Abstract
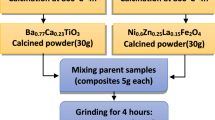
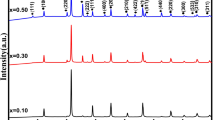
Multiferroic nanocomposite samples (1 − x) BiFeO3-xCo0.7Ni0.3Fe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0) were prepared by the hybrid processing method. The X-ray diffraction technique is used to confirm the formation of the ferroelectric (BiFeO3) and ferromagnetic (Co0.7Ni0.3Fe2O4) phases. The nature of metal–oxygen bonding in the multiferroic samples was identified by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis. The frequency dependence of AC conductivity suggests that the samples obey the power law Aωs. The value of frequency exponent ‘s’ was found to decrease with increasing temperature suggesting the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model as the most suitable mechanism to explain the transport properties of the samples. The hopping distance increases with increasing the content of the ferromagnetic phase in the nanocomposites (2.02 Å for x = 0.0 to 6.71 Å for x = 1.0). The Arrhenius plot analysis of AC conductivity confirms the presence of different conduction processes in low and high temperature regions. The enhancement in magnetization (Ms) is observed with increasing the content of the ferromagnetic phase (9.18 emu gm−1 for x = 0.2 to 36.19 emu gm−1 for x = 0.8 nanocomposites).

Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catalan G, Scott JF (2009) Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv Mater 21:2463–2485
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442:759–765
Khikhlovskyi SVV, Blake G (2010) The renaissance of multiferroics: bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) - a candidate multiferroic material in nanoscience. University of Groningen, Groningen
Khomskii DI (2006) Multiferroics: different ways to combine magnetism and ferroelectricity. J Magn Magn Mater 306:1–8
Cheong SW, Mostovoy M (2007) Multiferroics: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat Mater 6:13–20
Lee HS, Lee AS, Baek KY, Hwang SS (2012) Low dielectric materials for microelectronics. InTech, Rijeka, pp 59–75
Imanpreet K, Verma NK (2015) Magnetic and electrical properties of BFO-NFO nanocomposites. Mater Sci Semicond Process 33:32
Dhanalakhsmi B, Kollu P, Chandra Sekhar B, Parvatheeswara Rao B, Subba Rao BPSV (2017) Enhanced magnetic and magnetoelectric properties of Mn-doped multiferroic ceramics. Ceram Int 43:9272–9275
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H, Nagarajan V, Ogale SB, Liu B et al (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science. 299:1719–1722
Zhang YJ, Zhang HG, Yin JH, Zhang HW, Chen JL, Wang WQ et al (2010) Structural and magnetic properties in Bi1−xRxFeO3 (x=0–1, R=La, Nd, Sm, Eu, and Tb) polycrystalline ceramics. J Magn Magn Mater 322:2251–2255
Hu Z, Li M, Yu Y, Liu J, Pei L, Wang J et al (2010) Effect of Nd and high-valence Mn co-doping on the electrical and magnetic properties of multiferroic BiFeO3 ceramics. Solid State Commun 150:1088–1091
Deepti K, Raghavendra Reddy V, Gupta A, Phase DM, Lakshmi N, Deshpande SK, Awasthi AM (2007) Study of the effect of Mn doping on BiFeO3 system. J Phys Condens Mater 19:136202–136209
Kumar M, Yadav KL (2007) Magnetoelectric characterization of xNi0.75Co0.25Fe2O4-(1−x) BiFeO3 nanocomposites. J Phys Chem Solids 68:1791–1795
Kim DM, Lee MH, Park SJ et al (2014) Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of Mn modified BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics. J Electroceram 33:37–41
Zhang L, Xu Z, Cao LH, Yao X (2007) Synthesis of BF-PT perovskite powders by high-energy ball milling. Mater Lett 61:1130–1133
Nan CW, Bichurin MI, Dong S, Viehland D, Srinivasan G (2008) Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: historical perspective, status and future directions. J Appl Phys 103:031101–031135
Adhlakha N, Yadav KL (2014) Structural, dielectric, magnetic and optical properties of xNi0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4-(1−x) BiFeO3. J Mater Sci 49:4423–4438
Liu XM, Fu SY, Huang CJ (2005) Synthesis and magnetic characterization of novel CoFe2O4-BiFeO3 nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng B 121:255–260
Dhanalaxmi B, Caltun OF, Dumitru I, Pratap K, Parvatheeswara Rao B, Rao PSV (2015) Bi0.95Mn0.05FeO3 - Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposites with multiferroic properties. Mater. Today Proc 2:3806–3812
Yang H, Wang H, He L, Yao X (2010) Polarization relaxation mechanism of Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3/Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 composite with giant dielectric constant and high permeability. J Appl Phys 108:074105–074110
