Abstract
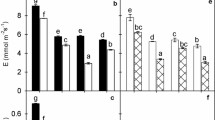
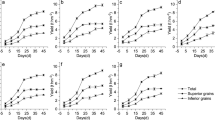
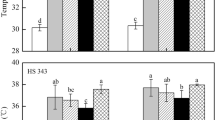
Despite global warming, the response of rice yield to long-term warming in cool regions and its physiological mechanisms remain unknown. This study used the widely cultivated japonica rice Jiyang100 in Northeast China. Taking rice grown under natural temperatures as a control (CK), field warming treatments were conducted at the tillering-panicle initiation (T1), whole growth (T2), and grain-filling (T3) stages. The positive effects of T1, T2, and T3 on the total number of spikelets per hole increased the yield in both years, with average increases of 11.5%, 9.9% and 6.5% compared to CK, respectively. Warming treatments improved the stay-green traits, photosynthesis, sucrose synthesis, and nitrogen metabolism of rice. The yield was positively correlated with the relative chlorophyll content (SPAD), soluble sugar content, sucrose content, and the activities of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS), nitrate reductase (NR), glutamine synthetase (GS), glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase (GOGAT) in flag leaves. In addition, SPAD had a positive correlation with soluble sugar content, soluble protein content, and the activities of NR, GS, GOGAT, glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), but a negative correlation with acid invertase (AI) activity. The stay-green ability was positively correlated to the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), soluble sugar content and soluble protein content. The coupling interactions of stay-green traits, nitrogen and carbon metabolism increased the yield potential and yield supply capacity, increased yield under long-term warming conditions in the cool regions. Under gradual warming, the physiological response of rice in cool regions promotes plant growth and development, thereby increasing yield.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SPAD:
-
Relative chlorophyll content
- Pn :
-
Net photosynthetic rate
- SPS:
-
Sucrose phosphate synthase
- SS:
-
Sucrose synthase
- AI:
-
Acid invertase
- NR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- GOGAT:
-
Glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase
- GDH:
-
Glutamate dehydrogenase
References
Baron, A. C., Tobin, T. H., Wallsgrove, R. M., & Tobin, A. K. (1994). A metabolic control analysis of the glutamine Synthetase/Glutamate synthase cycle in isolated barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) chloroplasts. Plant Physiology, 105(1), 415–424. https://doi.org/10.1104/PP.105.1.415.
Cai, C., Yin, X., He, S., Jiang, W., Si, C., Struik, P. C., Luo, W., Li, G., Xie, Y., & Ya, X. (2016). Responses of wheat and rice to factorial combinations of ambient and elevated CO2 and temperature in FACE experiments. Global Change Biology, 22(2), 856–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13065.
Cao, W. G., Jiao, Q. C., Liu, Q., & Chen, L. (2002). Study on the mechanism of Color changes of Commassie Brilliant Blue G-250. Acta Chimica Sinica, 60(9), 1656–1661. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2002.09.021.
Cao, Y. Y., Duan, Y., Yang, L. N., Wang, Z. Q., Zhou, S. C., & Yang, J. C. (2008). Effect of heat-stress during meiosis on grain yield of rice cultivars differing in heat-tolerance and its physiological mechanism. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 34(12), 2134–2142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-2780(09)60022-5.
Cao, W. Z., Chen, J. L., Zhu, Y., Yang, B. H., & Shi, P. H. (2017). Effects of short-term high temperature on grain quality and starch granules of rice (Oryza sativa L.) at post-anthesis stage. Protoplasma, 254(2), 935–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-1002-y.
Chen, W. J., & Kuai, B. K. (2001). Chlorophyll degradation in plants. Plant Physiology Communication, 37(4), 336–339.
Chen, J., Chen, C., Tian, Y. L., Zhang, X., Dong, W. J., Zhang, B., Zheng, C. Y., Deng, A. X., Song, Z. W., Peng, C. R., & Zhang, W. J. (2016). Differences in the impacts of nighttime warming on crop growth of rice-based cropping systems under field conditions. European Journal of Agronomy, 82, 80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.10.006.
Cheng, Y. Y., Wang, Y., Han, Y. L., Li, D. Y., Zhang, Z. K., Zhu, X. Q., Tan, J. F., & Wang, H. Z. (2019). The stimulatory effects of nanochitin whisker on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and on the enhancement of grain yield and crude protein of winter wheat. Molecule, 24(9), 1752–1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091752.
China Meteorological Administration. (2021). Blue Book on Climate Change in China. Science.
