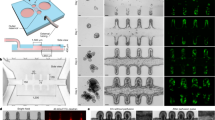
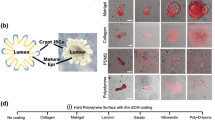
Abstract
Conventional 2D intestinal models cannot precisely recapitulate biomimetic features in vitro and thus are unsuitable for various pharmacokinetic applications, development of disease models, and understanding the host-microbiome interactions. Thus, recently, efforts have been directed toward recreating in vitro models with intestine-associated unique 3D crypt-villus (for small intestine) or crypt-lumen (for large intestine) architectures. This review comprehensively delineates the current advancements in this research area in terms of the different microfabrication technologies (photolithography, laser ablation, and 3D bioprinting) employed and the physiological relevance of the obtained models in mimicking the features of native intestinal tissue. A major thrust of the manuscript is also on highlighting the dynamic interplay between intestinal cells (both the stem cells and differentiated ones) and different biophysical, biochemical, and mechanobiological cues along with interaction with other cell types and intestinal microbiome, providing goals for the future developments in this sphere. The article also manifests an outlook toward the application of induced pluripotent stem cells in the context of intestinal tissue models. On a concluding note, challenges and prospects for clinical translation of 3D patterned intestinal tissue models have been discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- SI:
-
Small intestine
- LI:
-
Large intestine
- CBC:
-
Crypt base columnar cells
- TA:
-
Transit-amplifying
- M cell:
-
Microfold cell
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- PDMS:
-
Polydimethylsiloxane
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- PEG:
-
Poly(ethylene glycol)
- AA:
-
Acrylic acid
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- UV-LIGA:
-
Ultraviolet-lithography, electroplating, and molding
- PLA:
-
Poly(lactic acid)
- CVD:
-
Chemical vapor deposition
- PMMA:
-
Poly(methyl methacrylate)
- PLGA:
-
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
- PEVA:
-
Poly-ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate
- CAD:
-
Computer-aided design
- PEGDA:
-
Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate
- VMEPS:
-
Vertically moving extrusion-based printing system
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- TEER:
-
Transepithelial electrical resistance
- MUC17:
-
Mucin 17
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- PCL:
-
Poly-ε-caprolactone
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens-1
- P-gp:
-
P-Glycoprotein
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- CYP3A4:
-
Cytochrome P450 3A4
- EdU:
-
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine
- Olfm4:
-
Olfactomedin 4
- CK20:
-
Keratin 20
- MUC2:
-
Mucin 2
- E-cad:
-
E-cadherin
- ISC:
-
Intestinal stem cell
- RGD:
-
Arginine-glycine-aspartate
- GAGs:
-
Glycosaminoglycans
- Wnt:
-
Wingless-related integration site
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factors
- LGR5:
-
Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon gamma
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein 1
- BCRP:
-
Breast cancer resistance protein
- MRP2:
-
Multidrug resistance protein 2
- iPSCs:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- STAT1:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- ENS:
-
Enteric nervous system
- MIP-2:
-
Macrophage inflammatory protein 2
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin 10
- ISEMFs:
-
Intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fatty acids
- ELCs:
-
Enterocytes-like cells
- DELCs:
-
Definite endodermal-like cells
- IPLCs:
-
Intestinal progenitor-like cells
- HLCs:
-
Hindgut-like cells
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- 5-aza:
-
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine
- BIO:
-
6-Bromoindirubin-3′-oxime
- DAPT:
-
N-[(3,5-difluorophenyl)acetyl]-L-alanyl-2-phenyl-1,1-dimethylethyl ester-glycine
- WRN:
-
Wnt3A,R-spondin,Noggin
- PEPT1:
-
Peptide transporter 1
- SIOs:
-
Small intestinal organoids
- Cos:
-
Colonic organoids
- BMPs:
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins
- SATB2:
-
Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2
- HOX:
-
Homeobox
- WDR43:
-
WD Repeat Domain 43
- TALEN:
-
Transcription activator-like effector nuclease
- CFTR:
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
References
Dutton JS, Hinman SS, Kim R, Wang Y, Allbritton NL (2019) Primary cell-derived intestinal models: recapitulating physiology. Trends Biotechnol 37:744–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.12.001
Volk N, Lacy B (2017) Anatomy and physiology of the small bowel. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 27:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giec.2016.08.001
Campbell J, Berry J, Liang Y (2019) Anatomy and physiology of the small intestine. In: Shackelford’s surgery of the alimentary tract (8th edn), vol 1. Elsevier, pp 817–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-40232-3.00071-6
