2978–2985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.159
H. Ivnitsky, I. Katz, D. Minz, E. Shimoni, Y. Chen, J. Tarchitzky, R. Semiat, C.G. Dosoretz, Characterization of membrane biofouling in nanofiltration processes of wastewater treatment. Desalination 185, 255–268 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.03.081
O. Habimana, A.J.C. Semião, E. Casey, The role of cell-surface interactions in bacterial initial adhesion and consequent biofilm formation on nanofiltration/reverse osmosis membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 454, 82–96 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.11.043
J.S. Vrouwenvelder, S.A. Manolarakis, J.P. van der Hoek, J.A.M. van Paassen, W.G.J. van der Meer, J.M.C. van Agtmaal, H.D.M. Prummel, J.C. Kruithof, M.C.M. van Loosdrecht, Quantitative biofouling diagnosis in full scale nanofiltration and reverse osmosis installations. Water Res. 42, 4856–4868 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.09.002
D. Monroe, Looking for chinks in the armor of bacterial biofilms. 272 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050307
S. Wang, G. Guillen, E.M.V. Hoek, Direct observation of microbial adhesion to membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 6461–6469 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/es050188s
M. Kostakioti, M. Hadjifrangiskou, S.J. Hultgren, Bacterial biofilms: Development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 3, 1–24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a010306
H.C. Flemming, T.R. Neu, D.J. Wozniak, The EPS matrix: The “House of Biofilm Cells.” J. Bacteriol. 189, 7945–7947 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00858-07
G.O. Toole, H.B. Kaplan, R. Kolter, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000.54:49–79, (2000) 49–79
C. Dreszer, A.D. Wexler, S. Drusová, T. Overdijk, A. Zwijnenburg, H.C. Flemming, J.C. Kruithof, J.S. Vrouwenvelder, In-situ biofilm characterization in membrane systems using Optical Coherence Tomography: Formation, structure, detachment and impact of flux change. Water Res. 67, 243–254 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.006
N. Qureshi, B.A. Annous, T.C. Ezeji, P. Karcher, I.S. Maddox, Biofilm reactors for industrial bioconversion process: Employing potential of enhanced reaction rates. Microb. Cell Fact. 4, 1–21 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-4-24
J.C. Wang, J. Cordero, Y. Sun, M. Aranke, R. Wolcott, J.A. Colmer-Hamood, A.N. Hamood, Planktonic growth of pseudomonas aeruginosa around a dual-species biofilm supports the growth of Fusobacterium nucleatum within that biofilm. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3037191
S.A. Rice, K.S. Koh, S.Y. Queck, M. Labbate, K.W. Lam, S. Kjelleberg, Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J. Bacteriol. 187, 3477–3485 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.10.3477-3485.2005
Z.L. P. Stoodley, J. Boyle, A.B. Cunningham, I. Dodds, H.M. Lappin-Scott, Biofilm structure and influence on biofouling under laminar and turbulent flows. Methods. 1–10 (1998)
M.H. Muhammad, A.L. Idris, X. Fan, Y. Guo, Y. Yu, X. Jin, J. Qiu, X. Guan, T. Huang, Beyond risk: Bacterial biofilms and their regulating approaches. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1–20 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00928
P.R. Gogate, Application of cavitational reactors for water disinfection: Current status and path forward. J. Environ. Manage. 85, 801–815 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.07.001
M. Polanska, K. Huysman, C. Van Keer, Investigation of assimilable organic carbon (AOC) in flemish drinking water. Water Res. 39, 2259–2266 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.015
L.E. Applegate, C.W. Erkenbrecher, Monitoring and control of biological activity in Permasep® seawater RO plants. Desalination 65, 331–359 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-9164(87)90141-X
S.D. Richardson, Disinfection by-products and other emerging contaminants in drinking water, TrAC -. Trends Anal. Chem. 22, 666–684 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-9936(03)01003-3
F. Hammes, S. Meylan, E. Salhi, O. Köster, T. Egli, U. von Gunten, Formation of assimilable organic carbon (AOC) and specific natural organic matter (NOM) fractions during ozonation of phytoplankton. Water Res. 41, 1447–1454 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.001
