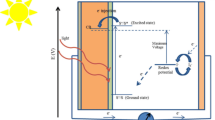
Abstract
The electrolyte additives are used in dye-sensitized solar cells to improve the photovoltaic performance of the devices, but they still remain their problems on the long-term stability of the solar cells and chemical safety. We have studied the use of two deep eutectic compounds based on choline chloride and phenol with two ratios of 1:2 and 1:3 as alternative electrolyte additives. These compounds own their advantages as eco-friendly chemicals, low cost, and simple synthesis process even at a large amount production. The two compounds, in comparison with the popular additive 4-tert-butylpyridine (4-TBP), were implemented in the functional devices which were characterized by current–voltage measurement and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Results showed that the two new additives could improve open circuit voltage values about 10–40 mV, whereas about 100 mV for 4-TBP, compared to the case without additives. Furthermore, using these new additives could result in a higher the short circuit current (Jsc) which was not observed with 4-TBP. These phenomena were explained by the shielding effects and charge transfer processes at the interfaces of electrodes and electrolyte. This study helped to design new efficient and eco-friendly additives for dye-sensitized solar cells in future scale-up production and commercialization.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’regan, B., Grätzel, M.: A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO 2 films. Nature. 353, 737–740 (1991)
Hagfeldt, A., Boschloo, G., Sun, L., Kloo, L., Pettersson, H.: Dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Rev. 110, 6595–6663 (2010)
Peter, L.M.: The gratzel cell: where next? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 1861–1867 (2011)
Nazeeruddin, M.K., Kay, A., Rodicio, I., Humphry-Baker, R., Müller, E., Liska, P., et al.: Conversion of light to electricity by cis-X2bis (2, 2’-bipyridyl-4, 4’-dicarboxylate) ruthenium (II) charge-transfer sensitizers (X= Cl-, Br-, I-, CN-, and SCN-) on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 6382–6390 (1993)
Boschloo, G., Häggman, L., Hagfeldt, A.: Quantification of the Effect of 4-tert-butylpyridine addition to I-/I 3-redox electrolytes in dye-sensitized nanostructured TiO2 solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B. 110, 13144–13150 (2006)
Kusama, H., Konishi, Y., Sugihara, H., Arakawa, H.: Influence of alkylpyridine additives in electrolyte solution on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cell. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 80, 167–179 (2003)
Phan, T.A.P., Nguyen, N.P., Nguyen, L.T., Nguyen, P.H., Le, T.K., Van, H.T., et al.: Direct experimental evidence for the adsorption of 4-tert-butylpyridine and 2,2′-bipyridine on TiO2 surface and their influence on dye-sensitized solar cells’ performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 509, 144878 (2020)
Kusama, H., Orita, H., Sugihara, H.: DFT investigation of the TiO2 band shift by nitrogen-containing heterocycle adsorption and implications on dye-sensitized solar cell performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 92, 84–87 (2008)
Zhang, C., Dai, J., Huo, Z., Pan, X., Hu, L., Kong, F., et al.: Influence of 1-methylbenzimidazole interactions with Li+ and TiO2 on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 53, 5503–5508 (2008)
Nguyen, P.T., Degn, R., Nguyen, H.T., Lund, T.: Thiocyanate ligand substitution kinetics of the solar cell dye Z-907 by 3-methoxypropionitrile and 4-tert-butylpyridine at elevated temperatures. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 93, 1939–1945 (2009)
Tuyet Nguyen, P., Rand Andersen, A., Morten Skou, E., Lund, T.: Dye stability and performances of dye-sensitized solar cells with different nitrogen additives at elevated temperatures—can sterically hindered pyridines prevent dye degradation? Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 94, 1582–1590 (2010)
Nguyen, P.T., Lam, B.X.T., Andersen, A.R., Hansen, P.E., Lund, T.: Photovoltaic performance and characteristics of dye-sensitized solar cells prepared with the n719 thermal degradation products [Ru(LH)2(NCS)(4- tert-butylpyridine)][N(Bu)4] and [Ru(LH)2(NCS)(1- methylbenzimidazole)][N(Bu)4]. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2, 2533–2539 (2011)
Lund, T., Nguyen, P.T., Tran, H.M., Pechy, P., Zakeeruddin, S.M., Grätzel, M.: Thermal stability of the DSC ruthenium dye C106 in robust electrolytes. Sol. Energy 110, 96–104 (2014)