Shroyer NF, Kocoshis SA (2011) Anatomy and physiology of the small and large intestines. In: Pediatric gastrointestinal and liver disease. Elsevier, pp 324–336.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-0774-8.10031-4
Turner JR (2009) Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:799–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2653
Allaire JM, Crowley SM, Law HT, Chang S-Y, Ko H-J, Vallance BA (2018) The intestinal epithelium: central coordinator of mucosal immunity. Trends Immunol 39:677–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2018.04.002
Ting H-A, von Moltke J (2019) The immune function of tuft cells at gut mucosal surfaces and beyond. J Immunol 202:1321–1329. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1801069
Jiminez JA, Uwiera TC, Douglas Inglis G, Uwiera RRE (2015) Animal models to study acute and chronic intestinal inflammation in mammals. Gut Pathog 7:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-015-0076-y
Williams CF, Walton GE, Jiang L, Plummer S, Garaiova I, Gibson GR (2015) Comparative analysis of intestinal tract models. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 6:329–350. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-022814-015429
Kararli TT (1995) Comparison of the gastrointestinal anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of humans and commonly used laboratory animals. Biopharm Drug Dispos 16:351–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2510160502
Costa J, Ahluwalia A (2019) Advances and current challenges in intestinal in vitro model engineering: a digest. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:144. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00144
Liu Y, Chen Y-G (2018) 2D- and 3D-based intestinal stem cell cultures for personalized medicine. Cells 7:225. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120225
Kim HJ, Huh D, Hamilton G, Ingber DE (2012) Human gut-on-a-chip inhabited by microbial flora that experiences intestinal peristalsis-like motions and flow. Lab Chip 12:2165. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40074j
Shin W, Hinojosa CD, Ingber DE, Kim HJ (2019) Human intestinal morphogenesis controlled by transepithelial morphogen gradient and flow-dependent physical cues in a microengineered gut-on-a-chip. iScience 15:391–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2019.04.037
Ji Y, Zhou J, Sun T, Tang K, Xiong Z, Ren Z, Yao S, Chen K, Yang F, Zhu F, Guo X (2018) Diverse preparation methods for small intestinal submucosa (SIS): decellularization, components, and structure. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 107A: 689–697. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36582
Rashtbar M, Hadjati J, Ai J, Jahanzad I, Azami M, Shirian S, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Sadroddiny E (2018) Characterization of decellularized ovine small intestine submucosal layer as extracellular matrix-based scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res—Part B Appl Biomater 106B: 933–944. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33899
Liao J, Xu B, Zhang R, Fan Y, Xie H, Li X (2020) Applications of decellularized materials in tissue engineering: advantages, drawbacks and current improvements, and future perspectives. J Mater Chem B 8:10023–10049. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB01534B
Zhao P, Li X, Fang Q, Wang F, Ao Q, Wang X, Tian X, Tong H, Bai S, Fan J (2020) Surface modification of small intestine submucosa in tissue engineering. Regen Biomater 7:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbaa014
Hewes SA, Wilson RL, Estes MK, Shroyer NF, Blutt SE, Grande-Allen KJ (2020) In Vitro models of the small intestine: engineering challenges and engineering solutions. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 26:313–326. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.teb.2019.0334
Kim R, Wang Y, Hwang S-HJ, Attayek PJ, Smiddy NM, Reed MI, Sims CE, Allbritton NL (2018) Formation of arrays of planar, murine, intestinal crypts possessing a stem/proliferative cell compartment and differentiated cell zone. Lab Chip 18:2202–2213. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8LC00332G
Ladd MR, Costello CM, Gosztyla C, Werts AD, Johnson B, Fulton WB, Martin LY, Redfield EJ, Crawford B, Panaparambil R, Sodhi CP, March JC, Hackam DJ (2019) Development of intestinal scaffolds that mimic native mammalian intestinal tissue. Tissue Eng Part A 25:1225–1241. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2018.0239
Chen Y, Lin Y, Davis KM, Wang Q, Rnjak-Kovacina J, Li C, Isberg RR, Kumamoto CA, Mecsas J, Kaplan DL (2015) Robust bioengineered 3D functional human intestinal epithelium. Sci Rep 5:13708. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13708
Pawlina W, Ross MH (2018) Histology: a text and atlas: with correlated cell and molecular biology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Gehart H, Clevers H (2019) Tales from the crypt: new insights into intestinal stem cells. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:19–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0081-y
Qi D, Shi W, Black AR, Kuss MA, Pang X, He Y, Liu B, Duan B (2020) Repair and regeneration of small intestine: a review of current engineering approaches. Biomaterials 240:119832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119832
