Abstract
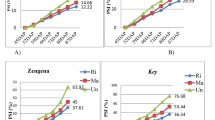
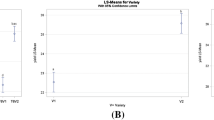
Potato production is limited due to late blight of potato. Field experiments were conducted to evaluate potato varieties and fungicides for the management of late blight. Three potato varieties and five fungicides including untreated control were arranged in a randomized complete block design in three replications at two research locations during the 2019 season. Disease severities, disease progress curves, disease progress rate, and tuber yield were significantly (P < 0.01) affected by potato varieties, fungicide applications, and their interactions at both locations. At Debre Berhan agricultural research center, the highest area under disease progress curve (AUDPC) value (948.8%-days) was computed from untreated control plots of Gudene variety while the lowest AUDPC value (223%-days) was computed from Gudene variety treated with Ridomil Gold. At Debre Berhan University research field, the highest (39.4 t ha−1) yield was recorded from the Gera variety treated with Ridomil Gold. Farmers at both locations are recommended to use Gera variety treated with Ridomil Gold.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abewoy D (2018) Review on impacts of climate change on vegetable production and its management practices. Adv Crop Sci Technol 6:1–7
Ajanga S (1993) Status of bacterial wilt of potato in Kenya.[Conference paper]. ACIAR Proceedings-Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (Australia)
Amin M, Mulugeta N, Selvaraj T (2013) Field evaluation of new fungicide, Victory 72 WP for management of potato and tomato late blight (Phytophthora infestans (Mont) de Bary) in West Shewa Highland, Oromia, Ethiopia. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 4:192
Arega A, Tekalign A, Solomon T, Tekile B (2018) Effect of inter and intra row spacing on tuber yield and yield components of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in guji zone, southern Ethiopia. J Adv Plant Sci 1:102
Arora R, Sharma S, Singh B (2014) Late blight disease of potato and its management. Potato J 41:16–40
Asamenew T, Bahru Z (2000) Transfer of improved potato varieties and production technologies in the southeastern highlands of Ethiopia. Afr Potato Assoc Proc 5:153–156
Asaye G, Abera M, Tesfaye A (2020) The fungicide and variety integration effect on late blight (Phytophthora infestans) disease of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in Western Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Int J Sustain Agric Res 7:15–29
Ashenafi M, Selvaraj T, Alemu L, Bekele K (2017) Evaluation of Potato cultivars and fungicides for the management of late blight (phytophthora infestans (mont) de bary) in Holleta, West Showa, Ethiopia. Int J Life Sci 5:161–179
Ayda TT (2015) Effect of fungicides and resistant genotypes on severity of potato late blight [Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary] and yield and yield components at Haramaya, Eastern Ethiopia. Harmaya University
Bekele B, Dickinson M, Asefa A, Abate E (2011) Incidence of potato viruses and bacterial wilt disease in the west Amhara sub-region of Ethiopia. Incidence of Potato Viruses and Bacterial Wilt Disease in the West Amhara Sub-Region of Ethiopia, 149–157
Binyam T (2014) Late blight of potato (Phytophthora infestans) biology, economic importance and its management approaches. J Biol Agric Healthc 4:215–225
Bizuneh WF, Abebe DA (2019) Malt barley (Hordeum distichon L.) varieties performance evaluation in North Shewa, Ethiopia. Afr J Agric Res 14:503–508
Campbell C (1990) Temporal analysis of epidemics. I: Description and comparison of diseases progress curves. Introduction to plant disease epidemiology
CIP (1984) Potatoes for the developing Countries. Lima, International Potato Center
Crowell EF, McGrath JM, Douches DS (2008) Accumulation of vitamin E in potato (Solanum tuberosum) tubers. Transgenic Res 17:205–217
CSA (2016) Agricultural sample survey: Report on area and production of crops (Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, Central Statistical Agency)
CSA (2017) Agricultural sample survey: Report on area and production of crops (Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, Central Statistical Adency)
Dangles OJ (2013) An agent-based modeling framework for integrated pest management dissemination programs
De Jong FM, De Snoo GR (2002) A comparison of the environmental impact of pesticide use in integrated and conventional potato cultivation in The Netherlands. Agr Ecosyst Environ 91:5–13
