Abstract
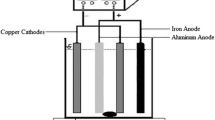
The removal efficiency of the emerging antibiotic waste, amoxicillin, from aqueous media was investigated using the electro-Fenton method with an aluminum anode through the one-factor-at-a-time method, and all the experiments were performed in a useful volume of 750 ml. While the optimum conditions were achieved, the removal kinetic of the contaminant from the environment was investigated. Optimal values of the process parameters including the concentration of the contaminant, process time, initial pH of the samples, electrolyte concentration, electrode distance, and the applied current density were determined as 100 mg.l−1, 90 min, neutral pH, 0.02 M Na2SO4, 5.5 cm, and 5.5 mA.cm−2, respectively. In order to find the optimum conditions, in addition to pollutant removal efficiency, energy consumption was also analyzed. The application of aluminum anodes was found to enhance the efficiency of the process in neutral pH (roughly 95% removal rate), which may be introduced as a potential solution for limitations of the conventional electro-Fenton process in degrading recalcitrant compounds such as amoxicillin. Finally, the obtained results were presented and discussed in detail.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weng X, Cai W, Lin S, Chen Z (2017) Degradation mechanism of amoxicillin using clay supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Appl Clay Sci 147:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.07.023
Singh V, Pandey B, Suthar S (2018) Phytotoxicity of amoxicillin to the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza: growth, oxidative stress, biochemical traits and antibiotic degradation. Chemosphere 201:492–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.010
Kıdak R, Doğan Ş (2018) Medium-high frequency ultrasound and ozone based advanced oxidation for amoxicillin removal in water. Ultrason Sonochem 40:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.01.033
Ensano BMB, Borea L, Naddeo V, Belgiorno V, de Luna MDG, Balakrishnan M, Ballesteros FC Jr (2019) Applicability of the electrocoagulation process in treating real municipal wastewater containing pharmaceutical active compounds. J Hazard Mater 361:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.093
Ayodele OB, Lim JK, Hameed BH (2012) Pillared montmorillonite supported ferric oxalate as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for degradation of amoxicillin. Appl Catal A-Gen 413:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.11.023
Jafari K, Heidari M, Rahmanian O (2018) Wastewater treatment for Amoxicillin removal using magnetic adsorbent synthesized by ultrasound process. Ultrason Sonochem 45:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.03.018
Ahmadzadeh S, Asadipour A, Pournamdari M, Behnam B, Rahimi HR, Dolatabadi M (2017) Removal of ciprofloxacin from hospital wastewater using electrocoagulation technique by aluminum electrode: optimization and modelling through response surface methodology. Process Saf Environ 109:538–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.026
Wang S (2008) A comparative study of Fenton and Fenton-like reaction kinetics in decolourisation of wastewater. Dyes Pigments 76(3):714–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.01.012
Ren G, Zhou M, Su P, Liang L, Yang W, Mousset E (2018) Highly energy-efficient removal of acrylonitrile by peroxi-coagulation with modified graphite felt cathode: Influence factors, possible mechanism. Chem Eng J 343:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.115
Garcia-Segura S, Eiband MMS, de Melo JV, Martínez-Huitle CA (2017) Electrocoagulation and advanced electrocoagulation processes: a general review about the fundamentals, emerging applications and its association with other technologies. J Electroanal Chem 801:267–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.07.047
Nidheesh PV (2018) Removal of organic pollutants by peroxi coagulation. Environ Chem Lett 16(4):1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0752-5
Radwan M, Alalm MG, Eletriby H (2018) Optimization and modeling of electro-Fenton process for treatment of phenolic wastewater using nickel and sacrificial stainless steel anodes. J Water Process Eng 22:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.02.003
Ding J, Jiang M, Zhao G, Wei L, Wang S, Zhao Q (2020) Treatment of leachate concentrate by electrocoagulation coupled with electro-Fenton-like process: efficacy and mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol 255:17668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117668
Dindas GB, Çalışkan Y, Çelebi EE, Tekbaş M, Bektaş N, Yatmaz HC (2020) Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater by combination of electrocoagulation, electro-Fenton and photocatalytic oxidation processes. J Environ Chem Eng 8(3):103777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103777
Hamdi N, Proietto F, Ben Amor H, Galia A, Inguanta R, Ammar S, Gadri A, Scialdone O (2020) Effective removal and mineralization of 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid through a pressurized electro-Fenton-like process with Ni− Cu− Al layered double hydroxide. ChemElectroChem 7(11):2457–2465. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202000463
Guvenc SY, Dincer K, Varank G (2019) Performance of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton processes for treatment of nanofiltration concentrate of biologically stabilized landfill leachate. J Water Process Eng 31:100863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100863
Ghalebizade M, Ayati B (2019) Acid orange 7 treatment and fate by electro-peroxone process using novel electrode arrangement. Chemosphere 235:1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.211
Dassanayake KB, Jayasinghe GY, Surapaneni A, Hetherington C (2015) A review on alum sludge reuse with special reference to agricultural applications and future challenges. Waste Manag 38:321–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.11.025
Sopaj F, Oturan N, Pinson J, Podvorica FI, Oturan MA (2019) Effect of cathode material on electro-Fenton process efficiency for electrocatalytic mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Chem Eng J 384:123249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123249
APHA, A.W.W.A. 2020. WEF (2020). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22.