Santos AJM, Lo Y-H, Mah AT, Kuo CJ (2018) The intestinal stem cell niche: homeostasis and adaptations. Trends Cell Biol 28:1062–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.08.001
Carulli AJ, Samuelson LC, Schnell S (2014) Unraveling intestinal stem cell behavior with models of crypt dynamics. Integr Biol 6:243. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ib40163d
Umar S (2010) Intestinal stem cells. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 12:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0130-3
Montgomery RK, Breault DT (2008) Small intestinal stem cell markers. J Anat 213:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00925.x
Smith NR, Gallagher AC, Wong MH (2016) Defining a stem cell hierarchy in the intestine: markers, caveats and controversies. J Physiol 594:4781–4790. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP271651
Roth S, Franken P, Sacchetti A, Kremer A, Anderson K, Sansom O, Fodde R (2012) Paneth cells in intestinal homeostasis and tissue injury. PLoS ONE 7:e38965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038965
Hooper LV (2015) Epithelial cell contributions to intestinal immunity. In: Advances in immunology. Elsevier, vol 126, pp 129–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ai.2014.11.003
Banerjee A, McKinley ET, von Moltke J, Coffey RJ, Lau KS (2018) Interpreting heterogeneity in intestinal tuft cell structure and function. J Clin Invest 128:1711–1719. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI120330
Mace OJ, Tehan B, Marshall F (2015) Pharmacology and physiology of gastrointestinal enteroendocrine cells. Pharmacol Res Perspect 3:e00155. https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.155
Worthington JJ, Reimann F, Gribble FM (2018) Enteroendocrine cells-sensory sentinels of the intestinal environment and orchestrators of mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol 11:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2017.73
Gribble FM, Reimann F, Roberts GP (2018) Gastrointestinal Hormones. In: Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract (6th edn.). Elsevier, pp 31–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809954-4.00002-5
Birchenough GMH, Johansson MEV, Gustafsson JK, Bergström JH, Hansson GC (2015) New developments in goblet cell mucus secretion and function. Mucosal Immunol 8:712–719. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2015.32
Kim YS, Ho SB (2010) Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: recent insights and progress. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 12:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0131-2
Snoeck V, Goddeeris B, Cox E (2005) The role of enterocytes in the intestinal barrier function and antigen uptake. Microbes Infect 7:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2005.04.003
Chougule P, Herlenius G, Hernandez NM, Patil PB, Xu B, Sumitran-Holgersson S (2012) Isolation and characterization of human primary enterocytes from small intestine using a novel method. Scand J Gastroenterol 47:1334–1343. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2012.708940
Gonzalez LM, Williamson I, Piedrahita JA, Blikslager AT, Magness ST (2013) Cell lineage identification and stem cell culture in a porcine model for the study of intestinal epithelial regeneration. PLoS ONE 8:e66465. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066465
Ohno H (2016) Intestinal M cells. J Biochem 159:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvv121
Mabbott NA, Donaldson DS, Ohno H, Williams IR, Mahajan A (2013) Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium. Mucosal Immunol 6:666–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2013.30
Paik S, Kim G, Chang S, Lee S, Jin D, Jeong K-Y, Lee IS, Lee J, Moon H, Lee J, Chang K, Choi SS, Moon J, Jung S, Kang S, Lee W, Choi H-J, Choi H, Kim HJ, Lee J-H, Cheon J, Kim M, Myoung J, Park H-G, Shim W (2020) Near-field sub-diffraction photolithography with an elastomeric photomask. Nat Commun 11:805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14439-1
Cho CH, Kwon S, Park J-K (2017) Assembly of hydrogel units for 3D microenvironment in a poly(dimethylsiloxane) channel. Micro Nano Syst Lett 5:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40486-016-0035-5
Wang Y, Kim R, Gunasekara DB, Reed MI, DiSalvo M, Nguyen DL, Bultman SJ, Sims CE, Magness ST, Allbritton NL (2018) Formation of human colonic crypt array by application of chemical gradients across a shaped epithelial monolayer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.10.007
Hinman SS, Wang Y, Allbritton NL (2019) Photopatterned membranes and chemical gradients enable scalable phenotypic organization of primary human colon epithelial models. Anal Chem 91:15240–15247. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04217
Wang Y, Gunasekara DB, Reed MI, DiSalvo M, Bultman SJ, Sims CE, Magness ST, Allbritton NL (2017) A microengineered collagen scaffold for generating a polarized crypt-villus architecture of human small intestinal epithelium. Biomaterials 128:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.03.005
