Abstract
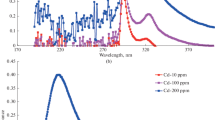
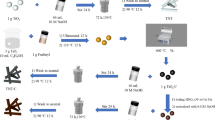
In this paper, a novel material for Co(II) adsorption, titanate sodium nanotubes (Na2Ti2O5-NTs) were synthesized and characterized, and then they were used to remove Co(II) from aqueous solution and compared with titanic acid nanotubes (H2Ti2O5-NTs) and potassium hexatitanate whiskers (K2Ti6O13). The results showed that the adsorption of Co(II) on the materials was dependent on pH values and was a spontaneous, endothermic process. Specifically, Na2Ti2O5-NTs exhibited much more efficient ability to adsorb Co(II) from aqueous solution, with the maximum adsorption capacity of 85.25 mg/g. Furthermore, Na2Ti2O5-NTs could selectively adsorb Co(II) from aqueous solution containing coexisting ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+). The results suggested that Na2Ti2O5-NTs were potential effective adsorbents for removal of Co(II) or cobalt-60 from wastewater.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Hernández-Barrales, F. Granados-Correa, Sorption of radioactive cobalt in natural Mexican clinoptilolite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (1999). doi:10.1007/BF02345901
J.S. Kim, M.A. Keane, The removal of iron and cobalt from aqueous solutions by ion exchange with Na-Y zeolite: batch, semi-batch and continuous operation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. (2002). doi:10.1002/jctb.618
S. Rengaraj, S.H. Moon, Kinetics of adsorption of Co (II) removal from water and wastewater by ion exchange resins. Water Res. (2002). doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00380-3
B. Ma, S. Oh, W.S. Shin et al., Removal of Co2 + , Sr2 + and Cs + from aqueous solution by phosphate-modified montmorillonite (PMM). Desalination (2011). doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.072
P.H. Tewari, A.B. Campbell, W. Lee, Adsorption of Co2 + by oxides from aqueous solution. Can. J. Chem. (1972). doi:10.1139/v72-263
A. Malekpour, M. Edrisi, S. Hajialigol et al., Solid phase extraction–inductively coupled plasma spectrometry for adsorption of Co (II) and Ni (II) from radioactive wastewaters by natural and modified zeolites. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1013-2
M.Y. He, Y. Zhu, Y. Yang et al., Adsorption of cobalt (II) ions from aqueous solutions by palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.clay.2011.09.013
Y.V. Hete, S.B. Gholase, R.U. Khope, Adsorption study of cobalt on treated granular activated carbon. J. Chem. (2012). doi:10.1155/2012/472517
F. Granados-Correa, S. Bulbulian, Co (II) adsorption in aqueous media by a synthetic Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1175-8
S. Wang, L.Q. Tan, J.L. Jiang et al., Preparation and characterization of nanosized TiO2 powder as an inorganic adsorbent for aqueous radionuclide Co (II) ions. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10967-012-2296-7
D. Gogoi, A.G. Shanmugamani, S.V.S. Rao et al., Studies on adsorptive removal of radioactive cobalt from alkaline waste generated in sodium cooled fast breeder reactors. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10967-012-2291-z
Z.J. Liu, L. Chen, Z.C. Zhang et al., Synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotube–hydroxyapatite composites and its application in the sorption of Co (II) from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2012.12.011
K.R. Kim, K.J. Lee, J.H. Bae, Characteristics of Cobalt Adsorption on Prepared TiO2 and Fe-Ti-O Adsorbents in High Temperature Water. Sep. Sci. Technol. (1995). doi:10.1080/01496399508015410
W.Z. Xu, S.T. Chen, C.X. Li et al., Study on the adsorption behavior of potassium hexatitanate whisker to cobalt. Metall. Anal. (2009). doi:10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2009.06.007
S. Thennarasu, K. Rajasekar, K.B. Ameen, Hydrothermal temperature as a morphological control factor: preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of titanate nanotubes and nanoribbons. J. Mol. Struct. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.06.064
Z.H. Li, Z.Q. Liu, Q.Z. Yan et al., Preparation and performance of titanate nanotube by hydrothermal treatment. Rare Metals (2008). doi:10.1016/S1001-0521(08)60112-6
S. Sreekantan, L.C. Wei, Study on the formation and photocatalytic activity of titanate nanotubes synthesized via hydrothermal method. J. Alloy. Compd. (2010). doi:10.1016/S1001-0521(08)60112-6
C.K. Lee, K.S. Lin, C.F. Wu et al., Effects of synthesis temperature on the microstructures and basic dyes adsorption of titanate nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.129
H.Y. Niu, J.M. Wang, Y.L. Shi et al., Adsorption behavior of arsenic onto protonated titanate nanotubes prepared via hydrothermal method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.02.005
S.S. Liu, C.K. Lee, H.C. Chen et al., Application of titanate nanotubes for Cu (II) ions adsorptive removal from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cej.2008.06.034
G.D. Sheng, S.T. Yang, D.L. Zhao et al., Adsorption of Eu(III) on titanate nanotubes studied by a combination of batch and EXAFS technique. Sci. China Chem. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11426-011-4370-3
Y.C. Chen, S.L. Lo, J. Kuo, Pb(II) adsorption capacity and behavior of titanate nanotubes made by microwave hydrothermal method. Coll. Surf. A (2010). doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.03.017
T. Wang, W. Liu, L. Xiong et al., Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd (II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes. J. Chem. Eng. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.029
J.L. Liu, M.B. Luo, Z.Z. Yuan et al., Synthesis, characterization, and application of titanate nanotubes for Th(IV) adsorption. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10967-013-2607-7