G.D. Harris, V.D. Adams, D.L. Sorensen, R.R. Dupont, Influence of photoreactivation and water quality on ultraviolet disinfection of secondary municipal wastewater. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 59, 781–787 (1987)
J.A. Parker, J.L. Darby, Particle-associated coliform in secondary effluents: shielding from ultraviolet light disinfection. Water Environ. Res. 67, 1065–1075 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2175/106143095x133310
S.F. Anis, R. Hashaikeh, N. Hilal, Reverse osmosis pretreatment technologies and future trends: A comprehensive review. Desalination 452, 159–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.11.006
S. Nouhi, H.M. Kwaambwa, P. Gutfreund, A.R. Rennie, Comparative study of flocculation and adsorption behaviour of water treatment proteins from Moringa peregrina and Moringa oleifera seeds. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54069-2
K. Ibn Abdul Hamid, P. Sanciolo, S. Gray, M. Duke, S. Muthukumaran, Impact of ozonation and biological activated carbon filtration on ceramic membrane fouling. Water Res. 126, 308–318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.012
H.J. Yang, H.S. Kim, Effect of coagulation on MF/UF for removal of particles as a pretreatment in seawater desalination. Desalination 247, 45–52 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.12.011
A. Venault, Y. Chang, D.M. Wang, D. Bouyer, A. Higuchi, J.Y. Lai, PEGylation of anti-biofouling polysulfone membranes via liquid- and vapor-induced phase separation processing. J. Memb. Sci. 403–404, 47–57 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.02.019
Q.L. Feng, J. Wu, G.Q. Chen, F.Z. Cui, T.N. Kim, J.O. Kim, A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52, 662–668 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4636(20001215)52:4%3c662::aid-jbm10%3e3.0.co;2-3
G. Borkow, J. Gabbay, Copper as a Biocidal Tool. Curr. Med. Chem. 12, 2163–2175 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867054637617
C.X. Liu, D.R. Zhang, Y. He, X.S. Zhao, R. Bai, Modification of membrane surface for anti-biofouling performance: Effect of anti-adhesion and anti-bacteria approaches. J. Memb. Sci. 346, 121–130 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.09.028
A. Dror-Ehre, H. Mamane, T. Belenkova, G. Markovich, A. Adin, Silver nanoparticle-E. coli colloidal interaction in water and effect on E. coli survival. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 339, 521–526 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.07.052
T. Tashiro, Antibacterial and bacterium adsorbing macromolecules. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 286, 63–87 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1002/1439-2054(20010201)286:2%3c63::AID-MAME63%3e3.0.CO;2-H
M. Khayet, J.P.G. Villaluenga, J.L. Valentin, M.A. López-Manchado, J.I. Mengual, B. Seoane, Filled poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) dense membranes by silica and silane modified silica nanoparticles: Characterization and application in pervaporation. Polymer (Guildf). 46, 9881–9891 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.07.081
T.H. Bae, T.M. Tak, Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on fouling mitigation of ultrafiltration membranes for activated sludge filtration. J. Memb. Sci. 249, 1–8 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.09.008
D.J. Lin, C.L. Chang, F.M. Huang, L.P. Cheng, Effect of salt additive on the formation of microporous poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes by phase inversion from LiC1o4/water/DMF/PVDF system. Polymer (Guildf). 44, 413–422 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00731-0
A. Bottino, G. Capannelli, A. Comite, Preparation and characterization of novel porous PVDF-ZrO2 composite membranes. Desalination 146, 35–40 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00469-1
L. Yan, Y.S. Li, C.B. Xiang, Preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride)(pvdf) ultrafiltration membrane modified by nano-sized alumina (Al2O3) and its antifouling research. Polymer (Guildf). 46, 7701–7706 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.05.155
N. Hilal, L. Al-Khatib, B.P. Atkin, V. Kochkodan, N. Potapchenko, Photochemical modification of membrane surfaces for (bio)fouling reduction: A nano-scale study using AFM. Desalination 158, 65–72 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(03)00434-X
H.L. Zhang, Y.B. Gao, J.G. Gai, Guanidinium-functionalized nanofiltration membranes integrating anti-fouling and antimicrobial effects. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6, 6442–6454 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta00342d
