Abstract
Sclerotinia stem rot (SSR), caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) De Bary, is one of the most devastating diseases of tomato. The control of the pathogen is challenging because of its high genetic variability, broad host range and lack of information on natural resistance in tomato germplasm. Through the availability of the genome sequence of S. sclerotiorum, progress has been made in the identification of genes associated with the early stages of pathogenesis. However, less than 60 genes have been functionally validated. Very little information is available on the function of genes associated with the later stage of pathogenesis and signalling pathways. Researches related to SSR management have addressed agricultural practices and the application of fungicides. Agricultural practices like field sanitisation, soil sterilisation, biofumigation and organic amendments have shown improvement in disease control, while smart crop monitoring using unmanned aerial systems and optical sensors can further aid in early detection. Application of biological fungicides has demonstrated potential in SSR control in tomato, while the application of ultraviolet radiation can further aid in sustainable disease control. Transgenic approaches via the expression of some genes targeting degradation of the important molecule of pathogenesis or overexpression of the tomato defence-related genes have shown promises to enhance resistance. However, the generation of disease-resistant varieties in tomato is still in infancy. This review focuses on the current advancement of S. sclerotiorum-tomato pathosystem research and identifies some gaps in knowledge while providing recommendations for future research towards sustainable control of SSR in tomato.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdeljalil NO-B, Vallance J, Gerbore J, Rey P, Daami-Remadi M (2016) Bio-suppression of Sclerotinia stem rot of tomato and biostimulation of plant growth using tomato-associated rhizobacteria. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 7:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7471.1000331
Abdullah MT, Ali NY, Suleman P (2008) Biological control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary with Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Crop Protect 27:1354–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2008.05.007
Abreu MJ, Souza EA (2015) Investigation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum strains variability in Brazil. Genet Mol Res 14:6879–6896. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.June.18.31
Aldrich-Wolfe L, Travers S, Nelson JBD (2015) Genetic variation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from multiple crops in the North Central United States. PLoS ONE 10:0139188. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139188
Ali MA, Atallah OO (2020) Controlling common bean white mould caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary. Zagazig J Agric Res 47:101–117. https://doi.org/10.21608/zjar.2020.70125
Allah S, El-Yazeid A, Gamal H, Bondok A (2020) Potential the biological or chemical control of lettuce white rot and maintain productivity. Arab Univ J Agric Sci 28:587–599. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajs.2020.23042.1159
Al-Taisan WA, Bahkali AH, Elgorban AM, El-Metwally MA (2014) Effective influence of essential oils and microelements against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Int J Pharmacol 10:275–281. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2014.275.281
Altenbach D, Robatzek S (2007) Pattern recognition receptors: from the cell surface to intracellular dynamics. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:1031–1039. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-9-1031
Amselem J, Cuomo CA, Van Kan A, Viaud M, Benito EP, Couloux A, Coutinho PM, De Vries RP, Dyer PS, Fillinger S, Fournier E, Gout L, Hahn M, Kohn L, Lapalu N, Plummer KM, Pradier J-M, Quévillon E, Sharon A, Simon A, Have AT, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Wincker P, Andrew M, Anthouard V, Beever RE, Beffa R, Benoit I, Bouzid O, Brault B, Chen Z, Choquer M, Collémare J, Cotton P, Danchin EG, Da Silva C, Gautier A, Giraud C, Giraud T, Gonzalez C, Grossetete S, Güldener U, Henrissat B, Howlett BJ, Kodira C, Kretschmer M, Lappartient A, Leroch M, Levis C, Mauceli E, Neuvéglise C, Oeser B, Pearson M, Poulain J, Poussereau N, Quesneville H, Rascle C, Schumacher J, Ségurens B, Sexton A, Silva E, Sirven C, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ, Templeton M, Yandava C, Yarden O, Zeng Q, Rollins JA, Lebrun M-H, Dickman M (2011) Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet 7:1002230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230
Atallah ZK, Larget B, Chen X, Johnson DA (2004) High genetic diversity, phenotypic uniformity, and evidence of outcrossing in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in the Columbia basin of Washington State. Phytopathology 94:737–742
Attanayake RN, Tennekoon V, Johnson DA, Porter LD, del Rio-Mendoza L, Jiang D, Chen W (2014) Inferring outcrossing in the homothallic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum using linkage disequilibrium decay. Heredity 113:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2004
Barari H, Alavi V, Badalyan SM (2010) Genetic and morphological diversities in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates in northern parts of Iran. World Appl Sci J 8:326–333
Bashi ZD, Hegedus DD, Buchwaldt L, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2010) Expression and regulation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum necrosis and ethylene-inducing peptides (NEPs). Mol Plant Pathol 11:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00571.x
Bastien M, Sonah H, Belzile F (2014) Genome-wide association mapping of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance to soybean with a genotyping-by-sequencing approach. Plant Genome 7:1. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.10.003
Baysal-Gurel F, Gardener BM, Miller SA (2012) Soilborne disease management in organic vegetable production. Organic Agri. https://eorganic.org/node/7581. Accessed 20 Mar 2021
Benelli G, Rajeswary M, Vijayan P, Senthilmurugan S, Alharbi NS, Kadaikunnan S, Khaled JM, Govindarajan M (2018) Boswellia ovalifoliolata (Burseraceae) essential oil as an eco-friendly larvicide? Toxicity against six mosquito vectors of public health importance, non-target mosquito fishes, backswimmers, and water bugs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 5:10264–10271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8820-0
Bertinetti C, Ugalde RA (1996) Studies on the response of carrot cells to a Sclerotinia sclerotiorum elicitor: induction of the expression of an extracellular glycoprotein mRNA. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:658–663. https://doi.org/10.1094/mpmi-9-0658
Bolton MD, Thomma BPHJ, Nelson BD (2006) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary: biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol Plant Pathol 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2005.00316.x
