Abstract
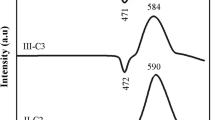
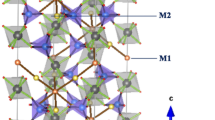
In the present study, the effect of Fe2O3/Al2O3 replacement on the crystallization characteristics of lithium aluminum phosphate glasses with a new composition of 12Li2O–(18–X) Al2O3–X Fe2O3–70 P2O5 (X = 0, 9 and 18 mol%) was investigated. The strength of glasses structure were decreased with incorporation of iron into the glass network instead of aluminum; this is evident from reduce the glass transition temperature, Tg, of the specimens. X-ray diffraction patterns evidenced the formation of Al(PO3)3, ALPO4, (Al0.5, Fe0.5)(PO3)3, and LiFe(P3O9) phases after the controlled heat-treatment process. It also showed that the Al(PO3)3 crystal structure can accept considerable amount of iron to form aluminum iron metaphosphate solid solution. A significant decrease in the grain microstructure of the glass-ceramics was observed as Al2O3 replaced by Fe2O3in the glasses. The magnetic properties of the prepared glass-ceramics were determined at the room temperature by using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The magnetic hysteresis loops of the crystallized glasses have paramagnetic behavior, and their magnetic parameters were dramatically improved by adding of Fe2O3 instead of Al2O3. The evolution of electrical properties in glass-ceramic as a function of Fe2O3/Al2O3 ratio was correlated with the type and size of the phases formed. The substitution of Al2O3 by Fe2O3 resulted in improving the conductivity of the glass-ceramics. The results gave excellent indications for use the prepared glass-ceramic as solid electrolyte materials.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, Z., Sun, H., Fu, L., Ye, F., Zhang, Y., Luo, W., et al.: Promises, challenges, and recent progress of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv. Mater. 30, 1705702 (2018)
Deubener, J., Allix, M., Davis, M., Duran, A., Höche, T., Honma, T., et al.: Updated definition of glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 501, 3–10 (2018)
Le Bourhis, E.: Glass rheology. Glass: mechanics and technology, pp. 83–134. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co KGaA, Weinheim (2008)
Holand, W., Beall, G.H.: Glass ceramic technology. Wiley (2012)
Pavić, L., Graca, M.P., Skoko, Ž., Moguš-Milanković, A., Valente, M.A.: Magnetic properties of iron phosphate glass and glass-ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 2517–2524 (2014)
Stefanovsky, S., Stefanovsky, O., Danilov, S., Kadyko, M.: Phosphate-based glasses and glass ceramics for immobilization of lanthanides and actinides. Ceram. Int. 2018,
Nitta, N., Wu, F., Lee, J.T., Yushin, G.: Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater. Today. 18, 252–264 (2015)
Cruz, A.M., Ferreira, E.B., Rodrigues, A.C.M.: Controlled crystallization and ionic conductivity of a nanostructured LiAlGePO4 glass–ceramic. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 355, 2295–2301 (2009)
Zhang, J., Luo, Z., Zhang, Y., Qin, C., Liang, H., Lu, A.: Controllable preparation and high ionic conductivity of Fe2O3-doped 46Li2O-4Al2O3-50P2O5 glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 500, 401–409 (2018)
Kun, H., Yanhang, W., Chengkui, Z., Huifeng, Z., Yonghua, L., Jiang, C., et al.: Influence of Al2O3 additions on crystallization mechanism and conductivity of Li2O–Ge2O–P2O5 glass–ceramics. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 406, 3947–3950 (2011)
Zhu, Y., Zhang, Y., Lu, L.: Influence of crystallization temperature on ionic conductivity of lithium aluminum germanium phosphate glass-ceramic. J. Power Sources. 290, 123–129 (2015)
Luo, Z., Lu, A., Liu, T., Song, J., Han, G.: La2O3 substitution in Li-Al-PON glasses for potential solid electrolytes applications. Solid State Ionics. 295, 104–110 (2016)
Mohaghegh, E., Nemati, A., Yekta, B.E., Banijamali, S.: Effects of Fe2O3 content on ionic conductivity of Li2O-TiO2-P2O5 glasses and glass-ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 190, 8–16 (2017)
Luo, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, J., Song, J., Lu, A.: La2O3-added lithium-ion conducting silicate oxynitride glasses. Solid State Ionics. 317, 76–82 (2018)
Muller, D., Berger, G., Grunze, I., Ladwig, G., Hallas, E., Haubenreisser, U.: Influence of aluminum ions on fluorescent spectra and upconversion in codoped CaF2–Al2O3–P2O5–SiO2: Ho3+ and Er3+ glass system. Phys. Chem. Glasses. 24, 37–45 (1983)
Pershina, S., Raskovalov, A., Antonov, B., Yaroslavtseva, T., Reznitskikh, O., Baklanova, Y.V., et al.: Extreme behavior of Li-ion conductivity in the Li2O–Al2O3–P2O5 glass system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 430, 64–72 (2015)
Karabulut, M., Marasinghe, G., Ray, C.S., Day, D., Waddill, G., Booth, C., et al.: An investigation of the local iron environment in iron phosphate glasses having different Fe (II) concentrations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 306, 182–192 (2002)
Reis, S., Moguš-Milanković, A., Ličina, V., Yang, J., Karabulut, M., Day, D., et al.: Iron redox equilibrium, structure and properties of zinc iron phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 353, 151–158 (2007)
Togashi, T., Honma, T., Shinozaki, K., Komatsu, T.: Electrochemical performance as cathode of lithium iron silicate, borate and phosphate glasses with different Fe2+ fractions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 436, 51–57 (2016)
