Abstract
Purpose
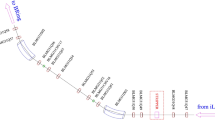
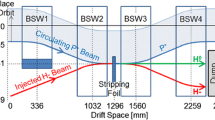
The China Spallation Neutron Source (CSNS) accelerator consists of an 80 MeV H− Linac and a 1.6 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS). For the injection system, the H− stripping scheme is adopted to inject the Linac beam to the RCS with high precision and high efficiency. The stripping process through foil plays an important role in the injection, and the related beam losses control need to be studied in detail.
Methods
In the beam commissioning, the parameters of the stripping foil have been studied, including: structure, material, thickness, stripping efficiency, temperature, and lifetime. The measurement results are compared with the design values and some parameters of the stripping foil are optimized. With a combination of the codes Py-ORBIT and FLUKA, the beam losses caused by the foil scattering and residual H− beam are simulated in detail and then compared with the actual measurement results.
Results
A double-layer HBC foil is instead of a single-layer DLC foil. With an actual thickness of 103 µg/cm2, the actual stripping efficiency is about 99.8%. The peak temperature of the main stripping foil is about 1400 K in the simulation. The foil lifetime under the design power is about 1.5 months. The beam losses caused by the foil scattering and residual H− beam are the main sources of the residual doses in the injection region.
Conclusion
The parameters of the stripping foil have been optimized and some improvements are proposed. The simulation results of the beam losses caused by the foil scattering and residual H− beam are nearly consistent with the measurement results which can provide some references for the CSNS-II.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wei, H.S. Chen, Y.W. Chen et al., China spallation neutron source: design, R&D, and outlook. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 600, 10–13 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2008.11.017
J. Wei, Synchrotrons and accumulators for high-intensity proton beams. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 1383–1432 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.1383
S. Wang, S.X. Fang, S.N. Fu et al., Introduction to the overall physics design of CSNS accelerators. Chin. Phys. C 33(S-II), 1–3 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1137/33/S2/001
J. Wei, S.N. Fu, J.Y. Tang et al., China Spallation Neutron Source: an overview of application prospects. Chin. Phys. C 33(11), 1033–1042 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1137/33/11/021
M.Y. Huang, S. Wang, J. Qiu, N. Wang, S.Y. Xu, Effects of injection beam parameters and foil scattering for CSNS/RCS. Chin. Phys. C 37(6), 067001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1137/37/6/067001
X.H. Lu, M.Y. Huang, S. Wang, Injection orbit matching for a rapid cycling synchrotron. Phys. Rev. Acceler. Beams 21, 062802 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.062802
M.Y. Huang, S.Y. Xu, X.H. Lu, S. Wang, Study on injection beam loss for China Spallation Neutron Source accelerator. Atom. Energy Sci. Technol. 53(9), 1708–1714 (2019). https://doi.org/10.7538/yzk.2019.53.09.1708 (in Chinese)
A.I. Drozhdin, I.L. Rakhno, S.I. Striganov, L.G. Vorobiev, Modeling multiturn stripping injection and foil heating for high intensity proton drivers. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Acceler. Beams 15, 011002 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.15.011002
M.Y. Huang, N. Wang, J. Qiu, S. Wang, N. Huang, Study of beam loss due to particle scattering in CSNS/RCS. Atom. Energy Sci. Technol. 46(S), 530–533 (2012)
W. Chou, M. Kostin, Z. Tang, Stripping efficiency and lifetime of carbon foils. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 590, 1–12 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2008.02.060
N.R.S. Tait, D.W.L. Tolfree, B.H. Armitage, D.S. Whitmell, New techniques for preparation of long lived carbon strippers under heavy ion bombardment. Nucl. Inst. Methods 167, 21–24 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(79)90469-5
N.R.S. Tait, D.W.L. Tolfree, D.S. Whitmell, B.H. Armitage, The behavior and physical characteristics of carbon stripper foils prepared by different methods. Nucl. Inst. Methods 163, 1–14 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(79)90027-2
M.A. Plum, S.M. Cousineau, J. Galambos et al., Stripper foil failure modes and cures at Osk Ridge Spallation Neutron Source. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Acceler. Beams 14, 030102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.14.030102
M.S. Gulley, P.B. Keating, H.C. Bryant et al., Measurement of H-, H0, and H+ yields produced by foil stripping of 800-MeV H- ions. Phys. Rev. A 53, 3201–3210 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.53.3201
R.C. Webber, C. Hojvat, Measurement of the electron loss cross sections for negative hydrogen ions on carbon at 200 MeV. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 26(3), 4012–4014 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.1979.4330681
