Abstract
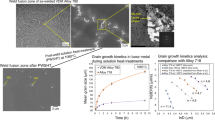
Large-scale Fe–6.5 wt.%Si ingot with excellent formability is required for a pilot line producing sheets through hot/cold rolling. The variation of the as-cast microstructure, ordered structures and the formability of the Fe–6.5 wt.%Si alloy ingots with the cooling rate during casting was investigated. Under air-cooling condition, inhomogeneous microstructures with a low proportion of equiaxed grains were formed, but the formation of ordered structures was partially inhibited, especially D03. Homogeneous microstructures with a high proportion of equiaxed grains were observed under the condition of furnace cooling, but the ordered structures were fully generated, and the degree of order is high. It is generally believed that high degree of order is the main factor of brittleness, but the homogeneous microstructure (including grain morphology and size) of the furnace-cooled sample helps to improve the formability. The influence of these two aspects on formability is contradictory. Therefore, the formability is tested through the flow stress during the compression and the microstructure after the compression. The results show that the furnace-cooled sample has better formability. For large-scale ingots, the control of as-cast microstructure becomes more significant than the control of degree of order. Slow cooling during casting is important for the large-scale ingots to have good formability meeting the requirements of direct hot rolling.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.I. Arai, K. Ishiyama, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 133 (1994) 233–237.
K. Raviprasad, M. Tenwick, H.A. Davies, K. Chattopadhyay, Scripta Metall. 20 (1986) 1265–1270.
S. Matsumura, H. Oyama, K. Oki, Mater. Trans. JIM 30 (1989) 695–706.
S. Matsumura, Y. Tanaka, Y. Koga, K. Oki, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 312 (2001) 284–292.
T. Yamaji, M. Abe, Y. Takada, K. Okada, T. Hiratani, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 133 (1994) 187–189.
R. Machado, A.H. Kasama, A.M. Jorge Jr., C.S. Kiminami, W.J. Botta Fo, C. Bolfarini, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 449 (2007) 854–857
R. Li, Q. Shen, L. Zhang, T. Zhang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 281 (2004) 135–139.
T. Ros-Yanez, Y. Houbaert, V. Gómez Rodríguez, J. Appl. Phys. 91 (2002) 7857–7859
H.T. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, Y. Sun, F. Gao, G.D. Wang, Mater. Lett. 91 (2013) 150–153.
H.Z. Li, H.T. Liu, Y. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, G.M. Cao, Z.H. Luo, F.Q. Zhang, S.L. Chen, L. Lyu, G.D. Wang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 370 (2014) 6–12.
H.T. Liu, H.Z. Li, H.L. Li, F. Gao, G.H. Liu, Z.H. Luo, F.Q. Zhang, S.L. Chen, G.M. Cao, Z.Y. Liu, G.D. Wang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 391 (2015) 65–74.
Y.F. Liang, F. Ye, J.P. Lin, Y.L. Wang, G.L. Chen, J. Alloy. Compd. 491 (2010) 268–270.
X.S. Fang, Y.F. Liang, F. Ye, J.P. Lin, J. Appl. Phys. 111 (2012) 094913.
W. Song, J.M. Zhang, Y. Liu, S.X. Wang, B. Wang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42 (2015) 656–663.
H. Li, Y.F. Liang, F. Ye, Mater. Trans. 56 (2015) 759–765.
Z. Zhang, W. Wang, H. Fu, J. Xie, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 530 (2011) 519–524.
Y.F. Liang, J.W. Ge, X.S. Fang, F. Ye, J.P. Lin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 570 (2013) 8–12.
H. Li, Y.F. Liang, W. Yang, F. Ye, J.P. Lin, J.X. Xie, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 628 (2015) 262–268.
P. Thevoz, J.L. Desbiolles, M. Rappaz, Metall. Trans. A 20 (1989) 311–322.
Z. Hou, F. Jiang, G. Cheng, ISIJ Int. 52 (2012) 1301–1309.
Z.B. Hou, G.G. Cheng, Adv. Mater. Res. 402 (2012) 123–131.
M.A. Martorano, C. Beckermann, C.A. Gandin, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34 (2003) 1657–1674.
J.S. Shin, Z.H. Lee, T.D. Lee, E.J. Lavernia, Scripa Mater. 45 (2001) 725–731.
Y. Mo, Z. Zhang, H. Fu, H. Pan, J. Xie, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 594 (2014) 111–117.
M.J. Marcinkowski, N. Brown, J. Appl. Phys. 33 (1962) 537–552.
K. Huang, R.E. Logé, Mater. Des. 111 (2016) 548–574.
G.E. Lakso, M.J. Marcinkowski, Metall. Trans. 5 (1974) 839–845.
R.K. Roy, M. Ghosh, A.K. Panda, R.N. Ghosh, A. Mitra, T. Indian I. Metals 63 (2010) 745–750.
K. Raviprasad, K. Chattopadhyay, Acta Metall. Mater. 41 (1993) 609–624.
M.J. Marcinkowski, R.M. Fisher, J. Appl. Phys. 34 (1963) 2135–2145.
T. Saburi, S. Nenno, Philos. Mag. 15 (1967) 813–824.
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51471031, U1660115) and the State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials (2016Z-17) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Xj., Liang, Yf., Wen, Sb. et al. Comprehensive impact of as-cast microstructure and ordered structures on formability of large-scale Fe–6.5 wt.%Si alloy ingots. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 180–187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00281-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00281-3