Brustolin R, Reis EM, Pedron L (2016) Longevity of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum sclerotia on the soil surface under field conditions. Summa Phytopathol 42:172–174
Burton-Freeman B, Reimers K (2011) Tomato consumption and health: emerging benefits. Am J Lifestyle Med 5:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827610387488
Cabral SM, Cabral JP (2000) The primary mode-of-action of vinclozolin: are oxygen free radicals directly involved? Pestic Biochem Physiol 66:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1006/pest.1999.2468
Cao F, Liu F, Guo H, Kong W, Zhang C, He Y (2018) Fast detection of Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum on oilseed rape leaves using low-altitude remote sensing technology. Sensors 18:4464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124464
Cavalcanti VP, Araújo NA, Machado NB, Júnior PS, Pasqual M, Alves E, Schwan-Estrada KR, Dória J (2020) Yeasts and Bacillus spp. as potential biocontrol agents of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in garlic. Sci Hortic 5:108931
Cessna SG, Sears VE, Dickman MB, Low PS (2000) Oxalic acid, a pathogenicity factor for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, suppresses the oxidative burst of the host pathogen. Plant Cell 12:2191–2199. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.11.2191
Chen C, Dickman MB (2005) cAMP blocks MAPK activation and sclerotial development via Rap-1 in a PKA-independent manner in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol Microbiol 55:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04390.x
Chowdhary K, Sharma S (2020) Plant growth promotion and biocontrol potential of fungal endophytes in the inflorescence of Aloe vera L. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect b: Biol Sci 90:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-020-01173-3
Clarkson JP, Coventry E, Kitchen J, Carter HE, Whipps JM (2013) Population structure of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in crop and wild hosts in the UK. Plant Pathol 62:309–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2012.02635.x
Cunha WG, Tinoco ML, Pancoti HL, Ribeiro RE, Aragão FJ (2010) High resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in transgenic soybean plants transformed to express an oxalate decarboxylase gene. Plant Pathol 59:654–660
da Silva LR, Inglis MC, Moraes MC, Magalhães DM, Sifuentes DN, Martins I, de Mello SC (2020) Morphological and protein alterations in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib) de Bary after exposure to volatile organic compounds of Trichoderma spp. Biol Control 11:104279
de Aguiar RA, da Cunha MG, Junior ML (2014) Management of white mold in processing tomatoes by Trichoderma spp. and chemical fungicides applied by drip irrigation. Biol Control 74:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2014.03.009
Deising HB, Reimann S, Pascholati SF (2008) Mechanisms and significance of fungicide resistance. Braz J Microbiol 39:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838220080002000017
Derbyshire M, Denton-Giles M, Hegedus D, Seifbarghy S, Rollins J, van Kan J, Seidl MF, Faino L, Mbengue M, Navaud O, Raffaele S (2017) The complete genome sequence of the phytopathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum reveals insights into the genome architecture of broad host range pathogens. Genome Biol Evol 9:593–618. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx030
Derbyshire MC, Denton-Giles M, Hane JK, Chang S, Mousavi-Derazmahalleh M, Raffaele S, Buchwaldt L, Kamphuis LG (2019) A whole genome scan of SNP data suggests a lack of abundant hard selective sweeps in the genome of the broad host range plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. PLoS ONE 14:0214201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214201
Deshwal VK (2012) Pseudomonas aeruginosa as biological control agent against plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotina sclerotiorum. Int J Plant Anim Environ Sci 2:14–17
Dhingra OD, Schurt DA, Oliveira RD, Rodrigues FA (2013) Potential of soil fumigation with mustard essential oil to substitute biofumigation by cruciferous plant species. Trop Plant Pathol 38:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1982-56762013005000014
Di Matteo A, Sacco A, Anacleria M, Pezzotti M, Delledonne M, Ferrarini A, Frusciante L, Barone A (2010) The ascorbic acid content of tomato fruits is associated with the expression of genes involved in pectin degradation. BMC Plant Biol 10:163. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-163
Dicloran (Botran) Chemical Fact Sheet 1/84. http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/fung-nemat/aceticacid-etridiazole/dicloran/fung-prof-dcna.html. Accessed 20 Mar 2021
Doble M, Kumar A (2001) Biodegradation of Pesticides. Biotreat Ind Effl 2005:89–100
Duan Y, Li T, Xiao X, Wu J, Li S, Wang J, Zhou M (2018) Pharmacological characteristics of the novel fungicide pyrisoxazole against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pestic Biochem Physiol 1:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.05.010
Duan Y, Xiu Q, Li H, Li T, Wang J, Zhou M (2019) Pharmacological characteristics and control efficacy of a novel SDHI fungicide pydiflumetofen against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Dis 103:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-05-18-0763-RE
Duncan RW, Fernando WD, Rashid KY (2006) Time and burial depth influencing the viability and bacterial colonization of sclerotia of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Soil Biol Biochem 38:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.05.003
Fan H, Yu G, Liu Y, Zhang X, Liu J, Zhang Y, Rollins JA, Sun F, Pan H (2017) An atypical forkhead-containing transcription factor SsFKH1 is involved in sclerotial formation and is essential for pathogenicity in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol Plant Pathol 18:963–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12453
Farzand A, Moosa A, Zubair M, Khan AR, Ayaz M, Massawe VC, Gao X (2020) Transcriptional profiling of diffusible lipopeptides and fungal virulence genes during Bacillus amyloliquefaciens EZ1509-mediated suppression of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology 110:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-19-0156-R
Favaron F, Sella L, D’Ovidio R (2004) Relationships among endo-polygalacturonase, oxalate, pH, and plant polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) in the interaction between Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and soybean. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:1402–1409. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.12.1402
Fernández-Ortuño D, Torés JA, De Vicente A, Pérez-García A (2008) Mechanisms of resistance to QoI fungicides in phytopathogenic fungi. Int Microbiol 11:1–9
Figueirêdo GSD, Figueirêdo LCD, Cavalcanti FCN, Santos ACD, Costa AFD, Oliveira NTD (2010) Biological and chemical control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum using Trichoderma spp. and Ulocladium atrum and pathogenicity to bean plants. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132010000100001