L. Tang, K.J.T. Livi, K.L. Chen, Polysulfone membranes modified with bioinspired polydopamine and silver nanoparticles formed in situ to mitigate biofouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2, 59–65 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00008
H.L. Zhang, B.H. Liu, M. Yang, P. Zhang, J.G. Gai, Sulfaguanidine nanofiltration active layer towards anti-adhesive and antimicrobial attributes for desalination and dye removal. RSC Adv. 9, 20715–20727 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra03340h
S.N. Jagannadh, H.S. Muralidhara, Electrokinetics Methods to Control Membrane Fouling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35, 1133–1140 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9503712
J.C. Te Lin, D.J. Lee, C. Huang, Membrane fouling mitigation: Membrane cleaning. Sep. Sci. Technol. 45, 858–872 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496391003666940
S.S. Madaeni, T. Mohamamdi, M.K. Moghadam, Chemical cleaning of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 134, 77–82 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(01)00117-5
L. Xiao, D.M. Davenport, L. Ormsbee, D. Bhattacharyya, Polymerization and functionalization of membrane pores for water related applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 4174–4182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie504149t
A. Schulze, M. Went, A. Prager, Membrane functionalization with hyperbranched polymers. Materials (Basel). 9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080706
H. Chakhtouna, N. Zari, H. Benzeid, A. el K. Qaiss, R. Bouhfid, Hybrid Nanocomposites based on Graphene and Titanium Dioxide for Wastewater Treatment Keywords, in: Graphene and Nanoparticles Hybrid Nanocomposites. 213–238 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4988-9_8
R. Wang, D. Chen, Q. Wang, Y. Ying, W. Gao, L. Xie, Recent advances in applications of carbon nanotubes for desalination: A review. Nanomaterials 10, 1–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061203
N. Song, X. Gao, Z. Ma, X. Wang, Y. Wei, C. Gao, A review of graphene-based separation membrane: Materials, characteristics, preparation and applications. Desalination 437, 59–72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.024
H. Chakhtouna, H. Benzeid, N. Zari, A. el kacem Qaiss, R. Bouhfid, Functional CoFe2O4-modified biochar derived from banana pseudostem as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of amoxicillin from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 266 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118592
S. Liu, T.H. Zeng, M. Hofmann, E. Burcombe, J. Wei, R. Jiang, J. Kong, Y. Chen, Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5, 6971–6980 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202451x
S. Romero-Vargas Castrillón, F. Perreault, A.F. De Faria, M. Elimelech, Interaction of graphene oxide with bacterial cell membranes: Insights from force spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2, 112–117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00066
A.M. Pinto, I.C. Gonçalves, F.D. Magalhães, Graphene-based materials biocompatibility: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 111, 188–202 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.05.022
P. Kumar, P. Huo, R. Zhang, B. Liu, Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. EurasianUnionScientists. 1, 31–33 (2020)
R. Bi, Q. Zhang, R. Zhang, Y. Su, Z. Jiang, Thin film nanocomposite membranes incorporated with graphene quantum dots for high flux and antifouling property. J. Memb. Sci. 553, 17–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.02.010
S. Bano, A. Mahmood, S.J. Kim, K.H. Lee, Graphene oxide modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with improved flux and antifouling properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 2065–2071 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta03607g
C. Wang, M.J. Park, D.H. Seo, H.K. Shon, Inkjet printing of graphene oxide and dopamine on nanofiltration membranes for improved anti-fouling properties and chlorine resistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 254, 117604 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117604
X.F. Sun, J. Qin, P.F. Xia, B.B. Guo, C.M. Yang, C. Song, S.G. Wang, Graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle membrane for biofouling control and water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 281, 53–59 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.059