Da Silva, D. L., Renato, P., Luis, D. M. T., da Silva, F. L., J. L. F., & Mattiuz, B. H. (2021). Silicon attenuates calcium deficiency in rocket plants by increasing the production of non-enzymatic antioxidants compounds. Scientia Horticulturae, 285(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCIENTA.2021.110169.
Dong, W. J., Chen, J., Zhang, B., Tian, Y. L., & Zhang, W. J. (2011). Responses of biomass growth and grain yield of midseason rice to the anticipated warming with FATI facility in East China. Field Crops Research, 123(3), 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.05.024.
Dou, Z. (2017). Effects of free-air warming during grainfilling stage on rice grain filling and quality and the reglation effects of nitrogen spikelet fertilizer Doctor’s thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University.
Du, J. J., & Chen, Z. W. (2010). A method for path analysis using SPSS linear regression. Biology Bulletin, 45(02), 4–6.
Guo, L. Y., Lu, Y. Y., Bao, S. Y., Zhang, Q., Geng, Y. Q., & Shao, X. W. (2021). Carbon and nitrogen metabolism in rice cultivars affected by salt-alkaline stress. Crop and Pasture Science, 72(5), 372–382. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP20445.
IPCC. (2022). Climate change 2021:The physical science basis Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press.
Jiang, S. K., Wang, L., & Yang, X. (2021). Effect of increasing temperature in different growth stages on rice yield and quality in cold regions. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 23(6), 10. https://doi.org/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2019.0983.
Kumar, P. A., Polisetty, R., & Abrol, Y. P. (1993). Interaction between Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism. Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2708-0_13.
Kumar, R., Harikrishna, Barman, D., Ghimire, Gurumurthy, S., Singh, P. K., Chinnusamy, V., Padaria, J. C., Ntamatungiro, S., Norman, R. J., Mcnew, R. W., & Wells, B. R. (1999). Comparison of plant measurements for estimating nitrogen accumulation and grain yield by flooded rice. Agronomy Journal, 91(4), 676–685. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1999.914676x.
Kumar, R., Harikrishna, Barman, D., Ghimire, Gurumurthy, S., Singh, P. K., Chinnusamy, V., Padaria, J. C., & Arora, A. (2022). Stay-green trait serves as yield stability attribute under combined heat and drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Plant Growth Regulation, 96(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10725-021-00758-W.
Lam, H. M., Coschigano, K., Oliveira, T., Melo-Oliveira, I. C., R., & Coruzzi, G. M. (1996). The molecular-genetics of nitrogen assimilation into amino acids in higher plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 47(1), 569–593. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.569.
Langhansova, L., Pumprova, K., Haisel, D., Ekrt, L., Pavicic, A., Zajickova, M., Vanek, T., & Dvorakova, M. (2021). European ferns as rich sources of antioxidants in the human diet. Food Chemistry, 356, 129637–129637. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2021.129637.
Lepeduš, H., Jakopec, M., Dunić, J. A., Krizmanić, G., Osmanović, S., & Cesar, V. (2017). Temperature-dependent chlorophyll accumulation and photosystem II assembly during etioplast to chloroplast transition in sunflower cotyledons. Acta Botanica Croatica, 76(1), 107–110. https://doi.org/10.1515/botcro-2016-0043.
Liu, Y. Z., Huang, N. R., Huang, Q. M., Chen, Z. M., Liu, B., Liang, Z. Y., Qiu, R. H., & Zhang, X. (2000). A preliminary study on the changes of photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll content of different types of high-yield rice varieties in late season. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, (1), 3.
Liu, L. J., Weng, Y. N., Fang, J., Zhao, Z. J., & Du, S. T. (2022). Understanding the effect of GO on nitrogen assimilation in wheat through transcriptomics and metabolic process analysis. Chemosphere, 296, 134000–134000. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2022.134000.
Ma, K., Zhou, Y. Y., Zhang, Z. A., Chen, Q. Y., & Jing, N. (2022). Photosynthetic response and yield formation mechanisms of rice under warming at different growth stages in cool region. International Journal of Plant Production. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-022-00186-4.
Nathawat, N. S., Kuhad, M. S., Goswami, C. L., Patel, A. L., & Kumar, R. (2005). Nitrogen-Metabolizing enzymes: Effect of Nitrogen sources and saline irrigation. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 28(6), 1089–1101. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-200058911.