M. Yada, Y. Inoue, M. Uota et al., Plate, wire, mesh, microsphere, and microtube composed of sodium titanate nanotubes on a titanium metal template. Langmuir (2007). doi:10.1021/la062654c
Y.P. Guo, N.H. Lee, H.J. Oh et al., Structure-tunable synthesis of titanate nanotube thin films via a simple hydrothermal process. Nanotechnology (2007). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/18/29/295608
N. Xiao, Z.H. Li, J.W. Liu et al., Effects of calcination temperature on the morphology, structure and photocatalytic activity of titanate nanotube thin films. Thin Sol. Film. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2010.07.120
Z.R. Tian, J.A. Voigt, J. Liu et al., Large oriented arrays and continuous films of TiO2-based nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2003). doi:10.1021/ja0369461
L.Y. Zheng, H.Y. Shi, Study on the Adsorption of Cobalt Titanate Nanotubes. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. (2013). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2013.08.037
C.Y. Liu, H.B. Yin, Y.M. Liu et al., Synthesis of potassium hexatitanate whiskers starting from metatitanic acid and potassium carbonate and sulfate by calcination method. Mater. Res. Bull. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.09.038
H.S. Klooster, NITROSO R-SALT, A NEW REAGENT FOR THE DETECTION OF COBALT. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1921). doi:10.1021/ja01437a007
M. Qamar, C.R. Yoon, H.J. Oh et al., Effect of post treatments on the structure and thermal stability of titanate nanotubes. Nanotechnology (2006). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/24/004
C.K. Lee, C.C. Wang, M.D. Lyu et al., Effects of sodium content and calcination temperature on the morphology, structure and photocatalytic activity of nanotubular titanates. J. Coll. Interface Sci. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2007.08.008
A. Arifi, H.A. Hanafi, Adsorption of cesium, thallium, strontium and cobalt radionuclides using activated carbon. J. At. Mol. Sci. (2010). doi:10.4208/jams.100809.112309a
X.M. Ren, J.X. Li, X.L. Tan et al., Comparative study of graphene oxide, activated carbon and carbon nanotubes as adsorbents for copper decontamination. Dalton Trans. (2013). doi:10.1039/C3DT32969K
F. Granados, V. Bertin, S. Bulbulian et al., 60 Co aqueous speciation and pH effect on the adsorption behavior on inorganic materials. Appl. Radiat. Isot. (2006). doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2005.06.016
Q. Chen, L.M. Peng, Structure and applications of titanate and related nanostructures. Int. J. Nanotech. (2007). doi:10.1504/IJNT.2007.012314
Q. Su, B.C. Pan, B.J. Pan et al., Fabrication of polymer-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide (HMO) for enhanced lead removal from waters. Sci. Total Environ. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.06.045
Y.S. Ho, Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, Sorption of dyes and copper ions onto biosorbents. Process Biochem. (2003). doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00239-X
L. Tan, Y. Jin, J. Chen et al., Sorption of radiocobalt (II) from aqueous solutions to Na-attapulgite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1121-z
K.G. Bhattacharyya, S.S. Gupta, Adsorption of Fe(III), Co (II) and Ni (II) on ZrO–kaolinite and ZrO–montmorillonite surfaces in aqueous medium. Coll. surf. A. (2008). doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.09.037
L. Chen, Y. Huang, L. Huang et al., Characterization of Co (II) removal from aqueous solution using bentonite/iron oxide magnetic composites. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1337-y
K. Li, Z. Liu, T. Wen et al., Sorption of radiocobalt (II) onto Ca-montmorillonite: effect of contact time, solid content, pH, ionic strength and temperature. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2012). doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1400-8
N.N. Nassar, Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on the adsorptive removal of nickel, cadmium and cobalt from wastewater by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoadsorbents. Can. J. Chem. Eng. (2012). doi:10.1002/cjce.20613
M. Liu, C. Chen, J. Hu et al., Synthesis of magnetite/graphene oxide composite and application for cobalt (II) removal. J. Phys. Chem. C (2011). doi:10.1021/jp208575m
D. Gogoi, A.G. Shanmugamani, S.V.S. Rao et al., Studies on removal of cobalt from an alkaline waste using synthetic calcium hydroxyapatite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10967-012-2378-6
Z.Q. Guo, Y. Li, S.W. Zhang et al., Enhanced sorption of radiocobalt from water by Bi(III) modified montmorillonite: a novel adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.004
D.M. Manohar, B.F. Noeline, T.S. Anirudhan, Adsorption performance of Al-pillared bentonite clay for the removal of cobalt (II) from aqueous phase. Appl. Clay Sci. (2006). doi:10.1016/j.clay.2005.08.008
I. Langmuir, The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1918). doi:10.1021/ja02242a004
Acknowledgments
Some samples were measured by ICP-OES which was provided by the Institute of Chemistry, Sichuan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Applied Basic Research Programs Funded Project of Sichuan Province (No 2012JY0100), National Natural Science Foundation and China Academy of Engineering Physics joint fund (No U1330125) and the National Fund of China for Fostering Talents in Basic Science (J1210004).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, DM., Li, FZ., Liao, JL. et al. Efficient removal of Co(II) from aqueous solution by titanate sodium nanotubes. NUCL SCI TECH 27, 143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0135-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0135-1