Abstract
Objectives
To systematically investigate the capability of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) in the assessment of SS by comparisons with conventional MRI and DWI.
Methods
From retrospective data, 21 patients with SS who underwent conventional MRI, DWI and SWI sequences were selected. The number of microbleeds in the brain parenchyma and extent of the lesions identified between the three techniques were compared using one-factor analysis of variance.
Results
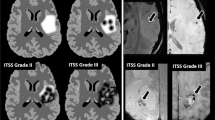
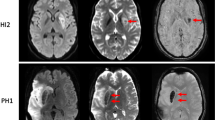
Susceptibility-weighted imaging showed excellent intra- and interobserver agreements in the assessment of SS, and also detected a larger number of SS with wider distribution in the surface of the brain and more cerebral microbleeds in brain parenchyma compared to the conventional MR sequences and DWI sequence (all p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Susceptibility-weighted imaging can provide excellent intra- and interobserver agreements and sensitive imaging biomarkers for detecting the presence of SS, especially the microbleeds in brain parenchyma, thus having the potential to improve early detection and progression monitoring of this disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fearnley JM, Stevens JM, Rudge P. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Brain. 1995;118(Pt 4):1051–66.
Kumar N. Superficial siderosis: associations and therapeutic implications. Arch Neurol. 2007;64(4):491–6. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.4.491.
Kumar N, Cohen-Gadol AA, Wright RA, Miller GM, Piepgras DG, Ahlskog JE. Superficial siderosis. Neurology. 2006;66(8):1144–52. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000208510.76323.5b.
Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(2):232–52. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1461.
Zhao H, Wang J, Lu Z, Wu Q, Lv H, Liu H, et al. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system induced by a single-episode of traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: A study using MRI-enhanced gradient echo T2 star-weighted angiography. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0116632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116632.
Koeppen AH, Michael SC, Li D, Chen Z, Cusack MJ, Gibson WM, et al. The pathology of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;116(4):371–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0421-z.
Li KW, Haroun RI, Clatterbuck RE, Murphy K, Rigamonti D. Superficial siderosis associated with multiple cavernous malformations: report of three cases. Neurosurgery. 2001;48(5):1147–50 (discussion 50-1).
Bracchi M, Savoiardo M, Triulzi F, Daniele D, Grisoli M, Bradac GB, et al. Superficial siderosis of the CNS: MR diagnosis and clinical findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993;14(1):227–36.
Kumar N. Neuroimaging in superficial siderosis: an in-depth look. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1628.
Whang JS, Kolber M, Powell DK, Libfeld E. Diffusion-weighted signal patterns of intracranial haemorrhage. Clin Radiol. 2015;70(8):909–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2015.04.006.
de Souza JM, Domingues RC, Cruz LC Jr, Domingues FS, Iasbeck T, Gasparetto EL. Susceptibility-weighted imaging for the evaluation of patients with familial cerebral cavernous malformations: a comparison with t2-weighted fast spin-echo and gradient-echo sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(1):154–8. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0748.
Hayashida Y, Kakeda S, Hiai Y, Ide S, Ogasawara A, Ooki H, et al. Diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhagic lesions: comparison between 3D-SWAN (3D T2*-weighted imaging with multi-echo acquisition) and 2D-T2*-weighted imaging. Acta Radiol. 2014;55(2):201–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185113495836.
Wang J, Gong X. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: MR findings with susceptibility-weighted imaging. Clin Imaging. 2011;35(3):217–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinimag.2010.06.003.
Agarwal A, Vijay K, Thamburaj K, Kanekar S, Kalapos P. Sensitivity of 3D gradient recalled echo susceptibility-weighted imaging technique compared to computed tomography angiography for detection of middle cerebral artery thrombus in acute stroke. Neurol Int. 2014;6(4):5521. https://doi.org/10.4081/ni.2014.5521.
Bulut HT, Sarica MA, Baykan AH. The value of susceptibility weighted magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of patients with familial cerebral cavernous angioma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):5296–302.
Wagner F, Haenggi MM, Wagner B, Weck A, Weisstanner C, Grunt S, et al. The value of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) in patients with non-neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Resuscitation. 2015;88:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.12.024.
Imaizumi T, Chiba M, Honma T, Niwa J. Detection of hemosiderin deposition by T2*-weighted MRI after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2003;34(7):1693–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000075771.88719.ce.
Linn J, Halpin A, Demaerel P, Ruhland J, Giese AD, Dichgans M, et al. Prevalence of superficial siderosis in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology. 2010;74(17):1346–50. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181dad605.
Lummel N, Bernau C, Thon N, Bochmann K, Linn J. Prevalence of superficial siderosis following singular, acute aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1480-6.
Kumar A, Aggarwal S, Willinsky R, TerBrugge KG. Posterior fossa surgery: an unusual cause of superficial siderosis. Neurosurgery. 1993;32(3):455–7 (discussion 7).
Silvera S, Oppenheim C, Touze E, Ducreux D, Page P, Domigo V, et al. Spontaneous intracerebral hematoma on diffusion-weighted images: influence of T2-shine-through and T2-blackout effects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(2):236–41.
Grisoli M, Maccagnano E, De Simone T, Savoiardo M. Superficial siderosis of the CNS: selective central myelin vulnerability and peripheral myelin sparing demonstrated by MRI. Eur J Neurol. 2007;14(5):e2–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01716.x.
Shoamanesh A, Martinez-Ramirez S, Oliveira-Filho J, Reijmer Y, Falcone GJ, Ayres A, et al. Interrelationship of superficial siderosis and microbleeds in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology. 2014;83(20):1838–43. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000000984.
Apoil M, Cogez J, Dubuc L, Bataille M, de la Sayette V, Touze E, et al. Focal cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage revealed by recurrent paresthesias: a clinico-radiological syndrome strongly associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;36(2):139–44. https://doi.org/10.1159/000353676.
Na HK, Park JH, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Kim ST, Werring DJ, et al. Cortical superficial siderosis a marker of vascular amyloid in patients with cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2015;84:1–7.
Charidimou A, Peeters A, Fox Z, Gregoire SM, Vandermeeren Y, Laloux P, et al. Spectrum of transient focal neurological episodes in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: multicentre magnetic resonance imaging cohort study and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2012;43(9):2324–30. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.112.657759.
van Rooden S, van der Grond J, van den Boom R, Haan J, Linn J, Greenberg SM, et al. Descriptive analysis of the Boston criteria applied to a Dutch-type cerebral amyloid angiopathy population. Stroke. 2009;40(9):3022–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.109.554378.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Lin for his kind proof-reading.
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant of Youth Research Project of Fujian Province Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Talent Training Project (Grant number: Fujian Health Science and Education Letter [2017] 411; contract number: 2017-1-46).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Xiao, Z., Huang, X. et al. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging in the diagnosis of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: what can it add to conventional MR imaging and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Chin J Acad Radiol 2, 63–69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-020-00022-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-020-00022-6