Nagamine, K., Reinsch, S., Mueller, R., Honma, T., Komatsu, T.: Crystallization behavior of lithium iron phosphate glass powders in different atmospheres. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 2890–2895 (2011)
Yang RJ, Wang YH, Liu SQ. The crystallization of lithium-iron-phosphate glasses containing alkali and alkali-earth metal oxides. Key Engineering Materials: Trans Tech Publ; 2015. p. 69–72
Megahed, A.: Density of mixed alkali silicate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses. 40, 130–134 (1999)
Doweidar, H., El-Egili, K., Ramadan, R., Al-Zaibani, M.: Structural units distribution, phase separation and properties of PbO–TiO2–B2O3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 466, 37–44 (2017)
Deshkar, A., Ahmadzadeh, M., Scrimshire, A., Han, E., Bingham, P., Guillen, D., et al.: Crystallization behavior of iron-and boron-containing nepheline (Na2 O● Al2 O3● 2SiO2) based glasses: implications on the chemical durability of high-level nuclear waste glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 1101–1121 (2019)
Langlet, M., Saltzberg, M., Shannon, R.: Aluminium metaphosphate glass-ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 972–982 (1992)
Nan, Y., Lee, W.E., James, P.F.: Crystallization behavior of CaO–P2O5 glass with TiO2, SiO2, and Al2O3 additions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 1641–1647 (1992)
Holloway, J.A., Denry, I.: Effect of aluminum phosphate additions on the crystallization and bioactivity of fluororichterite glass–ceramics for biomedical applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 2941–2946 (2007)
Stefanovsky, S., Stefanovskaya, O., Vinokurov, S., Danilov, S., Myasoedov, B.: Phase composition, structure, and hydrolytic durability of glasses in the Na 2 O-Al 2 O 3-(Fe 2 O 3)-P 2 O 5 system at replacement of Al 2 O 3 by Fe 2 O 3. Radiochemistry. 57, 348–355 (2015)
Metwalli, E., Brow, R.K., Stover, F.S.: Cation effects on anion distributions in aluminophosphate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 1025–1032 (2001)
Mohaghegh, E., Nemati, A., Yekta, B.E., Banijamali, S., Rezaei, F.: Influence of Fe2O3 on non-isothermal crystallization kinetics and microstructure of lithium titanium phosphate glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 408, 130–136 (2015)
Barth, T.F.W., Barth, T.F.W.: Theoretical petrology. Wiley (1962)
Kanamura, K., Koizumi, S., Dokko, K.: Hydrothermal synthesis of LiFePO 4 as a cathode material for lithium batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 2138–2142 (2008)
Nagakane, T., Yamauchi, H., Yuki, K., Ohji, M., Sakamoto, A., Komatsu, T., et al.: Glass-ceramic LiFePO4 for lithium-ion rechargeable battery. Solid State Ionics. 206, 78–83 (2012)
Liu, S., Yang, R., Wang, Y.: Effects of the substitution of P2O5 with B2O3 on the structure, iron valence, thermal and crystallization behavior of lithium-iron-phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 453, 158–163 (2016)
Ji, P., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Li, B., Zhang, G.: P2O5-Fe2O3-CaO-SiO2 ferromagnetic glass-ceramics for hyperthermia. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 15, 1261–1267 (2018)
Nayak, M.T., Desa, J.E., Babu, P.: Magnetic and spectroscopic studies of an iron lithium calcium silicate glass and ceramic. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 484, 1–7 (2018)
Bretcanu, O., Verné, E., Cöisson, M., Tiberto, P., Allia, P.: Magnetic properties of the ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics for hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305, 529–533 (2006)
Abo-Naf, S., Abdel-Hameed, S., Marzouk, M., Elwan, R.: Sol–gel synthesis, paramagnetism, photoluminescence and optical properties of Gd-doped and Bi–Gd-codoped hybrid organo-silica glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 2363–2373 (2015)
Marzouk, M., Abdel-Hameed, S.: Development and characterization of magnetic glass-ceramic: correlation between phosphate and borate matrices and 5-fluorouracil delivery. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 38, 107–115 (2017)
Salman, S., Salama, S., Abo-Mosallam, H.: The effect of aluminum and germanium oxides on the crystallization process and magnetic properties of Li2O–Fe2O3–SiO2 glass system. Ceram. Int. 41, 1521–1529 (2015)
Salman, S., Salama, S., Abo-Mosallam, H.: Contribution of some divalent oxides replacing Li2O to crystallization characteristics and properties of magnetic glass–ceramics based on Li2O–Fe2O3–Al2O3–SiO2. Ceram Int. 42, 8650–8656 (2016)
Liao, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, D., Li, Y., Su, H., Li, J., et al.: Magnetic properties of low temperature sintered LiZn ferrites by using Bi2O3-Li2CO3-CaO-SnO2-B2O3 glass as sintering agent. Ceram. Int. 44, 5513–5517 (2018)
Zaitsev, D.D., Kazin, P.E., Gravchikova, E.A., Trusov, L.A., Kushnir, S.E., Tretyakov, Y.D., et al.: Synthesis of magnetic glass ceramics containing fine SrFe12O19 particles. Mendeleev Commun. 14, 171–173 (2004)
Kosova, N., Osintsev, D., Uvarov, N., Devyatkina, E.: Lithium titanium phosphate as cathode, anode and electrolyte for Lithium rechargeable batteries. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 13, 253–260 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abo-Mosallam, H.A., Farag, M.M. Preparation, crystallization features and electro-magnetic properties of phosphate based glass-ceramics as solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries. J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 353–361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00406-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00406-7