P. Gunawan, C. Guan, X. Song, Q. Zhang, S.S.J. Leong, C. Tang, Y. Chen, M.B. Chan-Park, M. Chang, K. Wook, RXu. Wang, Hollow fiber membrane decorated with Ag / MWNTs: Toward effective water. ACS Nano. 5, 10033–10040 (2011)
K. Ko, Y.J. Yu, M.J. Kim, J. Kweon, H. Chung, Improvement in fouling resistance of silver-graphene oxide coated polyvinylidene fluoride membrane prepared by pressurized filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 194, 161–169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.11.016
M. Yasuyuki, K. Kunihiro, S. Kurissery, N. Kanavillil, Y. Sato, Y. Kikuchi, Antibacterial properties of nine pure metals: A laboratory study using Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Biofouling 26, 851–858 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2010.527000
G. Vimbela, S. Ngo, C. Fraze, L. Yang, D.A. Stout, Antibacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 13, 6497–6498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s183907
S. Maharubin, Y. Zhou, G.Z. Tan, Development and Investigation on a Silver Nanoparticle-Incorporated Electrofiltration System for Biofouling Control. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 17, 948–954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2018.2832210
S. Pal, Y.K. Tak, J.M. Song, Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1712–1720 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
N. Hachicho, P. Hoffmann, K. Ahlert, H.J. Heipieper, Effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on growth and adaptive response mechanisms of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 355, 71–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12460
G. Franci, A. Falanga, S. Galdiero, L. Palomba, M. Rai, G. Morelli, M. Galdiero, Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20, 8856–8874 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058856
J. Yin, Y. Yang, Z. Hu, B. Deng, Attachment of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) onto thin-film composite (TFC) membranes through covalent bonding to reduce membrane biofouling. J. Memb. Sci. 441, 73–82 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.03.060
R. Manjumeena, D. Duraibabu, J. Sudha, P.T. Kalaichelvan, Biogenic nanosilver incorporated reverse osmosis membrane for antibacterial and antifungal activities against selected pathogenic strains: An enhanced eco-friendly water disinfection approach, J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 49, 1125–1133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2014.897149
N. Zari, H. Mohammedi, A. Amine, M.M. Ennaji, DNA hydrolysis and voltammetric determination of guanine and adenine using different electrodes. Anal. Lett. 40, 1698–1713 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710701298479
S. Asapu, S. Pant, P. Majid, I.C. Escobar, C.L. Gruden, Study of copper-charged membranes for control of fouling due to bacteria and algae organic matter. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 5, 516–527 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2015.001
R. Guha, B. Xiong, M. Geitner, T. Moore, T.K. Wood, D. Velegol, M. Kumar, Reactive micromixing eliminates fouling and concentration polarization in reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Schience. 542, 8–17 (2017)
W. Ma, A. Soroush, T. Van Anh Luong, G. Brennan, M.S. Rahaman, B. Asadishad, N. Tufenkji, Spray- and spin-assisted layer-by-layer assembly of copper nanoparticles on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane for biofouling mitigation. Water Res. 99, 188–199 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.042
H. Chakhtouna, H. Benzeid, N. Zari, R. Bouhfid, A. el kacem Qaiss, Recent progress on Ag/TiO2 photocatalysts: Photocatalytic and bactericidal behaviors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 44638–44666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14996-y
A. Kubacka, M.S. Diez, D. Rojo, R. Bargiela, S. Ciordia, I. Zapico, J.P. Albar, C. Barbas, V.A.P. Martins Dos Santos, M. Fernández-García, M. Ferrer, Understanding the antimicrobial mechanism of TiO2 -based nanocomposite films in a pathogenic bacterium. Sci. Rep. 4, 1–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04134
V. Vatanpour, S. Siavash, R. Moradian, S. Zinadini, B. Astinchap, Novel antibifouling nanofiltration polyethersulfone membrane fabricated from embedding TiO2 coated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 90, 69–82 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.02.014