Castaño AG, García-Díaz M, Torras N, Altay G, Comelles J, Martínez E (2019) Dynamic photopolymerization produces complex microstructures on hydrogels in a moldless approach to generate a 3D intestinal tissue model. Biofabrication 11:025007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ab0478
Yang W-C, Chen Y-C, Huang Y-S, Fu Y-Y, Tang S-C, Fu C-C (2012) Engineering a biomimetic villus array for in vitro three-dimensional culture of intestinal epithelial cells. J Microelectromech Syst 21:1418–1425. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2012.2205902
Sung JH, Yu J, Luo D, Shuler ML, March JC (2011) Microscale 3-D hydrogel scaffold for biomimetic gastrointestinal (GI) tract model. Lab Chip 11:389–392. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0LC00273A
Kim SH, Chi M, Yi B, Kim SH, Oh S, Kim Y, Park S, Sung JH (2014) Three-dimensional intestinal villi epithelium enhances protection of human intestinal cells from bacterial infection by inducing mucin expression. Integr Biol 6:1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ib00157e
Yu J, Peng S, Luo D, March JC (2012) In vitro 3D human small intestinal villous model for drug permeability determination. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2173–2178. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24518
Costello CM, Hongpeng J, Shaffiey S, Yu J, Jain NK, Hackam D, March JC (2014) Synthetic small intestinal scaffolds for improved studies of intestinal differentiation. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:1222–1232. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25180
Costello CM, Phillipsen MB, Hartmanis LM, Kwasnica MA, Chen V, Hackam D, Chang MW, Bentley WE, March JC (2017) Microscale Bioreactors for in situ characterization of GI epithelial cell physiology. Sci Rep 7:12515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12984-2
Koppes AN, Kamath M, Pfluger CA, Burkey DD, Dokmeci M, Wang L, Carrier RL (2016) Complex, multi-scale small intestinal topography replicated in cellular growth substrates fabricated via chemical vapor deposition of Parylene C. Biofabrication 8:035011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/8/3/035011
Capel AJ, Rimington RP, Lewis MP, Christie SDR (2018) 3D printing for chemical, pharmaceutical and biological applications. Nat Rev Chem 2:422–436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-018-0058-y
Creff J, Courson R, Mangeat T, Foncy J, Souleille S, Thibault C, Besson A, Malaquin L (2019) Fabrication of 3D scaffolds reproducing intestinal epithelium topography by high-resolution 3D stereolithography. Biomaterials 221:119404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119404
Murphy SV, Atala A (2014) 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol 32:773–785. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2958
Truby RL, Lewis JA (2016) Printing soft matter in three dimensions. Nature 540:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21003
Kim W, Kim GH (2018) An innovative cell-printed microscale collagen model for mimicking intestinal villus epithelium. Chem Eng J 334:2308–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.001
Kim W, Kim G (2018) Intestinal villi model with blood capillaries fabricated using collagen-based bioink and dual-cell-printing process. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:41185–41196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b17410
Kim W, Kim GH (2020) An intestinal model with a finger-like villus structure fabricated using a bioprinting process and collagen/SIS-based cell-laden bioink. Theranostics 10:2495–2508. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.41225
Huang J, Chen Y, Tang C, Fei Y, Wu H, Ruan D, Paul ME, Chen X, Yin Z, Heng BC, Chen W, Shen W (2019) The relationship between substrate topography and stem cell differentiation in the musculoskeletal system. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:505–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2945-2
Agarwal T, Subramanian B, Maiti TK (2019) Liver tissue engineering: challenges and opportunities. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:4167–4182. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00745
Karbassi E, Fenix A, Marchiano S, Muraoka N, Nakamura K, Yang X, Murry CE (2020) Cardiomyocyte maturation: advances in knowledge and implications for regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Cardiol 17:341–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0331-x
Yi B, Shim KY, Ha SK, Han J, Hoang H-H, Choi I, Park S, Sung JH (2017) Three-dimensional in vitro gut model on a villi-shaped collagen scaffold. BioChip J 11:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-017-1307-8
Gommers LMM, Skrzypek K, Bolhuis-Versteeg L, Pinckaers NET, Vrijhof R, van der Wijst J, de Baaij JHF, Stamatialis D, Hoenderop JGJ (2019) Development of a villi-like micropatterned porous membrane for intestinal magnesium and calcium uptake studies. Acta Biomater 99:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2019.08.041
Clevers H (2013) The intestinal crypt, a prototype stem cell compartment. Cell 154:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.004
