Abstract
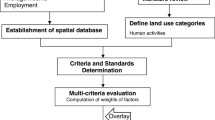
Land use changes significantly affect the sustainability of food security, environmental quality and the ecological balance in developing countries. Bangladesh is one such country, and it faces challenges caused by its limited resources of arable land. The urbanization of agricultural lands and urban developments in suburban areas add to these challenges. Therefore, the aim of this study is to characterize the land use changes that occur over time in suburban areas that have potential for industrial growth. This study also assesses potential locations for industrial development by using land suitability analysis (LSA) to emphasize both agricultural and industrial development in terms of sustainable growth. A geographical information system (GIS)-based multi-criteria analysis (MCA) model is developed for the LSA to distinguish compact parcels that are suitable for industrial economic zones. Nine criteria, including seven constraints and 23 factors, are evaluated using the spatial analysis tools in ArcGIS®. An analytical hierarchy process (AHP) is applied to prioritize these criteria based on experts opinion for the decision-making process of LSA. This study finds that the construction of densely clustered industrial areas has decreased the area of agricultural land by more than 10% in the last two decades. Furthermore, the results of the LSA show that only 4% of the land was highly suitable for industrial sites. On the other hand, four compact parcels that contain 16–10 ha of land and suitable for small industrial zones exist within the study area. Thus, the integrated GIS-MCA model can serve as a policy and planning tool for locating industrial economic zones while preserving agricultural lands and retaining environmental protections.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam AA, Asad R, Kabir ME (2016) Rural settlements dynamics and the prospects of densification strategy in rural Bangladesh. SpringerPlus 5(1):254
Anurag O, Prabhat KS, Priyanka KS (2010) Spatial multi criteria analysis for siting industries. Int J Ind Eng Res Dev (IJIERD) 1(1):94–114
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) (2011) Population & Housing Census, Community Report 2011
Bangladesh Ministry of Environment and Forests (2012) Bangladesh Rio +20: National Report on Sustainable Development, May 2012
Beinat E, Nijkamp P (eds) (1998) Multi-criteria analysis for land-use management, vol 9. Springer, Berlin
Belton V, Gear T (1982) On a shortcoming of Saaty’s method of analytic hierarchies. Omega 11(3):226–230
Bhushan N, Rai K (2004) Strategic decision making: applying the analytic hierarchy process. Springer, New York, p 172
Chandio IA, Matori AN, Lawal DU, Sabri S (2011) GIS-based land suitability analysis using AHP for public parks planning in Larkana City. Mod Appl Sci 5(4):177
Chandio IA, Matori ANB, WanYusof KB, Talpur MAH, Balogun AL, Lawal DU (2013) GIS-based analytic hierarchy process as a multi-criteria decision analysis instrument: a review. Arab J Geosci 6(8):3059–3066
Collins MG, Steiner FR, Rushman MJ (2001) Land-use suitability analysis in the United States: historical development and promising technological achievements. Environ Manag 28(5):611–621
Duc TT (2006) Using GIS and AHP technique for land-use suitability analysis. In: International symposium on geoinformatics for spatial infrastructure development in earth and allied sciences, pp 1–6
Eastman JR, Jin W, Keym PAK, Toledano J (1995) Raster procedures for multi-criteria/multi-objective decisions. Photogramm Eng Rem Sens 61(5):539–547
Edrahim F, Mehdi A, Habib F, Ali Md (2015) Industrial state site selection using MCDM method and GIS in Germi, Ardabil, IRAN. J Ind Intell Inf 3(4):324–329
Eldin N, Sui DA (2003) COM-based spatial decision support system for industrial site selection. J Geogr Inf Decis Anal 7(2):72–92
Eldrandaly KA, Eldin N, Sui DZ, Shouman MA, Nawara G (2005) Integrating GIS and MCDM Using COM technology. Int Arab J Inf Technol 2(2):162–167
Ferretti V, Pomarico S (2012) Integrated sustainability assessments: a spatial multicriteria evaluation for siting a waste incinerator plant in the Province of Torino (Italy). Environ Dev Sustain 14(5):843–867
Ferretti V, Pomarico S (2013) An integrated approach for studying the land suitability for ecological corridors through spatial multicriteria evaluations. Environ Dev Sustain 15(3):859–885
Hasan MN, Hossain MS, Bari MA, Islam MR (2013) Agricultural land availability in Bangladesh. SRDI, Dhaka, p 42
Hassan MM, Nazem MNI (2016) Examination of land use/land cover changes, urban growth dynamics, and environmental sustainability in Chittagong city, Bangladesh. Environ Dev Sustain 18(3):697–716