Findling S, Fekete A, Warzecha H, Krischke M, Brandt H, Blume E, Mueller MJ, Berger S (2014) Manipulation of methyl jasmonate esterase activity renders tomato more susceptible to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Funct Plant Biol 41:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp13103
Gama DDS, Santos ÍAFM, Abreu LMD, Medeiros FHVD, Duarte WF, Cardoso PG (2020) Endophytic fungi from Brachiaria grasses in Brazil and preliminary screening of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antagonists. Sci Agric 77:3. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992x-2018-0210
Gao Y, He L, Zhu J, Cheng J, Li B, Liu F, Mu W (2020) The relationship between features enabling SDHI fungicide binding to the Sc-Sdh complex and its inhibitory activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pest Manag Sci 76:2799–2808. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5827
García-Pedrajas MD, Cañizares MC, Sarmiento-Villamil JL, Jacquat AG, Dambolena JS (2019) Mycoviruses in biological control: from basic research to field implementation. Phytopathology 109:1828–1839. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-19-0166-RVW
Gerlagh M, Whipps JM, Budge SP, Goossen-Van de Geijn HM (1996) Efficiency of isolates of Coniothyrium minitans as mycoparasites of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Sclerotium cepivorum and Botrytis cinerea on tomato stem pieces. Eur J Plant Pathol 102:787–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01877154
Ghabrial SA, Suzuki N (2009) Viruses of plant pathogenic fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:353–384. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081932
Godoy G, Steadman JR, Dickman MB, Dam R (1990) Use of mutants to demonstrate the role of oxalic acid in pathogenicity of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 37:179–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/0885-5765(90)90010-U
Gomaa NA, Mahdy AMM, Fawzy RN, Ahmed GA (2016) Integrated management of tomato white mold disease caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum using the combined treatments of compost, chemical inducers and fungicides. Middle East J Agric 5:479–486
Gong AD, Sun GJ, Zhao ZY, Liao YC, Zhang JB (2020) Staphylococcus saprophyticus L-38 produces volatile 3, 3-dimethyl-1, 2-epoxybutane with strong inhibitory activity against Aspergillus flavus germination and aflatoxin production. World Mycotoxin J 13:247–258. https://doi.org/10.3920/WMJ2019.2495
Gorman C (2020) Epidemiology of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, causal agent of Sclerotinia Stem Rot, on SE US Brassica carinata. Auburn University, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing. 28016022
Graber ER, Frenkel O, Jaiswal AK, Elad Y (2014) How may biochar influence severity of diseases caused by soilborne pathogens? Carbon Manag 5:69–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2014.913360
Graham DR, Webb MJ (1991) Micronutrients and disease resistance and tolerance in plants. In: Mortvedt JJ, Cox FR, Shuman LM, Welch RM (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America Inc, Madison, pp 329–370
Gündüz GT, Pazir F (2013) Inactivation of Penicillium digitatum and Penicillium italicum under in vitro and in vivo conditions by using UV-C light. J Food Protect 76:1761–1766. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-12-511
Gupta M, Bagchi A, Ray AB (1991) Additional withanolides of Datura metel. J Nat Prod 54:599–602. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50074a042
Guyon K, Balagué C, Roby D, Raffaele S (2014) Secretome analysis reveals effector candidates associated with broad host range necrotrophy in the fungal plant pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. BMC Genomics 15:336. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-336
Hägerhäll C (1997) Succinate: quinone oxidoreductases: variations on a conserved theme. Biochim Biophys Acta 1320:107–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2728(97)00019-4
Hambleton S, Walker C, Kohn LM (2002) Clonal lineages of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum previously known from other crops predominate in 1999–2000 samples from Ontario and Quebec soybean. Can J Plant Pathol 24:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660209507014
Hamid R, Khan MA, Ahmad M, Ahmad MM, Abdin MZ, Musarrat J, Javed S (2013) Chitinases: an update. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 5:21. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.106559
Hammami I, Hsouna AB, Hamdi N, Gdoura R, Triki MA (2013) Isolation and characterization of rhizosphere bacteria for the biocontrol of the damping-off disease of tomatoes in Tunisia. C R Biol 336:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2013.10.006
Harper GE, Frampton CM, Stewart A (2002) Factors influencing survival of sclerotia of Sclerotium cepivorum in New Zealand soils. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 30:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.2002.9514196
He H, Hao X, Zhou W, Shi N, Feng J, Han L (2020) Identification of antimicrobial metabolites produced by a potential biocontrol Actinomycete strain A217. J Appl Microbiol 128:1143–1152. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14548
Heard S, Brown NA, Hammond-Kosack K (2015) An interspecies comparative analysis of the predicted secretomes of the necrotrophic plant pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS ONE 10:e0130534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130534
Hegedus DD, Rimmer SR (2005) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: when “to be or not to be” a pathogen? FEMS Microbiol Lett 251:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.07.040
Heller A, Witt-Geiges T (2013) Oxalic acid has an additional, detoxifying function in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 8:e72292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072292
Hemmati R, Javan-Nikkhah M, Linde CC (2009) Population genetic structure of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on canola in Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 125:617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9510-7
Hu X, Roberts DP, Xie L, Maul JE, Yu C, Li Y, Zhang S, Liao X (2013) Bacillus megaterium A6 suppresses Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on oilseed rape in the field and promotes oilseed rape growth. Crop Prot 52:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2013.05.018
Hu X, Roberts DP, Xie L, Maul JE, Yu C, Li Y, Jiang M, Liao X, Che Z, Liao X (2014) Formulations of Bacillus subtilis BY-2 suppress Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on oilseed rape in the field. Biol Control 70:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.12.005
Hu X, Roberts DP, Xie L, Yu C, Li Y, Qin L, Hu L, Zhang Y, Liao X (2016) Biological control of Sclerotinia disease by Aspergillus sp. on oilseed rape in the field. Biocontrol Sci Technol 26:1526–1537
