Abstract
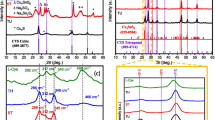
Copper indium sulfide (CuInS2) nanostructures have been successfully deposited on silicon substrates using the electrospinning method. As a result, different copper to indium (Cu/In) molar ratios have been used: 0.1, 0.5, 0.8, 1.2, and 1.4 at annealing temperature 300 °C. The optical properties have been measured using photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), which indicated a decrease in the optical band gap from 1.6 to 1.53 eV with increasing Cu/In molar ratio. The structural properties have been deduced using X-ray diffraction (XRD), which improved the crystallinity size and quality by increasing the Cu/In molar ratio. The c/a ratio at different Cu/In molar ratios ranges from 2.004 to 2.037 due to the zinc blende structure, and the crystallite size was varied from 22.53 to 56.33 nm. The average grain size was approximately 39 nm, and the lattice parameters vary from 5.53 to 5.5 Å and from 11.09 to 11.2 Å for a and c, respectively. The compositional properties are studied using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), which showed that the samples are almost stoichiometric with S-deficient and Cu-rich composition. The best-formed structure’s value was at molar ratio 1.4, where the real phase is 60.5%, and the secondary phase is 39.5% due to the increase in grain size, and that in turn occurred due to the decrease in the energy band gap. The morphological properties have been depicted using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). FESEM images indicated a change in the grain particles’ homogeneity and agglomeration due to changing the Cu/In molar ratio. According to the available literature, the obtained results promise to use CuInS2 as absorber material in photovoltaic devices’ nanostructure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Masjedi-arani, M. Salavati-niasari, A simple sonochemical approach for synthesis and characterization of Zn2SiO4 nanostructures. Ultrason. Sonochem. 29, 226–235 (2016)
X.B. Lu, R. He, C.X. Bai, Synthesis of ethylene carbonate from supercritical carbon dioxide/ethylene oxide mixture in the presence of bifunctional catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 186(1–2), 1–11 (2002)
S. Mortazavi-derazkola, M. Salavati-niasari, O. Amiri, A. Abbasi, Fabrication and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Ho nanostructures as a novel and highly efficient photocatalyst for degradation of organic pollution. J. Energy Chem. 26, 4956 (2017)
M. Salavati-niasari, Z. Fereshteh, F. Davar, Synthesis of oleylamine capped copper nanocrystals via thermal reduction of a new precursor. Polyhedron 28(1), 126–130 (2009)
L. H. Madkour, Nanoelectronic Materials, Fundamentals and Applications, no. September. 2019.
M. Ťapajna, Fabrication and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Ho nanostructures as a novel and highly efficient photocatalyst for degradation of organic pollution. Polyhedron 30(6), 1055–1060 (2011)
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 265, 29–44 (2019)
A. Abbasi, D. Ghanbari, M.S. Masood, Photo-degradation of methylene blue: photocatalyst and magnetic investigation of Fe2O3–TiO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 4800–4809 (2016)
D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis of urchin-like CdS-Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its application in flame retardancy of magnetic cellulose acetate. J Ind Eng Chem. 24, 284–292 (2015)
P. Arnou, C.S. Cooper, S. Uličná, A. Abbas, A. Eeles, L.D. Wright, A.V. Malkov, J.M. Walls, J.W. Bowers, Solution processing of CuIn(S,Se)2 and Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 thin film solar cells using metal chalcogenide precursors. Thin Solid Films 633, 76–80 (2017)
S. Lin, J. Sung, C. Lu, Effects of the surface sulfurization reactions on the structural and photovoltaic properties of Cu(In,Ga )( Se,S )2 solar cells. Thin Solid Films 616, 746–753 (2016)
Y. Lin, S. Wei, Y. Liang, W. Syus, A simple non-toxic simultaneous selenization / sulfurization process for Cu (In,Ga)(S,Se)2 solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 219(May), 283–291 (2018)