Crane SP, Bihler C, Brandt MS, Goennenwein STB, Gajek M, Ramesh R (2009) Tuning magnetic properties of magnetoelectric BiFeO3-NiFe2O4 nanostructures. J Magn Magn Mater 321:L5–L9
Hartono A, Satira S, Djamal M, Ramli R, Bahar H, Sanjaya E (2013) Effect of mechanical treatment temperature on electrical properties and crystallite size of PVDF film. Adv Mater Phys Chem 3:71–76
Fawzi AS, Sheikh AD, Mathe VL (2010) Composition dependent electrical, dielectric, magnetic and magnetoelectric properties of xCo0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 + (1−x) PLZT composites. J. Alloys Compd 493:601–608
Kumar A, Yadav KL (2010) Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of xCrFe2O4-(1−x) BiFeO3 multiferroic nanocomposites. Physica B 405:2362–2366
Mukherjee S, Chakraborty S (2014) Synthesis and characterization of lanthanum doped bismuth ferrite. Int J Nano Dimens 5:41–46
Varshney D, Kumar A, Verma K (2011) Effect of A site and B site doping on structural, thermal, and electrical properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Alloys Compd 509:8421–8426
Mukherjee A, Sk. Hossain M, Basu S, Pal M (2012) Effect of Y-doping on optical properties of multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 2:305–310
Chen Z, Hu J, Lu Z, He X (2011) Low-temperature preparation of lanthanum doped BiFeO3 crystallites by sol-gel hydrothermal method. Ceram Int 37:2359–2364
Koops CG (1951) On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys Rev 83:121
Maxwell JC (1933) Electricity and magnetism. Oxford Univ. Press, London
Wagner WK (1973) The distribution of relaxation times in typical dielectrics. Ann Phys 40:817–819
Bhattacharjee K, Ghosh CG, Mitra MK, Das GC, Mukherjee S, Chattopadhyay KK (2011) Novel synthesis of NixZn1-xFe2O4 (0≤x≤1) nanoparticles and their dielectric properties. J Nanopart Res 13:739–750
Parvatheeswara Rao B, Rao KH (1997) Effect of sintering conditions on resistivity and dielectric properties of Ni-Zn ferrites. J Mater Sci 32:6049–6054
Jonscher AK (1977) The universal dielectric response. Nature 267:673
Srinivas K, Sarah P, Suryanarayana SV (2003) Impedance spectroscopy study of polycrystalline Bi6Fe2Ti3O18. Bull Mater Sci 26:247–253
Lily KK, Prasad K, Choudhary RNP (2008) Impedance spectroscopy of (Na0.5Bi0.5) (Zr0.25Ti0.75)O3 lead-free ceramic. J. Alloys Compd 453:325–331
Elliott SR (1987) A. C. conduction in amorphous chalcogenide and pnictide semiconductors. Adv Phys 36:135–217
Ben Taher Y, Oueslati A, Maaloul NK, Khirouni K, Gargouri M (2015) Conductivity study and correlated barrier hopping (CBH) conduction mechanism in diphosphate compound. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 120:1537–1543
Panigrahi SC, Das PR, Parida PN, Sharma HBK, Chaudhary RNP (2013) Effect of Gd substitution on dielectric and transport properties of lead zirconium titanate ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 24:3275–3283
Behera C, Das PR, Choudhary RNP (2014) Structural and electrical properties of mechanothermally synthesized NiFe2O4 nanoceramics. J Electron Mater 43:3539–3549
Lakshman A, Rao PSVS, Rao BP, Rao KH (2005) Electrical properties of In3+ and Cr3+ substituted magnesium-manganese ferrites. J Phys D Appl Phys 38:673–678
Sharma HB, Nomita K, Gupta V, Lee JH, Bobby Singh S (2014) AC electrical conductivity and magnetic properties of BiFeO3-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 599:32–39
Lee YH, Wu JM, Lai CH (2006) Influence of La doping in multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 thin films. Appl Phys Lett 88:042903–042905
Park T, Papaefthymiou G, Viescas A, Moodenbaugh A, Wong S (2007) Size-dependent magnetic properties of single-crystalline multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 7:766–772
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) New Delhi for financial assistance to one of the authors, Huidrom Hemanta Singh (SRF, CSIR, File No. 09/476(0079)/2017-EMR-I). The authors are thankful to the NIT, Manipur for extending the valuable facilities for taking XRD and FTIR measurements. They are also thankful to Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF), IIT Guwahati for VSM measurement and STIC, Cochin University of Science and Technology Cochin, Kerala for SEM measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, H.H., Sharma, H.B. Structural, transport and magnetic properties of (1-x) BiFeO3-xCo0.7Ni0.3Fe2O4 nanocomposite samples (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0). Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3, 609–620 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00157-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00157-1