Hossain MS, Chowdhury SR, Das NG, Sharifuzzaman SM, Sultana A (2009) Integration of GIS and multicriteria decision analysis for urban aquaculture development in Bangladesh. Landsc Urban Plann 90(3):119–133
Ishizaka A, Labib A (2011) Review of the main developments in the analytic hierarchy process. Expert Syst Appl 38(11):14336–14345
Karim M (2015) Draft laws to protect agricultural land: tough actions proposed against violators. The Daily Observer. http://www.observerbd.com/2015/03/27/80268.php. Accessed 21 May 2017
LANDac (2016) Food security and land governance facrsheet: Bangladesh. http://www.landgovernance.org/resources/bangladesh-factsheet-2012/. Accessed 20 May 2017
Malczewski J (2004) GIS-based land-use suitability analysis: a critical overview. Progress Plann 62(1):3–65
Oguzitimur S (2011) Why fuzzy analytic hierarchy process approach for transport problems? In: European Regional Science Association ERSA Conference Papers. ERSA11, Vienna, p 438
Planning Commission (2009) Steps towards change-national strategy for accelerated poverty reduction II (Revised). FY 2009-11. Government Peoples Republic of Bangladesh, Dhaka
Quasem M (2011) Conversion of agricultural land to non-agricultural uses in Bangladesh: extent and determinants. Bangladesh Dev Stud 34(1):59–85
Rahman MT, Hasan MN (2003) Assessment of shifting of agricultural land to non-agricultural land in Bangladesh, SRDI, Ministry of Agriculture, Dhaka
Ramcharan EK, Dey PK (2005) The role of environmental factors in industrial site selection activities: a case of limestone quarry expansion in Barbados, West Indies. Impact Assess Proj Apprais 23(2):147–154. doi:10.3152/147154605781765670
Rashid MS (2003) A study of land transformation in Savar Upazila, Bangladesh, 1915–2001: an integrated approach using remote sensing, census, map and field data, Durham theses, Durham University
Rikalovic A, Cosic I, Lazarevic D (2014) GIS based multi-criteria analysis for industrial site selection. Procedia Eng 69:1054–1063
Rikalovic A, Cosic I, Labati RD, Piuri V (2015) A comprehensive method for industrial site selection: the macro-location analysis. IEEE Syst J PP(99):1–10. doi:10.1109/JSYST.2015.2444471
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty TL (1987a) Decision making, new information, ranking and structure. Math Model 8:125–132
Saaty RW (1987b) The analytic hierarchy process—what it is and how it is used. Math Modell 9(3):161–176
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26
Saaty TL, Vargas LG (1984) The legitimacy of rank reversal. Omega 12(5):513–516
Saleh A, Biswajeet P, Shattri M, Abdul Rashid Mohamed S (2015) GIS-based modeling for the spatial measurement and evaluation of mixed land use development for a compact city. GISci Rem Sens 52(1):18–39
Sharif MS, Esa AJ (2014) Dynamics of land price and land use change: a case of Savar Municipality, Bangladesh. J South Asian Stud 2(1):83–89
Shin YB, Lee S, Chun SG, Chung D (2013) A critical review of popular multi-criteria decision making methodologies. Issues Inf Syst 14(1):358–365
The Bangladesh Economic Zones Act (Act No.42) (2010). http://www.beza.gov.bd/investing-in-zones/legal-frameworks/bangladesh-ez-act2010/. Accessed 8 Apr 2017
Tong C, Hall CA, Wang H (2003) Land use change in rice, wheat and maize production in China (1961–1998). Agr Ecosyst Environ 95(2):523–536
Wang YM, Elhag TM (2006) An approach to avoiding rank reversal in AHP. Decis Support Syst 42(3):1474–1480
Wang YM, Luo Y (2009) On rank reversal in decision analysis. Math Comput Model 49(5):1221–1229
Worall L (ed) (1991) Spatial analysis and spatial policy using geographic information system. Belhaven Press, London
World Bank (2015) Population Density Report, http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.POP.DNST. Accessed 6 Jun 2017
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the University of Tsukuba to support this research to develop the multi-criteria modeling for land suitability analysis in Bangladesh. We also express our sincere thanks to the Local Government and Engineering Division (LGED), Detailed Area Plan (DAP) RAJUK, Department of Agriculture (Savar), Institute of Water Modeling (IWM), Bangladesh Garment Manufacturing and Exporters Associations (BGMEA) for their cordial cooperation during field work and survey. We also express our gratitude to MEXT-Super Global Program for providing scholarship to carry out research and education in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Muhsin, N., Ahamed, T. & Noguchi, R. GIS-based multi-criteria analysis modeling used to locate suitable sites for industries in suburban areas in Bangladesh to ensure the sustainability of agricultural lands. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci 2, 35–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-017-0046-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-017-0046-0