J.X. Chen, J.B. Yu, L. Kang et al., Stripper foil installation and aerodynamics analysis. High Power Laser Particle Beams 30(2), 025101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.11884/HPLPB201830.170114 (in Chinese)
I. Sugai, A. Takagi, Y. Takeda et al., Performance characteristics of HBC stripper foils irradiated by 650 keV H- and high intensity DC ion beams. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. B 328, 70–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2014.03.002
I. Sugai, Y. Takeda, M. Oyaizu et al., Development of thick hybrid-type carbon stripper foils with high durability at 1800K for RCS of J-PARC. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 561, 16–23 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2005.12.225
Y. Yamazaki, M. Yoshimoto, P.K. Saha et al., Analyses and the effect of impurities contained in charge stripper foils for the 3-GeV RCS of J-PARC. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 305, 859–864 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4106-5
M. Yoshimoto, Y. Yamazaki, T. Nakanoya et al., Progress status in fabrication of HBC stripper foil for 3-GeV RCS at J-PARC in Tokai site. EPJ Web Conf. 229, 01001 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/202022901001
W. Blokland, N. Evans, C. Luck et al., Injection foil temperature measurements at the SNS accelerator, in Proceedings of 61st ICFA advanced beam dynamics workshop (HB2018), Daejeon, Korea (2018), pp. 104–109. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-HB2018-TUP2WE01
P.K. Saha, M. Yoshimoto, S. Hatakeyama et al., First measurement and online monitoring of the stripper foil thinning and pinhole formation to achieve a longer foil lifetime in high-intensity accelerators. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 082801 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.082801
I. Sugai, Y. Takeda, M. Oyaizu et al., Development of hybrid type carbon stripper foils with high durability against 1800k for RCS of J-PARC, in Proceedings of PAC07, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA (2007), pp. 242–244. https://doi.org/10.1109/PAC.2007.4440172
S.G. Lebedev, A.S. Lebedev, Calculation of the lifetimes of thin stripper targets under bombardment of intense pulsed ions. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Acceler. Beams 11, 020401 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.11.020401
S.A. Miller, C.S. Jolivet, J.O. Stoner Jr. et al., New methods for testing cyclotron carbon stripper foils. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 590, 57–65 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2008.02.068
H. Hotchi, H. Harada, N. Hayashi et al., Beam commissioning and operation of the Japan proton accelerator research complex 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2012(1), 02B003 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1093/ptep/pts021
M.Y. Huang, S.Y. Xu, Y.W. An et al., Study on the anti-correlated painting injection scheme for the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron of the China Spallation Neutron Source. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 1007, 165408 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2021.165408
S.Y. Xu, H. Liu, J. Peng et al., Beam commissioning and beam loss control for CSNS accelerators. J. Instrum. 15, P07023 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/15/07/P07023
J. Gabambos, S. Danilov, D. Jeon et al., ORBIT-A ring injection code with space charge, in Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, New York, USA (1999), pp. 3143–3145. https://doi.org/10.1109/PAC.1999.792230
J.F. Ostiguy and J. Holmes, PyORBIT: a Python shell for ORBIT, in Proceedings of the 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference, Portland, USA (2003), pp. 3503–3505. https://doi.org/10.1109/PAC.2003.1289962
A. Shishlo, S. Cousineau, J. Holmes, T. Gorlov, The particle accelerator simulation code PyORBIT. Procedia Comput. Sci. 51, 1272–1281 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.05.312
F. Ballarini, G. Battistoni, M. Brugger et al., The physics of the FLUKA code: recent developments. Adv. Space Res. 40, 1339–1349 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.05.031
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Y.L. Zhang, L. Kang and other CSNS colleagues for helpful discussions. This work is jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 12075134 and U1832210) and the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Project No. 2021B1515120021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, MY., Xu, S., Chen, J. et al. Study on the H− stripping injection for the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron of the China Spallation Neutron Source. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 6, 201–208 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-022-00326-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-022-00326-4