Fabregat-Santiago, F., Bisquert, J., Palomares, E., Otero, L., Kuang, D., Zakeeruddin, S.M., et al.: Correlation between photovoltaic performance and impedance spectroscopy of dye-sensitized solar cells based on ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 6550–6560 (2007)
Jhong, H.R., Wong, D.S.H., Wan, C.C., Wang, Y.Y., Wei, T.C.: A novel deep eutectic solvent-based ionic liquid used as electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 11, 209–211 (2009)
Boldrini, C.L., Manfredi, N., Perna, F.M., Trifiletti, V., Capriati, V., Abbotto, A.: Dye-sensitized solar cells that use an aqueous choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent as effective electrolyte solution. Energy Technol. 5, 345–353 (2017)
Nguyen, P.T., Nguyen, T.-D.T., Nguyen, V.S., Dang, D.T.-X., Le, H.M., Wei, T.-C., et al.: Application of deep eutectic solvent from phenol and choline chloride in electrolyte to improve stability performance in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mol. Liq. 277, 157–62 (2019)
Abbott, A.P., Barron, J.C., Ryder, K.S., Wilson, D.: Eutectic-based ionic liquids with metal-containing anions and cations. Chem. Eur. J. 13, 6495–6501 (2007)
Smith, E.L., Abbott, A.P., Ryder, K.S.: Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 114, 11060–11082 (2014)
Vitale, P., Abbinante, V.M., Perna, F.M., Salomone, A., Cardellicchio, C., Capriati, V.: Unveiling the hidden performance of whole cells in the asymmetric bioreduction of aryl-containing ketones in aqueous deep eutectic solvents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 359, 1049–1057 (2017)
Wikene, K.O., Rukke, H.V., Bruzell, E., Tønnesen, H.H.: Investigation of the antimicrobial effect of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) as solvents in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. Biol. 171, 27–33 (2017)
Vidal, C., Merz, L., García-Álvarez, J.: Deep eutectic solvents: biorenewable reaction media for Au (I)-catalysed cycloisomerisations and one-pot tandem cycloisomerisation/Diels–Alder reactions. Green Chem. 17, 3870–3878 (2015)
Zhang, W.-H., Chen, M.-N., Hao, Y., Jiang, X., Zhou, X.-L., Zhang, Z.-H.: Choline chloride and lactic acid: a natural deep eutectic solvent for one-pot rapid construction of spiro [indoline-3, 4′-pyrazolo [3, 4-b] pyridines]. J. Mol. Liq. 278, 124–129 (2019)
Zounr, R.A., Tuzen, M., Deligonul, N., Khuhawar, M.Y.: A highly selective and sensitive ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid phase microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for determination of cadmium in food and water samples prior to electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 253, 277–283 (2018)
Carriazo, D., Serrano, M.C., Gutiérrez, M.C., Ferrer, M.L., del Monte, F.: Deep-eutectic solvents playing multiple roles in the synthesis of polymers and related materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 4996 (2012)
Nguyen, T.-D.T., Nguyen, P.T., Tran, P.H.: Dye-sensitized solar cells using deep eutectic solvents mixed with ethanol as an effective electrolyte medium. Sci. Technol. Dev. J. 21, 15–23 (2018)
Nguyen, D., Van Huynh, T., Nguyen, V.S., Doan Cao, P.-L., Nguyen, H.T., Wei, T.-C., et al.: Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as effective electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 11, 21560–21566 (2021)
Fabregat-Santiago, F., Bisquert, J., Garcia-Belmonte, G., Boschloo, G., Hagfeldt, A.: Influence of electrolyte in transport and recombination in dye-sensitized solar cells studied by impedance spectroscopy. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 87, 117–131 (2005)
Schlichthörl, G., Huang, S.Y., Sprague, J., Frank, A.J.: Band edge movement and recombination kinetics in dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells: a study by intensity modulated photovoltage spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B. 101, 8141–8155 (1997)
Adachi, M., Sakamoto, M., Jiu, J., Ogata, Y., Isoda, S.: Determination of parameters of electron transport in dye-sensitized solar cells using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B. 110, 13872–13880 (2006)
Funding
This research is funded by University of Science, VNU-HCM, under grant number HH 2021–09.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, D., Nguyen, M.T., Nguyen, T.T.D. et al. Deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and phenol as electrolyte additives in dye-sensitized solar cells: a comparison with 4-tert-butylpyridine. J Aust Ceram Soc 58, 913–921 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-022-00745-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-022-00745-y