Z. Habib, S.J. Khan, N.M. Ahmad, H.M.A. Shahzad, Y. Jamal, I. Hashmi, Antibacterial behaviour of surface modified composite polyamide nanofiltration (NF) membrane by immobilizing Ag-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom) 41, 3657–3669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1617355
Y.T. Chung, E. Mahmoudi, A.W. Mohammad, A. Benamor, D. Johnson, N. Hilal, Development of polysulfone-nanohybrid membranes using ZnO-GO composite for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial control. Desalination 402, 123–132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.09.030
D. Shanthana Lakshmi, S. Jaiswar, M. saxena, F. Tasselli, H.D. Raval, Preparation and performance of biofouling resistant PAN/chitosan hollow fiber membranes. 3 Biotech. 7, 224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0798-2
T. Istirokhatun, N. Rokhati, D. Nurlaeli, N.N. Arifianingsih, S. Sudarno, H. Susanto, Characteristics, biofouling properties and filtration performance of cellulose/chitosan membranes. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 10, 56–67 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2017.56.67
Y. Liu, Y. Su, X. Zhao, Y. Li, R. Zhang, Z. Jiang, Improved antifouling properties of polyethersulfone membrane by blending the amphiphilic surface modifier with crosslinked hydrophobic segments. J. Memb. Sci. 486, 195–206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.03.045
J. Xu, H. Lee, Anti-biofouling strategies for long-term continuous use of implantable biosensors. Chemosensors. 8, 1–29 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8030066
Y.N. Chou, F. Sun, H.C. Hung, P. Jain, A. Sinclair, P. Zhang, T. Bai, Y. Chang, T.C. Wen, Q. Yu, S. Jiang, Ultra-low fouling and high antibody loading zwitterionic hydrogel coatings for sensing and detection in complex media. Acta Biomater. 40, 31–37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.04.023
Q.F. An, W.D. Sun, Q. Zhao, Y.L. Ji, C.J. Gao, Study on a novel nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization with zwitterionic amine monomers. J. Memb. Sci. 431, 171–179 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.12.043
D. Ponnamma, N. Ninan, S. Thomas, Carbon Nanotube Tube Filled Polymer Nanocomposites and Their Applications in Tissue Engineering. Elsevier Ltd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101971-9.00014-4
L.D. Tijing, Y.C. Woo, M. Yao, J. Ren, H.K. Shon, Electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Strategies and applications. in: Compr. Membr. Sci. Eng., Elsevier Ltd. 418–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-409547-2.12262-0
S. Ramakrishna, K. Fujihara, W.E. Teo, T. Yong, Z. Ma, R. Ramaseshan, Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today. 9, 40–50 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(06)71389-X
M.K. Purkait, M.K. Sinha, P. Mondal, R. Singh, Introduction Membr. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813961-5.00001-2
A.K. Hołda, I.F.J. Vankelecom, Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 1–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42130
Y. Song, J.B. Fan, S. Wang, Recent progress in interfacial polymerization. Mater. Chem. Front. 1, 1028–1040 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6qm00325g
F. Zhang, Jb. Fan, S. Wang, Interfacial polymerization: From chemistry to functional materials. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 59, 21840–21856 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201916473
E. Guzmán, A. Mateos-Maroto, M. Ruano, F. Ortega, R.G. Rubio, Layer-by-Layer polyelectrolyte assemblies for encapsulation and release of active compounds. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 249, 290–307 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.009
J.E. Gu, S. Lee, C.M. Stafford, J.S. Lee, W. Choi, B.Y. Kim, K.Y. Baek, E.P. Chan, J.Y. Chung, J. Bang, J.H. Lee, Molecular layer-by-layer assembled thin-film composite membranes for water desalination. Adv. Mater. 25, 4778–4782 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302030
E. Nagy, Nanofiltration, basic equations mass transport through a membrane layer. 417–428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813722-2.00015-7
C. Kaya, G. Sert, N. Kabay, M. Arda, M. Yüksel, Ö. Egemen, Pre-treatment with nanofiltration (NF) in seawater desalination-Preliminary integrated membrane tests in Urla, Turkey. Desalination 369, 10–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.04.029
C. Yu, J. Wu, A.E. Contreras, Q. Li, Control of nanofiltration membrane biofouling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa using d-tyrosine. J. Memb. Sci. 423–424, 487–494 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.08.051