Hu S, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Zhu F (2020) Stimulatory effects of boscalid on virulence of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum indicate hormesis may be masked by inhibitions. Plant Dis 104:3. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-07-19-1421-RE
Huber DM, Graham RD (1999) The role of nutrition in crop resistance and tolerance to diseases. In: Rengel Z (ed) Mineral nutrition of crops: fundamental mechanisms and implications. Food Products Press, New York, pp 169–206
Hughes EW (2019) Spatially-explicit snap bean flowering and disease prediction using imaging spectroscopy from unmanned aerial systems. MS thesis
Huzar-Novakowiski J, Paul PA, Dorrance AE (2017) Host resistance and chemical control for management of Sclerotinia stem rot of soybean in Ohio. Phytopathology 107:937–949. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-01-17-0030-R
Iprodione—Fact Sheet 5/83. http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/fung-nemat/febuconazole-sulfur/iprodione/iprod_cfs_0583.html. Accessed 10 Mar 2021
Ito Y, Muraguchi H, Seshime Y, Oita S, Yanagi SO (2004) Flutolanil and carboxin resistance in Coprinus cinereus conferred by a mutation in the cytochrome b560 subunit of succinate dehydrogenase complex (Complex II). Mol Genet Genomic 272:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1060-2
Janisiewicz WJ, Takeda F, Glenn DM, Camp MJ, Jurick WM (2016) Dark period following UV-C treatment enhances killing of Botrytis cinerea conidia and controls gray mold of strawberries. Phytopathology 106:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-09-15-0240-R
Johnson ML, Berger L, Philips L, Speare R (2003) Fungicidal effects of chemical disinfectants, UV light, desiccation and heat on the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Dis Aquat Organ 57:255–260
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Jurick WM II, Rollins JA (2007) Deletion of the adenylate cyclase (sac1) gene affects multiple developmental pathways and pathogenicity in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Fungal Genet Biol 44:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2006.11.005
Kabbage M, Yarden O, Dickman MB (2015) Pathogenic attributes of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: switching from a biotrophic to necrotrophic. Lifestyle Plant Sci 233:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.018
Kamaruzzaman M, Lyu A, Zhang J, Wu M, Yang L, Chen W, Li G (2020) Competitive saprophytic ability of the hypovirulent isolate QT5–19 of Botrytis cinerea and its importance in biocontrol of necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Biol Control 142:104182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.104182
Kamthan A, Kamthan M, Azam M, Chakraborty N, Chakraborty S, Datta A (2012) Expression of a fungal sterol desaturase improves tomato drought tolerance, pathogen resistance and nutritional quality. Sci Rep 2:951. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00951
Kamvar ZN, Amaradasa BS, Jhala R, McCoy S, Steadman JR, Everhart SE (2017) Population structure and phenotypic variation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in the United States. Peer J 5:4152. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4152
Kanto T, Matsuura K, Yamada M, Usami T, Amemiya Y (2008) UV-B radiation for control of strawberry powdery mildew. In VI International Strawberry Symposium Mar 3, pp 359–362. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2009.842.68
Kaushal M, Kumar A, Kaushal R (2017) Bacillus pumilus strain YSPMK11 as plant growth promoter and bicontrol agent against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. 3 Biotech 7:90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0732-7
Kesarwani M, Azam M, Natarajan K, Mehta A, Datta A (2000) Oxalate decarboxylase from Collybia velutipes molecular cloning and its overexpression to confer resistance to fungal infection in transgenic tobacco and tomato. J Biol Chem 275:7230–7238. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.10.7230
Khalifa ME, Pearson MN (2014) Molecular characterisation of novel mitoviruses associated with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Arch Virol 159:3157–3160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2171-7
Kim HJ, Chen C, Kabbage M, Dickman MB (2011) Identification and characterization of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum NADPH oxidases. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:7721–7729. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2000.40155x
Köhl J, Kolnaar R, Ravensberg WJ (2019) Mode of action of microbial biological control agents against plant diseases: relevance beyond efficacy. Front Plant Sci 10:845. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00845
Lane DW, Kamphuis LG, Derbyshire MC, Denton-Giles M (2018) Heat-dried sclerotia of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum myceliogenically germinate in water and are able to infect Brassica napus. Crop Pasture Sci 69:765–774. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP18109
Lane D, Denton-Giles M, Derbyshire M, Kamphuis LG (2019) Abiotic conditions governing the myceliogenic germination of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum allowing the basal infection of Brassica napus. Australas Plant Pathol 48:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-019-0613-0
Lehner MS, Júnior TJP, Júnior BTH, Teixeira H, Vieira RF, Carneiro JES, Mizubuti ESG (2015) Low genetic variability in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum populations from common bean fields in Minas Gerais State, Brazil, at regional, local and micro-scales. Plant Pathol 64:921–931. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12322
Lehner MS, de Paula JTJ, Del Ponte EM, Mizubuti ES, Pethybridge SJ (2017) Independently founded populations of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from a tropical and a temperate region have similar genetic structure. PLoS ONE 12:3. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173915
Li H, Fu Y, Jiang D, Li G, Ghabrial SA, Yi X (2008) Down-regulation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum gene expression in response to infection with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus. Virus Res 135:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2008.02.011
Li Q, Ning P, Zheng L, Huang J, Li G, Hsiang T (2012) Effects of volatile substances of Streptomyces globisporus JK-1 on control of Botrytis cinerea on tomato fruit. Biol Control 61:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2011.10.014
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yu PL, Pan H, Rollins JA (2018) Introduction of large sequence inserts by CRISPR-Cas9 to create pathogenicity mutants in the multinucleate filamentous pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mbio 9:e00567-e618. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00567-18
Liang X, Rollins JA (2018) Mechanisms of broad host range necrotrophic pathogenesis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathol 108:1128–1140. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-06-18-0197-RVW