Shah, F., Nie, L. X., Cui, K. H., Shah, T., Wu, W., Chen, C., Zhu, L. Y., Ali, F., Fahad, S., & Huang, J. L. (2014). Rice grain yield and component responses to near 2°C of warming. Field Crops Research, 157, 98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.12.014.
Shahid, M. A., Balal, R. M., Khan, N., Zotarelli, L., Liu, G. D., Ghazanfar, M. U., Rathinasabapathi, B., Mattson, N. S., Martínez Nicolás, J. J., & Garcia-Sanchez, F. (2018). Ploidy level of citrus rootstocks affects the carbon and nitrogen metabolism in the leaves of chromium-stressed Kinnow mandarin plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 149, 70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.02.010.
Shahid, M. A., Balal, R. M., Khan, N., Zotarelli, L., Liu, G. D., Sarkhosh, A., Fernández-Zapata, J. C., Martínez Nicolás, J. J., & Garcia-Sanchez, F. (2019). Selenium impedes cadmium and arsenic toxicity in potato by modulating carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 180, 588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.037.
Shu, S., Tang, Y. Y., Luo, J. Y., Sun, J., Yuan, Y. H., Zhong, M., & Guo, S. R. (2016). Effects of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on carbon assimilation and antioxidant metabolism of tomato leaves under sub-low temperatures and weak light stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 52(08), 1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2016.0262.
Siddiqui, N., Mostofa, M. G., Rahman, M., Kumar, D. A., Mohammed, M. U. D., Rohman, M. M., Hafiz, H. R., Ansary, M. U., & Tran, L. S. P. (2021). Glutathione improves rice tolerance to submergence: Insights into its physiological and biochemical mechanisms. Journal of Biotechnology, 325(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.11.011.
Slewinski, T. L., Meeley, R., & Braun, D. M. (2010). Sucrose transporter1 functions in phloem loading in maize leaves. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(3), 881–892. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern335.
Song, J. N., Yang, J. L., & Jeong, B. R. (2022). Root GS and NADH-GDH play important roles in enhancing the ammonium tolerance in three bedding plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031061.
Sun, F. (2019). Studies on enzyme activities of nitrogen metabolism and the content of nitrogen-containing compounds in roots of soybean varieties released at different age Master’s thesis, Jilin Agricultural University.
Sun, Y., Xu, W. J., & Fan, A. L. (2006). Effects of salicylic acid on chlorophyll fluorescence and xanthophyll cycle in cucumber leaves under high temperature and strong light. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(3), 399–400.
Verma, V., Vishal, B., Kohli, A., & Kumar, P. P. (2021). Systems-based rice improvement approaches for sustainable food and nutritional security. Plant Cell Reports, 40(11), 2021–2036. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00299-021-02790-6.
Weichert, N., Saalbach, I., Weichert, H., Kohl, S., Erban, A., Kopka, J., Hause, B., Varshney, A., Sreenivasulu, N., Strickert, M., Kumlehn, J., Weschke, W., & Weber, H. (2010). Increasing sucrose uptake capacity of wheat grains stimulates storage protein synthesis. Plant Physiology, 152(2), 698–710. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.150854.
Yang, M. W. (2002). Study on rapid determination of chlorophyll content of leaves. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-002-0022-7.
Yang, Y. (2020). Effects of increasing temperature and density on dry matter, photosynthetic fluorescence and yield Master’s thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University.
Zhang, Z. L., & Qu, W. (2003). Plant physiology laboratory instruction. Higher Education Press.
Zhang, G. M., Wang, L. M., Wang, L. Z., Song, L. Q., Zhang, Y., Q., & Xu, L. M. (2000). The effect of low temperature on chlorophyll content and growth of maize at seedling stage. Heilongjiang Agricultural Science, 1, 10–12.
Zhao, X. Q., & Shi, W. M. (2006). Expression analysis of the glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthase gene families in young rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Plant Science, 170(4), 748–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.11.006.
Zhen, F., Wang, W., Wang, H., liu, B., Zhu, Y., Liu, L., Cao, W., & Tang, L. (2019). Effects of short-term heat stress at booting stage on rice-grain quality. Crop and Pasture Science, 70(6). https://doi.org/10.1071/CP18260.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an earmarked fund for the Jilin Provincial key research and development project (20230202009NC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, K., Zhou, Y., Ma, Y. et al. Increased Rice Yield by Improving the Stay-green Traits and Related Physiological Metabolism under Long-term Warming in Cool Regions. Int. J. Plant Prod. 18, 175–186 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-024-00284-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-024-00284-5