Wang Y, Gunasekara DB, Attayek PJ, Reed MI, DiSalvo M, Nguyen DL, Dutton JS, Lebhar MS, Bultman SJ, Sims CE, Magness ST, Allbritton NL (2017) In vitro generation of mouse colon crypts. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:2502–2513. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00368
Esch MB, Sung JH, Yang J, Yu C, Yu J, March JC, Shuler ML (2012) On chip porous polymer membranes for integration of gastrointestinal tract epithelium with microfluidic ‘body-on-a-chip’ devices. Biomed Microdevices 14:895–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9669-0
Shim K-Y, Lee D, Han J, Nguyen N-T, Park S, Sung JH (2017) Microfluidic gut-on-a-chip with three-dimensional villi structure. Biomed Microdevices 19:37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0179-y
Elomaa L, Keshi E, Sauer IM, Weinhart M (2020) Development of GelMA/PCL and dECM/PCL resins for 3D printing of acellular in vitro tissue scaffolds by stereolithography. Mater Sci Eng C 112:110958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110958
Lee M, Dunn JCY, Wu BM (2005) Scaffold fabrication by indirect three-dimensional printing. Biomaterials 26:4281–4289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.040
Costello CM, Sorna RM, Goh Y-L, Cengic I, Jain NK, March JC (2014) 3-D intestinal scaffolds for evaluating the therapeutic potential of probiotics. Mol Pharm 11:2030–2039. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp5001422
Hubbell JA (2014) Matrix efects. In: Principles of tissue engineering. Elsevier, pp 407–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398358-9.00021-5
Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM (2010) The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci 123:4195–4200. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.023820
Kim TG, Shin H, Lim DW (2012) Biomimetic scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater 22:2446–2468. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201103083
Godfrey M (2009) Extracellular matrix. In: Asthma and COPD. Elsevier, pp 265–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374001-4.00022-5
Muncie JM, Weaver VM (2018) Chapter one—the physical and biochemical properties of the extracellular matrix regulate cell fate. In: Litscher ES, Wassarman PMBT-CT in DB (eds) Extracellular matrix and egg coats. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–37
Wang Y, Kim R, Hinman SS, Zwarycz B, Magness ST, Allbritton NL (2018) Bioengineered systems and designer matrices that recapitulate the intestinal stem cell niche. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:440-453.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.01.008
Teller IC, Beaulieu J-F (2001) Interactions between laminin and epithelial cells in intestinal health and disease. Expert Rev Mol Med 3:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399401003623
Beaulieu JF (1992) Differential expression of the VLA family of integrins along the crypt-villus axis in the human small intestine. J Cell Sci 102:427–436
Meran L, Baulies A, Li VSW (2017) Intestinal stem cell niche: the extracellular matrix and cellular components. Stem Cells Int 2017:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7970385
Yamamoto S, Nakase H, Matsuura M, Honzawa Y, Matsumura K, Uza N, Yamaguchi Y, Mizoguchi E, Chiba T (2013) Heparan sulfate on intestinal epithelial cells plays a critical role in intestinal crypt homeostasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Liver Physiol 305:G241–G249. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00480.2012
Tong Z, Martyn K, Yang A, Yin X, Mead BE, Joshi N, Sherman NE, Langer RS, Karp JM (2018) Towards a defined ECM and small molecule based monolayer culture system for the expansion of mouse and human intestinal stem cells. Biomaterials 154:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.038
Hernandez-Gordillo V, Kassis T, Lampejo A, Choi G, Gamboa ME, Gnecco JS, Breault DT, Carrier R, Griffith LG (2019) Niche-inspired synthetic matrices for epithelial organoid culture. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/806919
Gjorevski N, Sachs N, Manfrin A, Giger S, Bragina ME, Ordóñez-Morán P, Clevers H, Lutolf MP (2016) Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nature 539:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20168
Broguiere N, Isenmann L, Hirt C, Ringel T, Placzek S, Cavalli E, Ringnalda F, Villiger L, Züllig R, Lehmann R, Rogler G, Heim MH, Schüler J, Zenobi-Wong M, Schwank G (2018) Growth of epithelial organoids in a defined hydrogel. Adv Mater 30:1801621. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201801621
DiMarco RL, Dewi RE, Bernal G, Kuo C, Heilshorn SC (2015) Protein-engineered scaffolds for in vitro 3D culture of primary adult intestinal organoids. Biomater Sci 3:1376–1385. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00108K
DiMarco RL, Hunt DR, Dewi RE, Heilshorn SC (2017) Improvement of paracellular transport in the Caco-2 drug screening model using protein-engineered substrates. Biomaterials 129:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.03.023
