Abstract
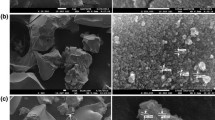
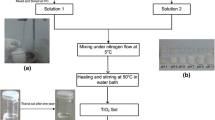
Nanocrystalline anatase titania particles were synthesized by low-temperature aqueous sol-gel transformations from new types of precursors [Ti{OPri}4] (A), [{acac}2Ti{OPri}{ONC9H6}] (1), and [{acac}2Ti{ONC9H6}2] (2) {where, ONC9H6 = 8-hydroxyquinoline}. Formation of all the precursors was confirmed by elemental analysis, molecular weight measurements, FTIR, and NMR (1H and 13C). Titania samples (a), (b), and (c) were formed by aqueous sol-gel transformations of (A), (1), and (2), respectively. The resulting nano-materials were characterized using XRD, TEM, SEM, EDX, SAED, FTIR, and UV-Visible spectroscopic techniques. From the X-ray pattern, the phase purity of the synthesized powders was confirmed as anatase TiO2. Crystallite size of all the oxide samples was measured by XRD and TEM, found to be 26 nm (a), 11 nm (b), and 8 nm (c). Surface morphologies of all the samples were evaluated by SEM. Selected area diffraction (SAED) of (b) and (c) are also corroborated the XRD results. The absorption spectra of oxide samples, (a), (b), and (c) show energy band gap of 2.9 eV, 3 eV, and 3.1 eV, respectively. SAED-EDX analysis confirmed the formation of pure anatase-phase titania nanoparticles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, R., Elzatahry, A.A., Al-Deyab, S.S., Zhao, D.: Nano Today. 7, 344 (2012)
Bai, J., Zhou, B.: Chem. Rev. 114, 10131 (2014)
Maziarz, W., Kusior, A., Trenczek-Zajac, A.: Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 7, 1718 (2016)
Pagliaro, M., Palmisano, G., Ciriminna, R., Loddo, V.: Energy Environ. Sci. 2, 838 (2009)
Rehman, F.U., Zhao, C., Jiang, H., Wang, X.: Biomater. Sci. 4, 40 (2016)
Kisch, H., Burgeth, G., Macyk, W.: Adv. Inorg. Chem. 56, 241 (2004)
Hanaor, D.A.H., Sorrell, C.C.: J. Mater. Sci. 46, 855 (2011)
Schubert, U.: Acc. Chem. Res. 40, 730 (2007)
Niederberger, M.: Acc. Chem. Res. 40, 793 (2007)
Rehan, M., Lai, X., Kale, G.M.: CrystEngComm. 13, 3725 (2011)
Gegova, R., Dimitriev, Y., Bachvarova-Nedelcheva, A., Iordanova, R., Loukanov, A., Iliev, T.: J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 48(2), 147 (2013)
Colmenares, J.C., Kuna, E., Lisowski, P.: Top. Curr. Chem. (Z). 59, 374 (2016)
Ding, S., Yin, X., Lü, X., Wang, Y., Huang, F., Wan, D.: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4, 306 (2012)
Yao, H., Fan, M., Wang, Y., Luo, G., Fei, W.: J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 17511 (2015)
Sakka, S. (ed.): Handbook of sol-gel science and technology: characterization and properties of sol-gel materials and products. Springer, Basel (2005)
Kessler, V.G., Spijksma, G.I., Seisenbaeva, G.A., Hakansson, S., Blank, D.H.A., Bouwmeester, H.J.M. J. Sol-gel Sci Technol 40, 163 (2006)
Schubert, U.: J. Mater. Chem. 15, 3701 (2005)
Chaudhary, A., Dhayal, V., Nagar, M., Bohra, R., Mobin, S.M., Mathur, P.: Polyhedron. 30, 821 (2011)
Olevsky, E.A., Bordia, R. (eds.): Advances in sintering science and technology, p. 211. John Wiley & Sons, Noida, India (2010)
Basu, B., Balani, K. (eds.): Advanced structural ceramics. Ceramic Transactions 209. John Wiley & Sons, La Jolla, California (2011)
Dhayal, V., Chaudhary, A., Choudhary, B.L., Nagar, M., Bohra, R., Mobin, S.M., Mathur, P.: Dalton Trans. 41, 9439 (2012)
Livage, J., Henry, M., Sanchez, C.: Prog. Solid State Chem. 18, 259 (1988)
Hench, L.L., West, J.K.: Chem. Rev. 90, 33 (1990)
Bradley, D.C., Mehrotra, R.C., Rothwell, I.P., Singh, A. (eds.): Alkoxo and aryloxo derivatives of metals. Academic Press, London (2001)
Sanwaria, A.R., Sharma, N., Chaudhary, A., Nagar, M.: J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 68, 245 (2013)
Gopal, R., Jain, J., Goyal, A., Gupta, D.K., Nagar, M.:Formation of nano-sized cubic zirconia by aqueous sol–gel route, J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0198-z
Vogel, A.I.: A text book of quantitative inorganic analysis, fifth edn. Longman, London (1989)
Bradley, D.C., Hancock, D.C., Wardlaw, W.: Titanium chloride alkoxides, J. Chem. Soc. 2773, (1952). https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9520002773
Puri, D.M., Pande, K.C., Mehrotra, R.C.: J. Less-Common Met. 4, 393 (1962)
Bradley, D.C., Abd-el-Halim, F.M., Mehrotra, R.C., Wardlaw, W.: J. Chem. Soc. 4609-4612, (1952). https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9520004609
Pathak, M., Bohra, R., Mehrotra, R.C.: Transit. Met. Chem. 28, 187 (2003)
Tong, X., Yang, P., Wang, Y., Qin, Y., Guo, X.: Nanoscale. 6, 6692 (2014)
Warren, B.E.: X-ray diffraction (Chapter 13). Dover Publication, New York (1990) (eds)
Tauc, J.: Amorphous & liquid semiconductors. Plenum, New York (1974)
Wilson, W.L., Szajowski, P.J., Brus, L.E.: Science. 262, 1242 (1993)
Acknowledgements
We are highly thankful to the Material Research Centre, MNIT, Jaipur, for providing facilities of Powder X-ray Diffraction, TEM, SEM, and EDX.
Funding
This study was financially supported by MHRD, Government of India, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, T., Gopal, R., Goyal, A. et al. Formation and optical properties of pure nano-sized anatase titania by low-temperature aqueous sol-gel route. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 689–695 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0278-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0278-0