Liang X, Liberti D, Li M, Kim YT, Hutchens A, Wilson R, Rollins JA (2015a) Oxaloacetate acetylhydrolase gene mutants of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum do not accumulate oxalic acid, but do produce limited lesions on host plants. Mol Plant Pathol 16:559–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12211
Liang X, Moomaw EW, Rollins JA (2015b) Fungal oxalate decarboxylase activity contributes to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum early infection by affecting both compound appressoria development and function. Mol Plant Pathol 16:825–836. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12239
Liu H, Fu Y, Jiang D, Li G, Xie J, Peng Y, Yi X, Ghabrial SA (2009) A novel mycovirus that is related to the human pathogen hepatitis E virus and rubi-like viruses. J Virol 83:1981–1991. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01897-08
Liu S, Zhang Y, Jiang J, Che Z, Tian Y, Chen G (2018) Carbendazim resistance and dimethachlone sensitivity of field isolates of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from oilseed rape in Henan Province, China. J Phytopathol 166:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12751
Liu D, Yan R, Fu Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Xiang W (2019) Antifungal, plant growth-promoting and genomic properties of an endophytic actinobacterium Streptomyces sp. NEAU-S7GS2. Front Microbiol 10:2077. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02077
López-Mondéjar R, Ros M, Pascual JA (2011) Mycoparasitism-related genes expression of Trichoderma harzianum isolates to evaluate their efficacy as biological control agent. Biol Control 56:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2010.10.003
Lumsden RD, Lewis JA, Millner PD (1983) Effect of composted sewage sludge on several soilborne pathogens and diseases. Phytopathology 73:1543–1548
Ma BX, Ban XQ, He JS, Huang B, Zeng H, Tian J, Chen YX, Wang YW (2016) Antifungal activity of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. essential oil against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on rapeseed plants (Brassica campestris L.). Crop Prot 89:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2016.07.003
Mahlein AK (2016) Plant disease detection by imaging sensors–parallels and specific demands for precision agriculture and plant phenotyping. Plant Dis 11(100):241–251. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-15-0340-FE
Mao X, Wang Y, Hou YP, Zhou M (2020) Activity of the succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicide penthiopyrad against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Dis 104:10. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-19-2253-RE
Marciano P, Lenna PD, Magro P (1983) Oxalic acid, cell wall-degrading enzymes and pH in pathogenesis and their significance in the virulence of two Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates on sunflower. Physiol Plant Pathol 22:339–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-4059(83)81021-2
Matheron ME, Porchas M (2004) Activity of boscalid, fenhexamid, fluazinam, fludioxonil, and vinclozolin on growth of Sclerotinia minor and S. sclerotiorum and development of lettuce drop. Plant Dis 88:665–668. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2004.88.6.665
Matias R, Fernandes V, Corrêa BO, Pereira SR, Oliveira AKM (2020) Phytochemistry and antifungal potential of Datura inoxia Mill. on soil phytopathogen control. Biosci J 36:3. https://doi.org/10.14393/BJ-v36n3a2020-47881
Mbengue M, Navaud O, Peyraud R, Barascud M, Badet T, Vincent R, Barbacci A, Raffaele S (2016) Emerging trends in molecular interactions between plants and the broad host range fungal pathogens Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Front Plant Sci 31:422. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00422
McCaghey M, Willbur J, Ranjan A, Grau CR, Chapman S, Diers B, Groves C, Kabbage M, Smith DL (2017) Development and evaluation of Glycine max germplasm lines with quantitative resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Front Plant Sci 8:1495. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01495
Mihajlović M, Rekanović E, Hrustić J, Tanović B (2017) Methods for management of soilborne plant pathogens. Pest Fitomed 32:9–24. https://doi.org/10.2298/PIF1701009M
Milgroom MG (1996) Recombination and the multilocus structure of fungal populations. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:457–477. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.34.1.457
Moellers TC (2016) Genome-wide association and epistasis studies of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance in soybean. Doctoral dissertation, Iowa State University Capstones. https://doi.org/10.31274/etd-180810-4643
Mueller DS, Dorrance AE, Derksen RC, Ozkan E, Kurle JE, Grau CR, Gaska JM, Hartman GL, Bradley CA, Pedersen WL (2002) Efficacy of fungicides on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and their potential for control of Sclerotinia stem rot on soybean. Plant Dis 86:26–31
Mwape VW, Mobegi, FM, Regmi, R, Newman TB, Kamphuis LG, Derbyshire MC (2021) Analysis of differentially expressed Sclerotinia sclerotiorum genes during the interaction with moderately resistant and highly susceptible chickpea lines. BMC Genomics 22:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07655-6
Nahar MS, Naher N, Alam MJ, Hussain MJ, Yasmin L, Mian MY, Miller SA, Rosa C (2019) Survey, morphology and white mold disease of country bean (Lablab purpureus L.) caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary in-relation to soil physico-chemical properties and weather conditions in Bangladesh. Crop Protect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2019.05.019
Ni L, Punja ZK (2019) Effects of a foliar fertilizer containing boron on the development of Sclerotinia stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) on canola (Brassica napus L.) leaves. J Phytopathol 168:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12865
Ojaghian MR, Wang L, qi Cui Z, Yang C, Zhongyun T, Xie GL (2014) Antifungal and SAR potential of crude extracts derived from neem and ginger against storage carrot rot caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Ind Crop Prod 55:130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.02.012
Ojaghian S, Wang L, Zhang JZ, Xie GL (2020) Inhibitory effect of Fungastop and Bion against carrot soft rot caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytoparasitica 48:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-019-00780-9
Omar I, O’neill TM, Rossall S (2006) Biological control of Fusarium crown and root rot of tomato with antagonistic bacteria and integrated control when combined with the fungicide carbendazim. Plant Pathol 55:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2005.01315.x
Otun S, Ntushelo K (2019) How to knock down a plant; the three weapons of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J Biol Sci 19:300–313. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2019.300.313
