Abstract
Purpose
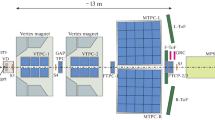
With the aim of determining mass yield distributions of primary fission products, a one-arm spectrometer was developed based on kinetic energy and time-of-flight correlation measurement technique.
Methods
An axial grid ionization chamber (GIC) was designed for energy detecting. In order to minimize energy losses and straggling, a thin silicon nitride film with a thickness of 100 nm was performed as the entrance window of the GIC. The energy resolution is 0.38% for 80 MeV 63Cu particles. Two-timing detectors based on the detection of secondary emission electrons by microchannel plates (MCPs) constitute the time pick-off system, and the time-of-flight resolution is better than 200 ps (FWHM) measured with a 241Am α source. With a flight path length of 47.6 cm, the path length resolution is 0.21%.
Results and conclusion
The first result of mass distribution from 252Cf spontaneous fission was reported. Energy losses of fragments in dead layers of the spectrometer were corrected event-by-event depend on the Monte Carlo calculation. The mass resolution for light fission fragments peak A = 107 amu is 1.3 aum.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
A.C. Wahl, A.E. Norris, R.A. Rouse et al., Products from thermal-neutron induce fission of 235U: a correlation of radiochemical charge and mass distribution data. Washington Univ., St. Louis, Mo. 1970. https://doi.org/10.2172/4185169
L. Toppare, H.N. Erten, N.K. Aras, Yields of products in the spontaneous fission of 252Cf by direct γ-ray spectroscopy. Can. J. Chem. 61(4), 649–651 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1139/v83-119
E. Moll, H. Schrader, G. Siegert et al., Analysis of 236U-fission products by the recoil separator “Lohengrin.” Nucl. Instrum. Methods 123(3), 615–617 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(75)90219-0
C. Budtz-Jørgensen, H.H. Knitter, C. Straede et al., A twin ionization chamber for fission fragment detection. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 258(2), 209–220 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9002(87)90058-1
H.W. Schmitt, W.E. Kiker, C.W. Williams, Precision measurements of correlated energies and velocities of 252Cf fission fragments. Phys. Rev 137(4B), B837 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.137.B837
H. Henschel, A. Kohnle, H. Hipp et al., Absolute measurement of velocities, masses and energies of fission fragments from californium-252 (SF). Nucl. Instrum. Methods 190(1), 125–134 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(81)90213-5
N. Boucheneb, P. Geltenbort, M. Asghar et al., High resolution measurements of mass, energy and nuclear charge correlations for 229Th (nth, f) with the cosi fan tutte spectrometer. Nucl. Phys. A 502, 261–270 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9474(89)90666-0
M. Asghar, N. Boucheneb, G. Medkour et al., Measurement of cold fission for 229Th (nth, f), 232U (nth, f) and 239Pu (nth, f) with the Cosi fan tutte spectrometer. Nucl. Phys. A 560(2), 677–688 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9474(93)90040-5
P. Schillebeeckx, C. Wagemans, P. Geltenbort et al., Investigation of mass, charge and energy of 241Pu (nth, f) fragments with the Cosi-Fan-Tutte spectrometer. Nucl. Phys. A 580(1), 15–32 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9474(94)90812-5
K. Meierbachtol, F. Tovesson, D. Shields et al., The SPIDER fission fragment spectrometer for fission product yield measurements. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 788, 59–66 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2015.02.032
J. Matarranz, I. Tsekhanovich, A.G. Smith et al., A multiparameter nuclear-fission experiment: can all be obtained at once? Phys. Procedia. 47, 76–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2013.06.012
M.O. Frégeau, S. Oberstedt, T. Gamboni et al., First results from the new double velocity-double energy spectrometer VERDI. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 817, 35–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2016.02.011
D. Doré, F. Farget, F.R. Lecolley et al., Falstaff: A new tool for fission fragment characterization. Nucl. Data Sheets. 119, 346–348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nds.2014.08.095
O. Bunemann, T.E. Cranshaw, J.A. Harvey, Design of grid ionization chambers. Can. J. Res. 27(5), 191–206 (1949). https://doi.org/10.1139/cjr49a-019
F.J. Hambsch, J. Van Aarle, R. Vogt, Is there a pulse height defect for methane? Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 361(1–2), 257–262 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9002(95)00190-5
G. Simon, J. Trochon, F. Brisard et al., Pulse height defect in an ionization chamber investigated by cold fission measurements. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 286(1–2), 220–229 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9002(90)90224-T
P. Grabitz, V. Andrianov, S. Bishop et al., Determination of nuclear charge distributions of fission fragments from 235U(nth, f) with calorimetric low temperature detectors. J. Low Temp. Phys. 184(3–4), 944–951 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-016-1566-0
A.E.D. Heylen, Ionization coefficients and sparking voltages from methane to butane. Int. J. Electron. 39(6), 653–660 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207217508920532
H. Schindler, R. Veenhof, Garfield++—simulation of ionisation based tracking detectors (2018). http://garfieldpp.web.cern.ch/garfieldpp.
S. Agostinelli, J. Allison, K. Amako et al., GEANT4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 506(3), 250–303 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01368-8
H.L. Adair, P.R. Kuehn, Preparation of 252Cf neutron and fission-fragment sources. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 114(2), 327–332 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(74)90551-5
J.D. Bowman, R.H. Heffner, A novel zero time detector for heavy ion spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 148(3), 503–509 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(78)91032-7
F. Busch, W. Pfeffer, B. Kohlmeyer et al., A position-sensitive transmission time detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 171(1), 71–74 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(80)90011-7
W. Starzecki, A.M. Stefanini, S. Lunardi et al., A compact time-zero detector for mass identification of heavy ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 193(3), 499–505 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(82)90242-7
K.E. Pferdekämper, H.G. Clerc, Energy spectra of secondary electrons ejected by ions from foils. Z Physik A 280, 155–164 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01409544
C.D. Coryell, M. Kaplan, R.D. Fink, Search for correlations of most probable nuclear charge ZP of primary fission fragments with composition and excitation energy. Can. J. Chem. 39(3), 646–663 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1139/v61-078
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11790322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Liu, S. & Yang, Y. Construction of high-resolution energy—time-of-flight spectrometer for determination of fission fragment mass distributions. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 6, 102–110 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-021-00303-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-021-00303-3