J. Zheng, M. Li, K. Yu, J. Hu, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Sulfonated multiwall carbon nanotubes assisted thin-film nanocomposite membrane with enhanced water flux and anti-fouling property. J. Memb. Sci. 524, 344–353 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.11.032
Y.C. Chiang, Y. Chang, C.J. Chuang, R.C. Ruaan, A facile zwitterionization in the interfacial modification of low bio-fouling nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 389, 76–82 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.10.017
L. Ren, J. Chen, Q. Lu, J. Han, H. Wu, Anti-biofouling nanofiltration membrane constructed by in-situ photo-grafting bactericidal and hydrophilic polymers. J. Memb. Sci. 617, 118658 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118658
S. Liu, F. Fang, J. Wu, K. Zhang, The anti-biofouling properties of thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes grafted with biogenic silver nanoparticles. Desalination 375, 121–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.08.007
X. Li, Y. Cao, H. Yu, G. Kang, X. Jie, Z. Liu, Q. Yuan, A novel composite nanofiltration membrane prepared with PHGH and TMC by interfacial polymerization. J. Memb. Sci. 466, 82–91 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.04.034
P.S. Zhong, N. Widjojo, T.S. Chung, M. Weber, C. Maletzko, Positively charged nanofiltration (NF) membranes via UV grafting on sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone (sPPSU) for effective removal of textile dyes from wastewater. J. Memb. Sci. 417–418, 52–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.06.013
T. Tsuru, T. Sudou, S.I. Kawahara, T. Yoshioka, M. Asaeda, Permeation of liquids through inorganic nanofiltration membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 228, 292–296 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.6955
J.A. Whu, B.C. Baltzis, K.K. Sirkar, Nanofiltration studies of larger organic microsolutes in methanol solutions. J. Memb. Sci. 170, 159–172 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00374-9
X.Q. Cheng, Y. Liu, Z. Guo, L. Shao, Nanofiltration membrane achieving dual resistance to fouling and chlorine for “green” separation of antibiotics. J. Memb. Sci. 493, 156–166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.06.048
X.D. Weng, Y.L. Ji, R. Ma, F.Y. Zhao, Q.F. An, C.J. Gao, Superhydrophilic and antibacterial zwitterionic polyamide nanofiltration membranes for antibiotics separation. J. Memb. Sci. 510, 122–130 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.02.070
Y.L. Ji, Q.F. An, X.D. Weng, W.S. Hung, K.R. Lee, C.J. Gao, Microstructure and performance of zwitterionic polymeric nanoparticle/polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membranes for salts/organics separation. J. Memb. Sci. 548, 559–571 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.057
O. Acosta, F. Vaillant, A.M. Pérez, M. Dornier, Concentration of polyphenolic compounds in blackberry (Rubus Adenotrichos Schltdl.) juice by nanofiltration. J. Food Process Eng. 40, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12343
A.M. Avram, P. Morin, C. Brownmiller, L.R. Howard, A. Sengupta, S.R. Wickramasinghe, Concentrations of polyphenols from blueberry pomace extract using nanofiltration. Food Bioprod. Process. 106, 91–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2017.07.006
X. Li, W. Cai, T. Wang, Z. Wu, J. Wang, X. He, J. Li, AF2400/PTFE composite membrane for hexane recovery during vegetable oil production. Sep. Purif. Technol. 181, 223–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.02.051
Funding
This work was supported by MAScIR, Moroccan Foundation for Advanced Science, Innovation, and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Brahim El Allaoui: Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, writing–original draft
Hanane Chakhtouna: Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, writing–original draft.
Nadia Zari: Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Rachid Bouhfid: Supervision, Writing—review & editing
Abou el kacem Qaiss: Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial, or otherwise.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allaoui, B.E., Chakhtouna, H., Zari, N. et al. Recent developments in functionalized polymer NF membranes for biofouling control. emergent mater. 5, 1345–1371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-022-00367-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-022-00367-x