X. Lyu, D. Zhuang, M. Zhao, N. Zhang, Y. Wei, Influences of sulfurization on performances of Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 cells fabricated based on the method of sputtering CIGSe quaternary target. J. Alloys Compd. 791, 1193–1199 (2019)
A. Kotbi, B. Hartiti, S. Fadili, H. Labrim, A. Ridah, P. Thevenin, Synthesis and characterization of sprayed CIGS thin films for photovoltaic application. Mater Today Proc. 24, 66–70 (2020)
T. Hurma, S. Kose, Effect of Cu and In content in precursor solution on the structural and optical properties of CuInS2 in CH ordered nanostructured films. Optik (Stuttg). 127(8), 3779–3782 (2016)
T.I. Jayaraj, U.R. Parthasarathy, R. Oommen, Enhanced optoelectronic and photoelectrochemical characteristics of nebulised spray pyrolysed ‘Cu’ rich CuInS2 thin film. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 49, 84–91 (2016)
C. Buchmaier et al., Room temperature synthesis of CuInS2 nanocrystals. R. Soc. Chem. 6, 106120–106129 (2016)
F. Aslan, M.Z. Zarbali, B. Yesilata, I.H. Mutlu, Effects of Cu/In ratio and annealing temperature on physical properties of dip-coated CuInS2 thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(1), 138–142 (2013)
Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, H. Gao, H. Zhang, Y. Mao, A novel inorganic hole-transporting material of CuInS2 for perovskite solar cells with high efficiency and improved stability. Org. Electron. 75(July), 105430 (2019)
A. Rayar, S. Chapi, The vision for polymer solar cells is power production at low cost. J. Nano- Electron. Phys. 12(5), 05008-1-05008–5 (2020)
X. Huang, R. Yu, X. Yang, X. Xu, H. Zhang, D. Zhang, Efficient CuInS2/ZnS based quantum dot light emitting diodes by engineering the exciton formation interface. J Lumin. 202, 339–344 (2018)
Ö. Yağci, R. Arat, N. Sarıer, B.C. Ömür, A. Altındal, Ethanol sensing with pure and boric acid doped eectrospun CuInS2 nanofibers in the presence of relative humidity. Mater Sci Semicond Process 104, 104651 (2019)
K. Zhang, S. Lv, Q. Zhou, D. Tang, CoOOH nanosheets-coated g-C3N4/CuInS2 nanohybrids for photoelectrochemical biosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen coupling hybridization chain reaction with etching reaction. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 307, 127631 (2020)
Z. Hao, Y. Cui, G. Wang, Colloidal synthesis of wurtzite CuInS2 nanocrystals and their photovoltaic application. Mater. Lett. 146, 77–80 (2015)
W. Yue et al., Hierarchical CuInS2 synthesized with the induction of histidine for polymer/CuInS2 solar cells. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 76, 14–24 (2018)
S. Lugo, I. López, Y. Peña, M. Calixto, T. Hernández, S. Messina, D. Avellaneda, Characterization of CuInS2 thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition and their implementation in a solar cell. Thin Solid Films 569, 76–80 (2014)
T. Logu, K. Sankarasubramanian, P. Soundarrajan, J. Archana, Y. Hayakawa, K. Sethuraman, Vanadium doping induces surface morphological changes of CuInS2 thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 122, 230–240 (2016)
T. Chtouki, L. Soumahoro, B. Kulyk, H. Bougharraf, H. Erguig, K. Ammous, B. Sahraoui, Comparative study on the structural, morphological, linear and nonlinear optical properties of CZTS thin films prepared by spin-coating and spray pyrolysis. Mater. Today Proc. 4, 5146–5153 (2017)
Y. Al-Douri, Synthesis and characterization of Cu2CdSnS4 quaternary alloy nanostructures. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 6693–6707 (2018)
S. Chapi, Optical, electrical and electrochemical properties of PCL5/ITO transparent conductive films deposited by spin-coating – materials for single-layer devices. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 5(3), 322–329 (2020)
S. Chapi, Structural and electrochemical properties of polymer blend based ZnO nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes by spin-coating method. J. Nano- Electron. Phys. 12(2), 1–5 (2020)
S. Chapi, H. Devendrappa, Optical, electrical, thermal and electrochemical studies of spin-coated polyblend-ZnO nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(11), 11974–11985 (2016)
J. Yuan, C. Shao, L. Zheng, M. Fan, H. Lu, C. Hao, D. Tao, Fabrication of CuInS2 thin film by electrodeposition of Cu-In alloy. Vacuum 99, 196–203 (2014)