Wang L, Murthy SK, Barabino GA, Carrier RL (2010) Synergic effects of crypt-like topography and ECM proteins on intestinal cell behavior in collagen based membranes. Biomaterials 31:7586–7598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.036
Hadden WJ, Young JL, Holle AW, McFetridge ML, Kim DY, Wijesinghe P, Taylor-Weiner H, Wen JH, Lee AR, Bieback K, Vo B-N, Sampson DD, Kennedy BF, Spatz JP, Engler AJ, Choi YS (2017) Stem cell migration and mechanotransduction on linear stiffness gradient hydrogels. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:5647–5652. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1618239114
Xia T, Liu W, Yang L (2017) A review of gradient stiffness hydrogels used in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 105:1799–1812. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36034
Altay G, Larrañaga E, Tosi S, Barriga FM, Batlle E, Fernández-Majada V, Martínez E (2019) Self-organized intestinal epithelial monolayers in crypt and villus-like domains show effective barrier function. Sci Rep 9:10140. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46497-x
Speer JE, Gunasekara DB, Wang Y, Fallon JK, Attayek PJ, Smith PC, Sims CE, Allbritton NL (2019) Molecular transport through primary human small intestinal monolayers by culture on a collagen scaffold with a gradient of chemical cross-linking. J Biol Eng 13:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-019-0165-4
Speer JE, Wang Y, Fallon JK, Smith PC, Allbritton NL (2019) Evaluation of human primary intestinal monolayers for drug metabolizing capabilities. J Biol Eng 13:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-019-0212-1
Kim HJ, Ingber DE (2013) Gut-on-a-Chip microenvironment induces human intestinal cells to undergo villus differentiation. Integr Biol 5:1130. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ib40126j
Delon LC, Guo Z, Oszmiana A, Chien C-C, Gibson R, Prestidge C, Thierry B (2019) A systematic investigation of the effect of the fluid shear stress on Caco-2 cells towards the optimization of epithelial organ-on-chip models. Biomaterials 225:119521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119521
Zhang J, Li W, Sanders MA, Sumpio BE, Asit P, Basson MD (2003) Regulation of the intestinal epithelial response to cyclic strain by extracellular matrix proteins. FASEB J 17:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-0663fje
Poling HM, Wu D, Brown N, Baker M, Hausfeld TA, Huynh N, Chaffron S, Dunn JCY, Hogan SP, Wells JM, Helmrath MA, Mahe MM (2018) Mechanically induced development and maturation of human intestinal organoids in vivo. Nat Biomed Eng 2:429–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0243-9
Lozoya-Agullo I, Araújo F, González-Álvarez I, Merino-Sanjuán M, González-Álvarez M, Bermejo M, Sarmento B (2017) Usefulness of Caco-2/HT29-MTX and Caco-2/HT29-MTX/Raji B coculture models to predict intestinal and colonic permeability compared to Caco-2 monoculture. Mol Pharm 14:1264–1270. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b01165
Wang Q, Wang K, Solorzano-Vargas RS, Lin P-Y, Walthers CM, Thomas A-L, Martín MG, Dunn JCY (2018) Bioengineered intestinal muscularis complexes with long-term spontaneous and periodic contractions. PLoS ONE 13:e0195315. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195315
Kasendra M, Tovaglieri A, Sontheimer-Phelps A, Jalili-Firoozinezhad S, Bein A, Chalkiadaki A, Scholl W, Zhang C, Rickner H, Richmond CA, Li H, Breault DT, Ingber DE (2018) Development of a primary human small intestine-on-a-chip using biopsy-derived organoids. Sci Rep 8:2871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21201-7
Vila A, Torras N, Castaño AG, García-Díaz M, Comelles J, Pérez-Berezo T, Corregidor C, Castaño Ó, Engel E, Fernández-Majada V, Martínez E (2020) Hydrogel co-networks of gelatine methacrylate and poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate sustain 3D functional in vitro models of intestinal mucosa. Biofabrication 12:025008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ab5f50
Zhou W, Chen Y, Roh T, Lin Y, Ling S, Zhao S, Lin JD, Khalil N, Cairns DM, Manousiouthakis E, Tse M, Kaplan DL (2018) Multifunctional bioreactor system for human intestine tissues. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00794
Lahar N, Lei NY, Wang J, Jabaji Z, Tung SC, Joshi V, Lewis M, Stelzner M, Martín MG, Dunn JCY (2011) Intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts support in vitro and in vivo growth of human small intestinal epithelium. PLoS ONE 6:e26898. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026898
Jabaji Z, Brinkley GJ, Khalil HA, Sears CM, Lei NY, Lewis M, Stelzner M, Martín MG, Dunn JCY (2014) Type I collagen as an extracellular matrix for the in vitro growth of human small intestinal epithelium. PLoS ONE 9:e107814. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107814
Puzan M, Hosic S, Ghio C, Koppes A (2018) Enteric nervous system regulation of intestinal stem cell differentiation and epithelial monolayer function. Sci Rep 8:6313. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24768-3