EARO (2002) Agricultural sample survey: Report on area and production of crops (Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, Ethiopian Agricultural Research Organization)
EARO (2004) Directory of Released crop varieties and their recommended cultural practices (Addis Ababa, Ethiopa)
FAOSTAT (2018) Datasbase of agricultural production. (Rome, Italy, Food and Agriculture Organization)
Finckh M, Schulte-Geldermann E, Bruns C (2006) Challenges to organic potato farming: disease and nutrient management. Potato Res 49:27–42
Ghazanfar MU, Sahi ST, Wakil W, Iqbal Z (2010) Evaluation of various fungicides for the management of late blight of potato (Phytophthora infestans). Pak J Phytopathol 22:83–88
Girma F, Ayalew A, Dechassa N (2013) Management of Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) of potato (Solanum tuberosum) through potato cultivars and fungicides in Hararghe highlands, Ethiopia. Int J Life Sci 2:130–138
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley
Guchi E (2015) Disease management practice on potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in Ethiopia. World J Agric Res 3:34–42
Gupta SK, Thind T (2018) Disease problems in vegetable production. Scientific Publishers
Haas BJ, Kamoun S, Zody MC, Jiang RH, Handsaker RE, Cano LM, Grabherr M, Kodira CD, Raffaele S, Torto-Alalibo T (2009) Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature 461:393–398
Hakiza J, Turyamureeba G, Kakuhenzire R, Odongo B, Mwanga R, Kanzikwera R, Adipala E (2000) Potato and sweetpotato improvement in Uganda: a historical perspective. In: African Potato Asso Conf Proc 47–58
HARC (2005) Annual Research Report. (Holleta, Ethiopia, Holleta Agricultural Research Center)
Hassen A, Worku A, Tafere M, Tolla M, Ahmed A, Dagnew S, Selassie Y, Molla D, Abebe T (2015) Best fit practice manual for potato production and utilization. BDU-CASCAPE Working Paper 8. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: EIAR Annual report, 37
Haverkort A, Boonekamp P, Hutten R, Jacobsen E, Lotz L, Kessel G, Visser R, Van der Vossen E (2008) Societal costs of late blight in potato and prospects of durable resistance through cisgenic modification. Potato Res 51:47–57
Haverkort AJ, Struik P, Visser R, Jacobsen E (2009) Applied biotechnology to combat late blight in potato caused by Phytophthora infestans. Potato Res 52:249–264
Hirpa A, Meuwissen MP, Tesfaye A, Lommen WJ, Oude Lansink A, Tsegaye A, Struik PC (2010) Analysis of seed potato systems in Ethiopia. Am J Potato Res 87:537–552
Horton D, Sawyer RL (1985) The potato as a world food crop, with special reference to developing areas. Potato physiology, 1–34
Horton DE (1987) Potatoes: Production, marketing, and programs for developing countries. International Potato Center
Kefelegn H, Chala A, Kassa B, Tiwari P (2012) Evaluation of different potato variety and fungicide combinations for the management of potato late blight (Phytophthora infestans) in Southern Ethiopia. Int J Life Sci 1:8–15
Lal M, Yadav S, Chand S, Kaushik S, Singh B, Sharma S (2015) Evaluation of fungicides against late blight (Phytophthora infestans) on susceptible and moderately resistant potato cultivars. Indian Phytopathol 68:345–347
Lammerts van Bueren E, Tiemens-Hulscher M, Struik P (2008) Cisgenesis does not solve the late blight problem of organic potato production: alternative breeding strategies. Potato Res 51:89–99
Legesse NH, Bizuneh WF, Shifamo BT (2021) Potato variety screening for its late blight of potato (Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary) resistance and yield performance in Northern Shewa, Central Highlands of Ethiopia. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 54:2440–2463
Mesfin T, Wendirad M, Bekele K (2009) Review of research on diseases of root and tuber crops in Ethiopia. Increasing crop production through improved plant protection 2, 169-202
Mohammed W (2017) Genetic gain of tuber yield and late blight [Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary] resistance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties in Ethiopia. East Afr J Sci 11:1–16
Mukalazi J, Adipala E, Sengooba T, Hakiza J, Olanya M, Kidanemariam H (2001) Variability in potato late blight severity and its effect on tuber yield in Uganda. Afr Crop Sci J 9:195–201
Namanda S, Adipala E, Olanya O, Hakiza J, El-Bedewy R, Bhagsari A (2001) Integration of host resistance and minimum fungicide application for management of potato late blight in Uganda. In: Fifth Biennial Conference of the African Crop Science Society (Abstract), October, 19–26