V. Renuga, C.N. Mohan, A. Manikandan, Influence of Mn2 + ions on both core/shell of CuInS2/ZnS nanocrystals. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 265–274 (2018)
N. Chumha, T. Thongtem, S. Thongtem, S. Kittiwachana, Cyclic microwave radiation synthesis, photoconductivity, and optical properties of CuInS2 hollow sub-microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 447, 292–299 (2018)
L. Thirumalaisamy, S. Palanivel, R. Raliya, S. Kavadiya, Single-step growth of CuInS2 nanospheres morphology thin films by electrospray chemical aerosol deposition technique. Mater. Lett. 238, 206–209 (2019)
R. Garza-Hernández, S. Lugo-Loredo, F.S. Aguirre-Tostado, The role of copper during the growth of stoichiometric Cu2ZnSnS4 by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method. Ceram. Int. 46(4), 5185–5192 (2020)
W.-G. Chang, L.-L. Tao, Hydrothermal synthesis and optical properties of CuInS2 micro-/nanomaterials by using gemini surfactant as soft template. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 86(3), 549–553 (2019)
J. Lontchi, M. Abaab, Study of structural, optical and electrical properties of thermal evaporated undoped and Na doped CuInS2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 633, 81–86 (2017)
W. Ligang, W. Yanlai, Y. Wei, Z. Jun, X. Jingang, Effect of sulfurization time on the formation of CuInS2 thin films. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 44(4), 805–807 (2015)
X. Lu, F. Deng, M. Liu, X. Luo, A. Wang, The regulation on visible-light photocatalytic activity of CuInS2 by different Cu/In molar ratio. Mater. Chem. Phys. 212, 372–377 (2018)
T. Logu, K. Sankarasubramanian, P. Soundarrajan, M. Sampath, K. Sethuraman, Growth of N type CuInS2 microspheres on P type CuInS2 seed layer prepared using facile low cost chemical methods. Superlattice. Microst. 83, 690–698 (2015)
S. Ananthakumar, J. Ram Kumar, S. Moorthy Babu, Evolution of non-phosphine solvents in colloidal synthesis of I-III-VI2 and I2-II-IV-VI4 group semiconductor nanomaterials – Current status. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 67, 152–174 (2017)
A.D.P. Leach, J.E. Macdonald, Optoelectronic properties of CuInS2 nanocrystals and their origin. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7(3), 572–583 (2016)
A. Antony, A.S. Asha, R. Yoosuf, R. Manoj, M.K. Jayaraj, Growth of CuInS2 thin films by sulphurisation of Cu-In alloys. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 81(4), 407–417 (2004)
A. Frank, R. Changizi, C. Scheu, Challenges in TEM sample preparation of solvothermally grown CuInS2 films. Micron 109(December 2017), 1–10 (2018)
Y. Al-Douri, A.A. Odeh, Y.A. Wahab, C.H. Voon, Correlation between magnetization and particle size of CdS nanostructures by solvothermal method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32(2), 283–289 (2019)
J. Ben Belgacem, M. Nouiri, K. Medjnoun, K. Djessas, Z. Ben Ayadi, CuInS2 thin films obtained through an innovative CSVT deposition method from solvothermal-generated precursors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 83(August 2017), 224–230 (2018)
C. Sun et al., A High-Yield Synthesis of Chalcopyrite CuInS2 Nanoparticles with Exceptional Size Control. J Nanomater. 2009, 1–7 (2009)
B. Gao, H. Xue, F. Tang, Y. Cheng, Effect of structural phase transformations under pressure on electronic and optical properties of CuInS2. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17(11), 1564–1569 (2017)
Structural and optical features, Y. Al-Douri, A. Abu Odeh, and A. S. Ibraheam, Transition metals doped In2S3 nanostructure. Mater. Res. Express 6, 4–13 (2019)
A.S. Ibraheam, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, M.R. Ghezzar, A. Addou, W.K. Ahmed, Cadmium effect on optical properties of Cu2Zn1-xCdxSnS4 quinternary alloys nanostructures. Sol. Energy 114, 39–50 (2015)
S. Fiechter, Y. Tomm, M. Kanis, R. Scheer, W. Kautek, On the homogeneity region, growth modes and optoelectronic properties of chalcopyrite type CuInS2. Phys. Status Solidi 245(9), 1761–1771 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alalousi, M.A., Abu Odeh, A., Ibraheam, A.S. et al. The effect of Cu/In molar ratio on the analysis and characterization of CuInS2 nanostructures. emergent mater. 4, 413–422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00176-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00176-8