Abstract
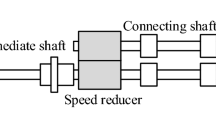
A robust torsional vibration suppression strategy is proposed for the main drive system of the rolling mill subject to uncertainties, disturbances and input saturation. With given model information incorporated into observer design, an extended state observer that relies only on roller speed measurements is developed to estimate the system states and lumped uncertainties of the rolling mill main drive system. To handle the motor torque saturation, an auxiliary signal system with the same order as the plant is constructed. The error between the control input and plant input is taken as the input of the constructed auxiliary system, and a number of signals are generated to compensate for the effect of the motor torque saturation. Furthermore, a robust output feedback controller is introduced to obtain better transient and steady-state performance of the rolling mill main drive system and the stability of the closed-loop system is strictly proved via Lyapunov theory. Finally, comparative simulations are performed to verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control strategy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.F. Zhang, X.Q. Yan, Q.H. Lin, Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 29 (2016) 180–187.
P.M. Shi, J.Z. Li, J.S. Jiang, B. Liu, D.Y. Han, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 1, 7–12.
M. Zhang, Y. Peng, J.L. Sun, H.R. Li, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26 (2019) 953–961.
L.P. Wang, Y.L. Zhao, Q.Y. Zhu, Y. Liu, Q.K. Han, ISIJ Int. 60 (2020) 1237–1244.
X.G. Liu, Z.Y. Wu, J. Lu, J.L. Xu, J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 13 (2019) 0079.
P.M. Shi, K.W. Xia, B. Liu, J.S. Jiang, Journal of Mechanical Engineering 48 (2012) No. 17, 57–64.
D.Y. Han, P.M. Shi, D.W. Zhao, Shock Vibration 35 (2016) No. 12, 1–6.
B. Liu, S. Liu, Y.K. Zhang, Y. Wen, Journal of Mechanical Engineering 46 (2010) No. 8, 160–166.
D.X. Hou, L. Xu, P.M. Shi, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 574–585.
X. Yang, K.X. Peng, C.N. Tong, Abstract Appl. Anal. 2013 (2013) 387890.
U.M. Nath, C. Dey, R.K. Mudi, IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 5 (2021) 1255–1260.
J. Hao, G.S. Zhang, W.Q. Liu, Y.Q. Zheng, L. Ren, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68 (2020) 21051678.
K. Erenturk, IET Control Theory Appl. 2 (2008) 635–642.
K. Tsuda, T. Sakuma, K. Umeda, S. Sakaino, T. Tsuji, IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 6 (2017) 320–327.
J.Q. Han, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56 (2009) 900–906.
J.Y. Yao, Z.X. Jiao, D.W. Ma, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61 (2014) 3630–3637.
Q. Guo, Y. Zhang, B.G. Celler, S.W. Su, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63 (2016) 6909–6920.
W.Z. Shi, J.H. Wei, J.H. Fang, IEEE Access 6 (2018) 64503–64514.
R.X. Cui, L.P. Chen, C.G. Yang, M. Chen, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64 (2017) 6785–6795.
Z.H. Peng, J. Wang, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 48 (2018) 535–544.
D. Lin, X.Y. Wang, Y. Yao, Nonlinear Dynam. 67 (2012) 2889–2897.
K.N. Yong, M. Chen, Y. Shi, Q.X. Wu, Automatica 122 (2020) 109268.
X.Y. Zhu, D.D. Li, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 149 (2021) 107209.
C. Qian, C.C. Hua, L.L. Zhang, Z.H. Bai, J. Franklin Inst. 17 (2020) 12886–12903.
R. Zhang, W. Yang, W. Liang, Y. Zhang, Control Engineering of China 25 (2018) No. 12, 16–21.
H. Khalil, L. Praly, Int. J. Robust Nonlin. 24 (2014) 991–1015.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U20A20187 and 61933009) and the Top talents of Hebei provincial Education Department (Grant No. BJ2019047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Jq., Chen, Sz., Hua, Cc. et al. Extended-state-observer-based robust torsional vibration suppression for rolling mill main drive system with input saturation. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 985–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00933-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00933-5