Min S, Kim S, Cho S-W (2020) Gastrointestinal tract modeling using organoids engineered with cellular and microbiota niches. Exp Mol Med 52:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0386-0
Thursby E, Juge N (2017) Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J 474:1823–1836. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160510
Hou Q, Ye L, Liu H, Huang L, Yang Q, Turner J, Yu Q (2018) Lactobacillus accelerates ISCs regeneration to protect the integrity of intestinal mucosa through activation of STAT3 signaling pathway induced by LPLs secretion of IL-22. Cell Death Differ 25:1657–1670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0070-2
Kim HJ, Li H, Collins JJ, Ingber DE (2016) Contributions of microbiome and mechanical deformation to intestinal bacterial overgrowth and inflammation in a human gut-on-a-chip. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:E7–E15. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1522193112
Donohoe DR, Garge N, Zhang X, Sun W, O’Connell TM, Bunger MK, Bultman SJ (2011) The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab 13:517–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.018
Kaiko GE, Ryu SH, Koues OI, Collins PL, Solnica-Krezel L, Pearce EJ, Pearce EL, Oltz EM, Stappenbeck TS (2016) The colonic crypt protects stem cells from microbiota-derived metabolites. Cell 165:1708–1720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.018
Peng L, He Z, Chen W, Holzman IR, Lin J (2007) Effects of butyrate on intestinal barrier function in a Caco-2 cell monolayer model of intestinal barrier. Pediatr Res 61:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000250014.92242.f3
Matsumoto M, Kibe R, Ooga T, Aiba Y, Kurihara S, Sawaki E, Koga Y, Benno Y (2012) Impact of intestinal microbiota on intestinal luminal metabolome. Sci Rep 2:233. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00233
Löser C, Eisel A, Harms D, Fölsch UR (1999) Dietary polyamines are essential luminal growth factors for small intestinal and colonic mucosal growth and development. Gut 44:12–16. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.44.1.12
Iwao T, Toyota M, Miyagawa Y, Okita H, Kiyokawa N, Akutsu H, Umezawa A, Nagata K, Matsunaga T (2014) Differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into functional enterocyte-like cells using a simple method. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 29:44–51. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.DMPK-13-RG-005
Iwao T, Kodama N, Kondo Y, Kabeya T, Nakamura K, Horikawa T, Niwa T, Kurose K, Matsunaga T (2015) Generation of enterocyte-like cells with pharmacokinetic functions from human induced pluripotent stem cells using small-molecule compounds. Drug Metab Dispos 43:603–610. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.114.062604
Ozawa T, Takayama K, Okamoto R, Negoro R, Sakurai F, Tachibana M, Kawabata K, Mizuguchi H (2015) Generation of enterocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells for drug absorption and metabolism studies in human small intestine. Sci Rep 5:16479. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16479
Spence JR, Mayhew CN, Rankin SA, Kuhar MF, Vallance JE, Tolle K, Hoskins EE, Kalinichenko VV, Wells SI, Zorn AM, Shroyer NF, Wells JM (2011) Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature 470:105–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09691
Múnera JO, Sundaram N, Rankin SA, Hill D, Watson C, Mahe M, Vallance JE, Shroyer NF, Sinagoga KL, Zarzoso-Lacoste A, Hudson JR, Howell JC, Chatuvedi P, Spence JR, Shannon JM, Zorn AM, Helmrath MA, Wells JM (2017) Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into colonic organoids via transient activation of bmp signaling. Cell Stem Cell 21:51-64.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2017.05.020
Workman MJ, Gleeson JP, Troisi EJ, Estrada HQ, Kerns SJ, Hinojosa CD, Hamilton GA, Targan SR, Svendsen CN, Barrett RJ (2018) Enhanced utilization of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human intestinal organoids using microengineered chips. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:669-677.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.12.008
Fleischer A, Vallejo-Díez S, Martín-Fernández JM, Sánchez-Gilabert A, Castresana M, del Pozo A, Esquisabel A, Ávila S, Castrillo JL, Gaínza E, Pedraz JL, Viñas M, Bachiller D (2020) iPSC-derived intestinal organoids from cystic fibrosis patients acquire CFTR activity upon TALEN-mediated repair of the p. F508del mutation. Mol Ther—Methods Clin Dev 17:858–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2020.04.005
Gleeson JP, Estrada HQ, Yamashita M, Svendsen CN, Targan SR, Barrett RJ (2020) Development of physiologically responsive human ipsc-derived intestinal epithelium to study barrier dysfunction in IBD. Int J Mol Sci 21:1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041438
Kabeya T, Mima S, Imakura Y, Miyashita T, Ogura I, Yamada T, Yasujima T, Yuasa H, Iwao T, Matsunaga T (2020) Pharmacokinetic functions of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived small intestinal epithelial cells. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 35:374–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dmpk.2020.04.334