Kong FX, Lin XF, Sun GD, Chen JF, Guo CM, Xie YF (2019) Enhanced organic removal for shale gas fracturing flowback water by electrocoagulation and simultaneous electro-peroxone process. Chemosphere 218:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.055
Limousy L, Ghouma I, Ouederni A, Jeguirim M (2017) Amoxicillin removal from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared by chemical activation of olive stone. Pollut Res 24(11):9993–10004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7404-8
Suhan MBK, Shuchi SB, Anis A, Haque Z, Islam MS (2020) Comparative degradation study of remazol black B dye using electro-coagulation and electro-Fenton process: kinetics and cost analysis. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100335
Kaur R, Kushwaha JP, Singh N (2019) Amoxicillin electro-catalytic oxidation using Ti/RuO2 anode: mechanism, oxidation products and degradation pathway. Electrochim Acta 296:856–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.114
Naje AS, Chelliapan S, Zakaria Z, Ajeel MA, Alaba PA (2017) A review of electrocoagulation technology for the treatment of textile wastewater. Rev Chem Eng 33(3):263–292. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2016-0019
Núñez J, Yeber M, Cisternas N, Thibaut R, Medina P, Carrasco C (2019) Application of electrocoagulation for the efficient pollutants removal to reuse the treated wastewater in the dyeing process of the textile industry. J Hazard Mater 371:705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.030
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K (2014) A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 2(1):557–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.10.011
Li H, Hu J, Wang C, Wang X (2017) Removal of amoxicillin in aqueous solution by a novel chicken feather carbon: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Air Soil Pollut 228(6):201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3385-6
Wang B, Xu X, Tang H, Mao Y, Chen H, Ji F (2020) Highly efficient adsorption of three antibiotics from aqueous solutions using glucose-based mesoporous carbon. Appl Surf Sci 528:147048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147048
Ghernaout D, Alghamdi A, Ghernaout B (2019) Electrocoagulation process: a mechanistic review at the dawn of its modeling. J Environ Sci Allied Res 2:51–67
Bensadok KS, Benammar S, Lapicque F, Nezzal G (2008) Electrocoagulation of cutting oil emulsions using aluminium plate electrodes. J Hazard Mater 152(1):423–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.121
Izadi A, Hosseini M, Darzi GN, Bidhendi GN, Shariati FP (2018) Treatment of paper-recycling wastewater by electrocoagulation using aluminum and iron electrodes. J Environ Health Sci Eng 16(2):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-018-0314-6
Nidheesh PV, Singh TA (2017) Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation process: recent trends and removal mechanism. Chemosphere 181:418–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.082
Davarnejad R, Nikseresht M (2016) Dairy wastewater treatment using an electrochemical method: Experimental and statistical study. J Electroanal Chem 775(15):364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.06.016
Kim T, Kim TK, Zoh KD (2020) Removal mechanism of heavy metal (Cu, Ni, Zn, and Cr) in the presence of cyanide during electrocoagulation using Fe and Al electrodes. J Water Process Eng 33:101109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101109
Chezeau B, Boudriche L, Vial C, Boudjemaa A (2020) Treatment of dairy wastewater by electrocoagulation process: advantages of combined iron/aluminum electrodes. Sep Sci Technol 55(14):2510–2527. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1638935
Keyikoglu R, Can OT, Aygun A, Tek A (2019) Comparison of the effects of various supporting electrolytes on the treatment of a dye solution by electrocoagulation process. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 33:100210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2019.100210
Tahreen A, Jami MS, Ali F (2020) Role of electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment: a developmental review. J Water Process Eng 37:101440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101440
Ghosh S, Debsarkar A, Dutta A (2019) Technology alternatives for decontamination of arsenic-rich groundwater—a critical review. Environ Technol Innov 13:277–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.12.003
Tiwari A, Sahu O (2017) Treatment of food-agro (sugar) industry wastewater with copper metal and salt: chemical oxidation and electro-oxidation combined study in batch mode. Water Resour Ind 17:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2016.12.001
Hakizimana JN, Gourich B, Chafi M, Stiriba Y, Vial C, Drogui P, Naja J (2017) Electrocoagulation process in water treatment: a review of electrocoagulation modeling approaches. Desalination 404:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.10.011
Zhang Y, Luo G, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Zhou M (2020) Kinetic study of the degradation of rhodamine B using a flow-through UV/electro-Fenton process with the presence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Chemosphere 240:124929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124929
Kalantary RR, Farzadkia M, Kermani M, Rahmatinia M (2018) Heterogeneous electro-Fenton process by Nano-Fe3O4 for catalytic degradation of amoxicillin: process optimization using response surface methodology. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):4644–4652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.043
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
- A commercially available aluminum plate was used as the anode for the electro-Fenton process.
- High decomposition rate of amoxicillin was achieved via relatively low-cost materials.
- A remarkable removal rate in neutral pH ranges was measured using the Al plate.
- Less energy was consumed compared to similar studies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayebi, B., Ayati, B. Degradation of Emerging Amoxicillin Compound from Water Using the Electro-Fenton Process with an Aluminum Anode. Water Conserv Sci Eng 6, 45–54 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-021-00101-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-021-00101-4