Abstract
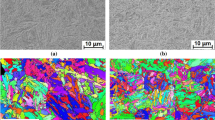
Based on the chemical composition of traditional hot-stamped steel (e.g., 22MnB5 and 30MnB5), Nb and V microalloying elements are added into 30MnB5 steel to meet the requirements of ultra-high strength, excellent ductility and potent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement (HE) at the same time. The influence of hot-stamped steel on HE was studied by conducting a hydrogen permeation method and pre-charged hydrogen slow strain rate test. Meanwhile, the experimental steel microstructures and corresponding fracture surfaces are observed and analyzed to characterize HE behavior. The results show that a finer microstructure, a lower apparent diffusion coefficient of hydrogen and a smaller percentage of strength and plasticity reduction are obtained due to the addition of the vanadium element into hot-stamped steel. Compared to the V free experimental steel, the steel with 0.14 wt.% V has a large number of dispersive precipitates and more grain boundary areas, which makes hydrogen atoms dispersedly distribute.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Karbasian, A.E. Tekkaya, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210 (2010) 2103–2118.
M. Merklein, M. Wieland, M. Lechner, S. Bruschi, A. Ghiotti, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 228 (2016) 11–24.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi, W. Bleckb, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211 (2011) 1117–1125.
D.W. Fan, S.K. Han, B.C. De Cooman, Steel Res. Int. 80 (2009) 241–248.
X.F. Li, J. Zhang, Y.F. Wang, B. Li, P. Zhang, X.L. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 641 (2015) 45–53.
M.B. Djukic, V.S. Zeravcic, G. Bakic, A. Sedmak, B. Rajicic, Procedia Mater. Sci. 3 (2014) 1167–1172.
X.L. Zhao, Y.J. Zhang, W.J. Hui, C.Y. Wang, H. Dong, J. Iron Steel Res. 31 (2019) 837–847.
X.F. Li, J. Zhang, S.C. Shen, Y.F. Wang, X.L. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 682 (2017) 359–369.
L. Jemblie, V. Olden, O.M. Akselsen, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42 (2017) 11980–11995.
M. Koyama, C.C. Tasan, E. Akiyama, K. Tsuzaki, D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 70 (2014) 174–187.
Y. Han, J.J. Shi, L. Xu, W.Q. Cao, H. Dong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 530 (2011) 643–651.
M.H. Cai, Z. Li, Q. Chao, P.D. Hodgson, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 (2014) 5624–5634.
S.Q. Zhang, Y.H. Huang, B.T. Sun, Q.L. Liao, H.Z. Lu, B. Jian, H. Mohrbacher, W. Zhang, A.M. Guo, Y. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 626 (2015) 136–143.
Y.S. Chen, D. Haley, S.S.A. Gerstl, A.J. London, F. Sweeney, R.A. Wepf, W.M. Rainforth, P.A.J. Bagot, M.P. Moody, Science 355 (2017) 1196–1199.
X.D. Tan, Y.B. Xu, X.L. Yang, Z.Q. Liu, D. Wu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 594 (2014) 149–160.
T.Y. Hsu, X.J. Jin, Y.H. Rong, J. Alloy. Compd. 577 (2013) S568–S571.
A. Shibata, S. Daido, D. Terada, N. Tsuji, Mater. Trans. 54 (2013) 1570–1574.
S.W. Seo, G.S. Jung, J.S. Lee, C.M. Bae, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, D.W. Suh, Mater. Sci. Technol. 31 (2015) 436–442.
L.F. Lv, L.M. Fu, Y.L. Sun, A.D. Shan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 731 (2018) 369–376.
J. Li, J.S. Wu, Z.H. Wang, S.Q. Zhang, X.G. Wu, Y.H. Huang, X.G. Li, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42 (2017) 22175–22184.
L.F. Li, B. Song, J. Cheng, Y.H. Yang, Z. Liu, Mater. Corros. 69 (2018) 590–600.
L.F. Li, B. Song, J. Cheng, Z.B. Yang, Z.Y. Cai, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43 (2018) 17353–17363.
S.Q. Zhang, E. Fan, J.F. Wan, J. Liu, Y.H. Huang, X.G. Li, Corros. Sci. 139 (2018) 83–96.
D.J. Kong, Y.Z. Wu, D. Long, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 1, 40–46.
G.W. Yang, X.J. Sun, Z.D. Li, X.X. Li, Q.L. Yong, Mater. Des. 50 (2013) 102–107.
W.J. Chen, S. Wang, Z.Z. Zhao, J.T. Liang, J. Guo, Mater. Res. Express 6 (2019) 1065e3.
X. Zhu, W. Li, H.S. Zhao, L. Wang, X.J. Jin, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 13031–13040.
M.L. Martin, J.A. Fenske, G.S. Liu, P. Sofronis, I.M. Robertson, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 1601–1606.
X.F. Li, J. Zhang, E. Akiyama, Y.F. Wang, Q.Z. Li, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43 (2018) 17898–17911.
B.S. Kumar, V. Kain, M. Singh, B. Vishwanadh, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 700 (2017) 140–151.
W.K. Kim, S.U. Koh, B.Y. Yang, K.Y. Kim, Corros. Sci. 50 (2008) 3336–3342.
E. Lunarska, Y. Ososkov, Y. Jagodzinsky, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 22 (1997) 279–284.
Z.Z. Zhao, J.T. Liang, A.M. Zhao, J.H. Liang, D. Tang, Y.P. Gao, J. Alloy. Compd. 691 (2017) 51–59.
F. Peng, Y.B. Xu, X.L. Gu, Y. Wang, X.D. Liu, J.P. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 723 (2018) 247–258.
Q.L. Yong, Secondary phase in the steel, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2006.
K. Takasawa, R. Ikeda, N. Ishikawa, R. Ishigaki, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37 (2012) 2669–2675.
S. Bechtle, M. Kumar, B.P. Somerday, M. Launey, R.O. Ritchie, Acta Mater. 57 (2009) 4148–4157.
B.A. Szost, R.H. Vegter, P.E.J. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, Mater. Des. 43 (2013) 499–506.
A.J. Haq, K. Muzaka, D.P. Dunne, A. Calka, E.V. Pereloma, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38 (2013) 2544–2556.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51574028) and the Development Program of Thirteenth Five-year Plan Period (Grant No. 2017YFB0304400) for Grant and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Wj., Gao, Pf., Wang, S. et al. Effect of vanadium on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength hot-stamped steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 211–222 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00469-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00469-y