Negoro R, Takayama K, Kawai K, Harada K, Sakurai F, Hirata K, Mizuguchi H (2018) Efficient generation of small intestinal epithelial-like cells from human iPSCs for drug absorption and metabolism studies. Stem Cell Rep 11:1539–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.10.019
Onozato D, Yamashita M, Nakanishi A, Akagawa T, Kida Y, Ogawa I, Hashita T, Iwao T, Matsunaga T (2018) Generation of intestinal organoids suitable for pharmacokinetic studies from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Drug Metab Dispos 46:1572–1580. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.118.080374
Naumovska E, Aalderink G, Wong Valencia C, Kosim K, Nicolas A, Brown S, Vulto P, Erdmann KS, Kurek D (2020) Direct on-chip differentiation of intestinal tubules from induced pluripotent stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 21:4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144964
Yamada S, Kanda Y (2019) Retinoic acid promotes barrier functions in human iPSC-derived intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Pharmacol Sci 140:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2019.06.012
Loffet E, Brossard L, Mahe MM (2020) Pluripotent stem cell derived intestinal organoids with an enteric nervous system. In: Spence JRBT-M in CB (ed) Human pluripotent stem cell derived organoid models. Academic Press, New York, pp 175–199
Yoshida S, Miwa H, Kawachi T, Kume S, Takahashi K (2020) Generation of intestinal organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells for drug testing. Sci Rep 10:5989. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63151-z
Takahashi Y, Sato S, Kurashima Y, Yamamoto T, Kurokawa S, Yuki Y, Takemura N, Uematsu S, Lai C-Y, Otsu M, Matsuno H, Osawa H, Mizushima T, Nishimura J, Hayashi M, Yamaguchi T, Kiyono H (2018) A Refined culture system for human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal epithelial organoids. Stem Cell Rep 10:314–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.11.004
Crespo M, Vilar E, Tsai S-Y, Chang K, Amin S, Srinivasan T, Zhang T, Pipalia NH, Chen HJ, Witherspoon M, Gordillo M, Xiang JZ, Maxfield FR, Lipkin S, Evans T, Chen S (2017) Colonic organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling colorectal cancer and drug testing. Nat Med 23:878–884. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4355
Forbester JL, Goulding D, Vallier L, Hannan N, Hale C, Pickard D, Mukhopadhyay S, Dougan G (2015) Interaction of salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium with intestinal organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Infect Immun 83:2926–2934. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00161-15
Matai I, Kaur G, Seyedsalehi A, McClinton A, Laurencin CT (2020) Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials 226:119536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119536
Mandrycky C, Wang Z, Kim K, Kim D-H (2016) 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol Adv 34:422–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.011
Murata D, Arai K, Nakayama K (2020) Scaffold-free bio-3d printing using spheroids as “bio-inks” for tissue (re-)construction and drug response tests. Adv Healthc Mater 9:1901831. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201901831
McCormack A, Highley CB, Leslie NR, Melchels FPW (2020) 3D Printing in suspension baths: keeping the promises of bioprinting afloat. Trends Biotechnol 38:584–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.12.020
Zhang J, Hu Q, Wang S, Tao J, Gou M (2019) Digital light processing based three-dimensional printing for medical applications. Int J Bioprint 6:1. https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v6i1.242
Ayan B, Heo DN, Zhang Z, Dey M, Povilianskas A, Drapaca C, Ozbolat IT (2020) Aspiration-assisted bioprinting for precise positioning of biologics. Sci Adv 6:eaaw5111. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw5111
Gao B, Yang Q, Zhao X, Jin G, Ma Y, Xu F (2016) 4D bioprinting for biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol 34:746–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.03.004
Acknowledgements
TA would like to acknowledge the INSPIRE scheme, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for providing the fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TA was involved in conceptualization, writing–original draft, writing–reviewing and editing; VO was involved in writing–original draft; LL was involved in writing–original draft; AA was involved in writing–original draft; TKM was involved in conceptualization, writing–reviewing and editing; PM was involved in writing–reviewing and editing; MV was involved in writing–reviewing and editing; GY was involved in writing–reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Valentina Onesto and Lallepak Lamboni are equal contribution to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, T., Onesto, V., Lamboni, L. et al. Engineering biomimetic intestinal topological features in 3D tissue models: retrospects and prospects. Bio-des. Manuf. 4, 568–595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-020-00120-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-020-00120-5