Nieder R, Benbi DK, Reichl FX (2018) Health risks associated with pesticides in soils, In: Soil components and human health. Springer, 503–573
Olanya O, Adipala E, Hakiza J, Kedera J, Ojiambo P, Mukalazi J, Forbes G, Nelson R (2001) Epidemiology and population dynamics of Phytophthora infestans in Sub-Saharan Africa: progress and constraints. Afr Crop Sci J 9:185–193
Pacilly FC, Groot JC, Hofstede GJ, Schaap BF, van Bueren ETL (2016) Analysing potato late blight control as a social-ecological system using fuzzy cognitive mapping. Agron Sustain Dev 36:1–18
Plank JE (1963) Plant diseases: epidemics and control. Academic Press New York, vol 111
Prabha N, Nanda H, Sharma SK (2018) Genetic Divergence analysis in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 7:3152–3157
Robert G, James H (1991) A Biometrical Approach: Principles of Statistics. New York, 15, 143-151
Rotem J, Sari A (1983) Fertilization and age-conditioned predisposition of potatoes to sporulation of and infection by Phytophthora infestane/Einfluß der Düngung und altersbedingter Prädisposition der Kartoffel auf Sporulation von und Infektion durch Phytophthora infestans. Z Pflanzenkrankh Pflanzenschutz/J Plant Dis Protect 90(1):83–88
SAS (2003) SAS/STATA Guide for personal computer version 9.1 (carry, NC, USA, SAS Institute Inc.)
Scott GJ, Rosegrant MW, Ringler C (2000) Roots and tubers for the 21st century: trends, projections, and policy options, vol 31. Intl Food Policy Res Inst
Thierfelder C, Cheesman S, Rusinamhodzi L (2013) Benefits and challenges of crop rotations in maize-based conservation agriculture (CA) cropping systems of southern Africa. Int J Agric Sustain 11:108–124
Tsedaley B, Hussen T, Tsegaw T (2014) Tuber yield loss assessment of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties due to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) and its management Haramaya, Eastern Ethiopia. J Biol Agric Healthc 4:45–54
van der Werf HM (1996) Assessing the impact of pesticides on the environment. Agr Ecosyst Environ 60:81–96
Van Weymers PS, Baker K, Chen X, Harrower B, Cooke DE, Gilroy EM, Birch PR, Thilliez GJ, Lees AK, Lynott JS (2016) Utilizing “Omic” technologies to identify and prioritize novel sources of resistance to the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans in potato germplasm collections. Front Plant Sci 7:672
Vossen, JH, Jo, KR., Vosman, B (2014) Mining the genus Solanum for increasing disease resistance. In: Tuberosa R, Frison E, Graner A (eds) Genomics of Plant Genetic Resources: vol 2. Crop productivity, food security, and nutritional quality. Springer, WUR Plant Breeding. pp 27–46
Wang S, Hu T, Zhang F, Forrer H, Cao K (2007) Screening for plant extracts to control potato late blight. Front Mech Eng China 1:43–46
Wheeler BEJ (1969) An introduction to plant diseases. An introduction to plant diseases
Wondimu SE, Heyie AC, Legesse NH (2022) Evaluation of malt barley cultivars for resistance against leaf scald (Rhynchosporium secalis)(Oudem JJ. Davis) and for yield and yield traits in North Shewa, Central high lands of Ethiopia. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect. 55(9),:1045–1061
Zwankhuizen M, Zadoks J (2002) Phytophthora infestans’s 10-year truce with Holland: a long-term analysis of potato late-blight epidemics in the Netherlands. Plant Pathol 51:413–423
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Debre Berhan Agricultural Research center for providing technical support, and the research field. They also would like to thank College of Agriculture of Debre Berhan University for providing the research field for the field experiment, providing planting materials, and laboratory equipment for identification and characterization of the pathogen. They also send their heartfelt thanks to Debre Berhan Agricultural Research center Pathology department researchers for their unforgettable material support, guidance, and data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The research was not involving humans and animals as experimental units. The research was conducted by keeping the research ethics.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gedlu, D., Hailu, N. & Kefelegn, H. Integrated management of potato late blight (Phytophthora infestans (Mont) de Bary) through resistant varieties and fungicides in North Shewa, Ethiopia. J Plant Pathol 105, 95–106 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-022-01269-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-022-01269-x