Oyedotun KS, Lemire BD (2004) The quaternary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae succinate dehydrogenase homology modeling, cofactor docking, and molecular dynamics simulation studies. J Biol Chem 279:9424–9431. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311876200
Pan Y, Xu Y, Li X, Yao C, Gao Z (2015) SsPemG1 encodes an elicitor-homologous protein and regulates pathogenicity in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 92:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2015.08.010
Pan Y, Wei J, Yao C, Reng H, Gao Z (2018) SsSm1, a Cerato-platanin family protein, is involved in the hyphal development and pathogenic process of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Sci 270:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.02.001
Panday A, Sahoo MK, Osorio D, Batra S (2015) NADPH oxidases: an overview from structure to innate immunity-associated pathologies. Cell Mol Immun 12:5–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.89
Panth M, Hassler SC, Baysal-Gurel F (2020) Methods for management of soilborne diseases in crop production. Agriculture 10:16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10010016
Pathak DV, Yadav R, Kumar M (2017) Microbial pesticides: development, prospects and popularization in India. Plant–microbe interactions in agro-ecological perspectives. Springer, Singapore, pp 455–471
Pesticide Fact Sheet Boscalid (2003) https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/fs_PC-128008_01-Jul-03.pdf. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
Pesticide Fact Sheet Fenhexamid (1999) https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/fs_PC-090209_20-May-99.pdf. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
Pesticide Fact Sheet Fluazinam (2001) https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/fs_PC-129098_10-Aug-01.pdf. Accessed 15 Mar 2021
Poulaki EG, Gkizi D, Tjamos SE (2020) Potential of zeolite to control Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Rhizoctonia solani in lettuce and the induction of defence-related genes. J Phytopathol 168:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12875
Poussereau N, Creton S, Billon-Grand G, Rascle C, Fevre M (2001) Regulation of acp1, encoding a non-aspartyl acid protease expressed during pathogenesis of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Microbiology 147:717–726. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-3-717
PPDB: Pesticide Properties DataBase (2019) https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
PubChem NCBI (2005) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Chlorothalonil. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
Purdy LH, Bardin R (1953) Mode of infection of tomato plants by the ascospores of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Dis Rep 37:6
Qi J, Zhang M, Lu C, Hettenhausen C, Tan Q, Cao G, Zhu X, Wu G, Wu J (2018) Ultraviolet-B enhances the resistance of multiple plant species to lepidopteran insect herbivory through the jasmonic acid pathway. Sci Rep 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18600-7
Ran H, Liu L, Li B, Cheng J, Fu Y, Jiang D, Xie J (2016) Co-infection of a hypovirulent isolate of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum with a new botybirnavirus and a strain of a mitovirus. Virol J 13:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-016-0550-2
Ranjan A, Jayaraman D, Grau C, Hill JH, Whitham SA, Ané JM, Smith DL, Kabbage M (2018) The pathogenic development of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean requires specific host NADPH oxidases. Mol Plant Pathol 19:700–714. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12555
Reddy PP (2014) Biointensive integrated pest management in horticultural ecosystems. Scientific Publishers. ISBN: 978-81-322-1844-9
Reilly TJ, Smalling KL, Wilson ER (2011) Occurrence and environmental effects of boscalid and other fungicides in three targeted use areas in the United States. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts.
Ribeiro AI, Costa ES, Thomasi SS, Brandão DFR, Vieira PC, Fernandes JB, Forim MR, Ferreira AG, Pascholati SF, Gusmão LFP, da Silva MFDGF (2018) Biological and chemical control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum using Stachybotrys levispora and its secondary metabolite griseofulvin. J Agric Food Chem 66:7627–7632
Rodríguez MA, Venedikian N, Bazzalo ME, Godeas A (2004) Histopathology of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum attack on flower parts of Helianthus annuus heads in tolerant and susceptible varieties. Mycopathologia 157:291–302. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MYCO.0000024177.82916.b7
Saand MA, Xu YP, Munyampundu JP, Li W, Zhang XR, Cai XZ (2015) Phylogeny and evolution of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel (CNGC) gene family and functional analyses of tomato CNGCs. DNA Res 22:471–483. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsv029
Sabaté DC, Brandan CP, Petroselli G, Erra-Balsells R, Audisio MC (2018) Biocontrol of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary on common bean by native lipopeptide-producer Bacillus strains. Microbiol Res 1:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.04.003
Sandino J, Pegg G, Gonzalez F, Smith G (2018) Aerial mapping of forests affected by pathogens using UAVs, hyperspectral sensors, and artificial intelligence. Sensors 18:944. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040944
Seifbarghi S, Borhan MH, Wei Y, Coutu C, Robinson SJ, Hegedus DD (2017) Changes in the Sclerotinia sclerotiorum transcriptome during infection of Brassica napus. BMC Genomics 18:266. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3642-5
Sexton AC, Howlett BJ (2004) Microsatellite markers reveal genetic differentiation among populations of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from Australian canola fields. Curr Genet 46:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-004-0543-3
Shah MR, Mukherjee PK, Eapen S (2010) Expression of a fungal endochitinase gene in transgenic tomato and tobacco results in enhanced tolerance to fungal pathogens. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0006-x
Shah N, Gislason AS, Becker M, Belmonte MF, Fernando WD, de Kievit TR (2020) Investigation of the quorum-sensing regulon of the biocontrol bacterium Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain PA23. PLoS ONE 15:0226232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226232
Sharma P, Sain SK (2004) Induction of systemic resistance in tomato and cauliflower by Trichoderma spp. against stalk-rot pathogen, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib) de Bary. J Biol Control 18:21–28. https://doi.org/10.18311/jbc/2004/4042
Sharma P, Meena PD, Singh S, Rai PK (2017) Efficacy of micro-nutrients, fungicides and bio-agents against sclerotinia stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) of Indian Mustard. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6:620–626. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.076
Sierotzki H, Scalliet G (2013) A review of current knowledge of resistance aspects for the next-generation succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicides. Phytopathology 103:880–887. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-01-13-0009-RVW
Silva EA, da Silva VP, Alves CC, Alves JM, Souchie EL, Barbosa LC (2018) Chemical composition of the essential oil of Psidium guajava leaves and its toxicity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Semina: Ciências Agrárias 39:865–874. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0359.2018v39n2p865
Singh S, Singh N, Kumar V, Datta S, Wani AB, Singh D, Singh K, Singh J (2016) Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environ Chem Lett 14:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0566-2
Smolińska U, Kowalska B (2018) Biological control of the soil-borne fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum––a review. J Plant Pathol 100:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-0023-0
Son M, Jisuk Yu, Kim K-H (2015) Five questions about mycoviruses. PLoS Pathog 11:e1005172. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005172
Soylu S, Yigitbas H, Soylu EM, Kurt Ş (2007) Antifungal effects of essential oils from oregano and fennel on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J Appl Microbiol 103:1021–1030. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03310.x
Suthaparan A, Stensvand A (2012) Suppression of powdery mildew (Podosphaera pannosa) in greenhouse roses by brief exposure to supplemental UV-B radiation. Plant Dis 96:1653–1660. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-12-0094-RE
Suthaparan A, Solhaug KA, Bjugstad N, Gislerød HR, Gadoury DM, Stensvand A (2016) Suppression of powdery mildews by UV-B: application frequency and timing, dose, reflectance, and automation. Plant Dis 100:1643–1650. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-12-15-1440-RE
Tang L, Yang G, Ma M, Liu X, Li B, Xie J, Fu Y, Chen T, Yu Y, Chen W, Jiang D (2020) An effector of a necrotrophic fungal pathogen targets the calcium-sensing receptor in chloroplasts to inhibit host resistance. Mol Plant Pathol 21:686–701. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12922
Terna TP, Simon A (2017) Biological control of some fungal pathogens of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.) using ethanolic leaf extracts of plants. J Environ Agricult Sci 13:9–15
Tian B, Xie J, Fu Y, Cheng J, Li B, Chen T, Zhao Y, Gao Z, Yang P, Barbetti MJ, Tyler BM (2020) A cosmopolitan fungal pathogen of dicots adopts an endophytic lifestyle on cereal crops and protects them from major fungal diseases. ISME J 4:3120–3135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00744-6
Tomato Genome Consortium (2012) The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 485:635. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11119
Torres MJ, Brandan CP, Sabaté DC, Petroselli G, Erra-Balsells R, Audisio MC (2017) Biological activity of the lipopeptide-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PGPBacCA1 on common bean Phaseolus vulgaris L. pathogens. Biol Control 105:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.12.001
Torriani SFF, Frey R, Buitrago C, Wullschleger J, Waldner M, Kuehn R, Scalliet G, Sierotzki H (2017) Succinate-dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) resistance evolution in plant pathogens. Modern fungicides and antifungal compounds. 8:89–94. Deutsche Phytomedizinische Gesellschaft, Braunschweig. ISBN: 978-3-941261-15-0
Tortelli B, Cappellaro S, Andrade J, Mezomo MÃ, Steffen PÃ, Silva VN, Milanesi PM (2020) Treatments for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on inoculated bean seeds and effects on health and physiological quality. J Agric Stud 8:371–386. https://doi.org/10.5296/jas.v8i1.16207
Tuominen J, Lipping T, Kuosmanen V, Haapanen R (2009) Remote sensing of forest health, chapter 02. In: Ho PGP (ed) Geoscience and remote sensing. InTech, Rijeka
Upadhyay NK, Ratan VV, Yadav K, Kumar A, Awasthi D, Chandra S, Rai JP (2019) Management of white mold fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib) De Bary causes disease in tomato under in vitro conditions. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 8:2733–2743. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.808.315
USEPA/Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Vinclozolin p.5 EPA-738-R-00-023 (October 2000) Available from, as of May 28 (2009). http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
Van Hemelrijck W, Van Laer S, Hoekstra S, Aiking A, Creemers P (2010) UV-C radiation as an alternative tool to control powdery mildew on apple and strawberry. In: Proceedings of the ecofruit congress, 14th international conference on organic fruit-growing, pp 22–24
Van Loenen MC, Turbett Y, Mullins CE, Feilden NE, Wilson MJ, Leifert C, Seel WE (2003) Low temperature-short duration steaming of soil kills soil-borne pathogens, nematode pests and weeds. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EJPP.0000003830.49949.34
Van ANK, Kosuge T (1976) Metabolism of the fungicide 2, 6-dichloro-4-nitroaniline in soil. J Agric Food Chem 24:584–588. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60205a029
Verma KS, Haq SU, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2017) RAPD and ISSR marker assessment of genetic diversity in Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: a unique source of germplasm highly adapted to drought and high-temperature stress. 3 Biotech 7:288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0918-z
Vinclozolin - Fact Sheet. http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/extoxnet/pyrethrins-ziram/vinclozolin-ext.html. Accessed 13 Mar 2021
Vinodkumar S, Nakkeeran S, Renukadevi P, Malathi VG (2017) Biocontrol potentials of antimicrobial peptide producing Bacillus species: multifaceted antagonists for the management of stem rot of carnation caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Front Microbiol 8:446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00446
Vitorino LC, Silva FO, Cruvinel BG, Bessa LA, Rosa M, Souchie EL, Silva FG (2020) Biocontrol potential of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and physiological changes in soybean in response to Butia archeri palm rhizobacteria. Plants 9:64. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010064
Vuong TD, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2008) Identification of QTL for resistance to sclerotinia stem rot in soybean plant introduction 194639. Crop Sci 48:2209–2214. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2008.01.0019
Walz A, Zingen-Sell I, Loeffler M, Sauer M (2008) Expression of an oxalate oxidase gene in tomato and severity of disease caused by Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Pathol 57:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01815.x
Wang H, Liu G, Zheng Y, Wang X, Yang Q (2004) Breeding of the Brassica napus Cultivar Zhongshuang 9 with High-resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and dynamics of its important defense enzyme activity. Sci Agric Sin 37:23–28
Wang Y, Duan YB, Zhou MG (2015) Molecular and biochemical characterization of boscalid resistance in laboratory mutants of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Pathol 64:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12246
Wang M, Geng L, Sun X, Shu C, Song F, Zhang J (2020) Screening of Bacillus thuringiensis strains to identify new potential biocontrol agents against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Plutella xylostella in Brassica campestris L. Biol Control 24:104262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104262
Westrick NM, Ranjan A, Jain S, Grau CR, Smith DL, Kabbage M (2019) Gene regulation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum during infection of Glycine max: on the road to pathogenesis. BMC Genomics 20:157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5517-4
Williams B, Kabbage M, Kim HJ, Britt R, Dickman MB (2011) Tipping the balance: Sclerotinia sclerotiorum secreted oxalic acid suppresses host defenses by manipulating the host redox environment. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002107. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002107
Wu J, Cai G, Tu J, Li L, Liu S, Luo X, Zhou L, Fan C, Zhou Y (2013) Identification of QTLs for resistance to Sclerotinia stem rot and BnaC. IGMT5. A as a candidate gene of the major resistant QTL SRC6 in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 8:7
Wu J, Zhao Q, Liu S, Shahid M, Lan L, Cai G, Zhang C, Fan C, Wang Y, Zhou Y (2016) Genome-wide association study identifies new loci for resistance to Sclerotinia stem rot in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci 7:1418. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067740
Xia S, Xu Y, Hoy R, Zhang J, Qin L, Li X (2020) The notorious soilborne pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: An update on genes studied with mutant analysis. Pathogens 9:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010027
Xiao X, Xie J, Cheng J, Li G, Yi X, Jiang D, Fu Y (2014a) Novel secretory protein Ss-Caf1 of the plant-pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is required for host penetration and normal sclerotial development. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27:40–55. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-13-0145-R
Xiao X, Cheng J, Tang J, Fu Y, Jiang D, Baker TS, Ghabrial SA, Jiatao X (2014b) A Novel partitivirus that confers hypovirulence on plant pathogenic fungi. J Virol 88:10120–10133. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01036-1410.1094/MPMI-05-13-0145-R
Xie J, Ghabrial SA (2012) Molecular characterizations of two mitoviruses co-infecting a hyovirulent isolate of the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Virology 428:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.03.015
Xie J, Xiao X, Fu Y, Liu H, Cheng J, Ghabrial SA, Li G, Jiang D (2011) A novel mycovirus closely related to hypoviruses that infects the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Virol 418:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2011.07.008
Xu L, Chen W (2013) Random T-DNA mutagenesis identifies a Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene as a virulence factor of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-07-12-0177-R
Xu L, Xiang M, White D, Chen W (2015a) pH dependency of sclerotial development and pathogenicity revealed by using genetically defined oxalate-minus mutants of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Environ Microbiol 17:2896–2909. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12818
Xu D, Pan Y, Zhang H, Li X, Dai Y, Cao S, Gao Z (2015b) Detection and characterization of carbendazim resistance in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates from oilseed rape in Anhui Province of China. Genet Mol Res 4:16627–16638. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015
Xu L, Li G, Jiang D, Chen W (2018) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: an evaluation of virulence theories. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:311–338. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080417-050052
Yang G, Tang L, Gong Y, Xie J, Fu Y, Jiang D, Li G, Collinge DB, Chen W, Cheng J (2018) A cerato-platanin protein SsCP1 targets plant PR1 and contributes to virulence of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. New Phytol 217(2):739–755. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14842
Yu X, Li Bo, Yanping Fu, Jiang D, Ghabrial SA, Li G, Peng Y, Xie J, Cheng J, Huang J, Yi X (2010) A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 18:8387–8392. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913535107
Zhang W, Fraiture M, Kolb D, Löffelhardt B, Desaki Y, Boutrot FF, Tör M, Zipfel C, Gust AA, Brunner F (2013) Arabidopsis receptor-like protein30 and receptor-like kinase suppressor of BIR1-1/EVERSHED mediate innate immunity to necrotrophic fungi. Plant Cell 25(10):4227–4241. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117010
Zhang H, Wu Q, Cao S, Zhao T, Chen L, Zhuang P, Zhou X, Gao Z (2014) A novel protein elicitor (SsCut) from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum induces multiple defense responses in plants. Plant Mol Biol 86:495–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0244-3
Zhang X, Xu J, Muhayimana S, Xiong H, Liu X, Huang Q (2020a) Antifungal effects of 3-(2-pyridyl) methyl-2-(4-chlorphenyl) iminothiazolidine against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pest Manag Sci 76:2978–2985. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5843
Zhang H, Xie J, Fu Y, Cheng J, Qu Z, Zhao Z, Cheng S, Chen T, Li B, Wang Q, Liu X (2020b) A 2-kb mycovirus converts a pathogenic fungus into a beneficial endophyte for brassica protection and yield enhancement. Mol Plant 13:1420–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.08.016
Zhao X, Han Y, Li Y, Liu D, Sun M, Zhao Y, Lv C, Li D, Yang Z, Huang L, Teng W, Qiu L, Zheng H, Li W (2015) Loci and candidate gene identification for resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) via association and linkage maps. Plant J 82:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12810
Zhu W, Wei W, Fu Y, Cheng J, Xie J, Li G, Yi X, Kang Z, Dickman M, Jiang D (2013) A secretory protein of necrotrophic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum that suppresses host resistance. PLoS ONE 8:e53901. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053901
Acknowledgements
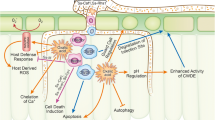
Author PM thank Mr. Wong Gwo Rong for help in the preparation of Fig. 1 and Ms Kanan Kuntala Luitel for her assistance with artwork.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme FP005-2020 (FRGS/1/2020/STG03/UM/02/1) provided by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no known conflict of interest that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazumdar, P. Sclerotinia stem rot in tomato: a review on biology, pathogenicity, disease management and future research priorities. J Plant Dis Prot 128, 1403–1431 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-021-00509-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-021-00509-z