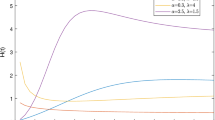
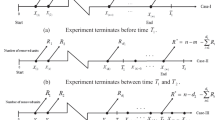
Abstract
In recent life-testing experiments, Progressive Type-II (PT2) censoring has been used by several researchers in various problems. However, one drawback of PT2 is that the length of the experiment might be fairly long. Progressive Type-II hybrid (PT2H) and later adaptive progressive Type-II (APT2) censorings were used to overcome this disadvantage. This study investigates the advantages and disadvantages of these censoring techniques using the Exponential Power (EP) distribution. The EP distribution is known for its ability to model increasing and bathtub-shaped failure rates, and it has gained acceptance in several domains, especially in the areas of reliability-related decision-making and cost analysis. This makes the EP model a useful alternative to the most widely used Weibull distribution in some instances. To assess the efficiency of both Maximum Likelihood Estimators and Bayesian estimators generated through PT2, PT2H, and APT2, we have conducted a comprehensive simulation study. Additionally, we compare the performance of PT2, PT2H, and APT2 when applied to the EP distribution with popular time models using real data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdam N, Kinaci I, Saracoglu B (2017) Statistical inference of stress-strength reliability for the exponential power (ep) distribution based on progressive type-ii censored samples. Hacettepe J Math Stat 46(2):239–253
Almetwally E, Almongy H, Rastogi M, Ibrahim M (2020) Maximum product spacing estimation of weibull distribution under adaptive type-ii progressive censoring schemes. Ann Data Sci 7(2):257–279
Ateya SF, Mohammed HS (2017) Statistical inferences based on an adaptive progressive type-ii censoring from exponentiated exponential distribution. J Egypt Math Soc 25(4):393–399
Balakrishnan N (2007) Progressive censoring methodology: an appraisal. TEST 16(2):211–259
Balakrishnan N, Aggarwala R (2000) Progressive censoring: theory, methods, and applications. BirkhÄauser, Boston
Balakrishnan N, Burkschat M, Cramer E, Hofmann G (2008) Fisher information based progressive censoring plans. Comput Stat Data Anal 53(2):366–380
Balakrishnan N, Cramer E (2014) The art of progressive censoring. In: Statistics for industry and technology
Balakrishnan N, Kundu D (2013) Hybrid censoring: models, inferential results and applications. Comput Stat Data Anal 57(1):166–209
Burkschat M (2008) On optimality of extremal schemes in progressive type ii censoring. J Stat Plan Inference 138(6):1647–1659
Burkschat M, Cramer E, Kamps U (2006) On optimal schemes in progressive censoring. Stat Probab Lett 76(10):1032–1036
Chen S-M, Bhattacharyya GK (1987) Exact confidence bounds for an exponential parameter under hybrid censoring. Commun Stat Theory Methods 16(8):2429–2442
Chen Z (2000) A new two-parameter lifetime distribution with bathtub shape or increasing failure rate function. Stat Probab Lett 49(2):155–161
Childs A, Chandrasekar B, Balakrishnan N, Kundu D (2003) Exact likelihood inference based on type-i and type-ii hybrid censored samples from the exponential distribution. Ann Inst Stat Math 55(2):319–330
Dasgupta R (2011) On the distribution of burr with applications. Sankhya B 73:1–19
Efron B (1982) The jackknife, the bootstrap and other resampling plans. In: SIAM
Epstein B (1954) Truncated life tests in the exponential case. Ann Math Stat 25:555–564
Gajjar A, Khatri C (1969) Progressively censored samples from log-normal and logistic distributions. Technometrics 11(4):793–803
Gupta RD, Kundu D (2001) Exponentiated exponential family: an alternative to gamma and weibull distributions. Biom J J Math Methods Biosci 43(1):117–130
Hastings WK (1970) Monte carlo sampling methods using markov chains and their applications. Biometrika. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/57.1.97
Hemmati F, Khorram E (2017) On adaptive progressively type-ii censored competing risks data. Commun Stat Simul Comput 46(6):4671–4693
Herd GR (1956) Estimation of the parameters of a population from a multi-censored sample. Iowa State University
Jeong H-S, Park J-I, Yum B-J (1996) Development of r, t hybrid sampling plans for exponential lifetime distributions. J Appl Stat 23(6):601–608
Kundu D (2007) On hybrid censored weibull distribution. J Stat Plan Inference 137(7):2127–2142
Kundu D, Joarder A (2006) Analysis of type-ii progressively hybrid censored data. Comput Stat Data Anal 50(10):2509–2528
Lawless JF (2011) Statistical models and methods for lifetime data. Wiley
Leemis LM (1986) Lifetime distribution identities. IEEE Trans Reliab 35(2):170–174
Metropolis N, Rosenbluth AW, Rosenbluth MN, Teller AH, Teller E (1953) Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J Chem Phys 21(6):1087–1092
Mohan R, Chacko M (2021) Estimation of parameters of kumaraswamy-exponential distribution based on adaptive type-ii progressive censored schemes. J Stat Comput Simul 91(1):81–107
Ng HKT, Kundu D, Chan PS (2009) Statistical analysis of exponential lifetimes under an adaptive type-ii progressive censoring scheme. Naval Res Logist (NRL) 56(8):687–698
Rajarshi S, Rajarshi M (1988) Bathtub distributions: a review. Commun Stat Theory Methods 17(8):2597–2621
Smith RM, Bain LJ (1975) An exponential power life-testing distribution. Commun Stat Theory Methods 4(5):469–481
Wu S-J (2008) Estimation of the two-parameter bathtub-shaped lifetime distribution with progressive censoring. J Appl Stat 35(10):1139–1150
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors are equally contributed to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A.
Appendix A.
PT2
PT2H
APT2
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anakha, K.K., Chacko, V.M. Statistical Estimation of Exponential Power Distribution on Different Progressive Type-II Censoring Schemes. J Indian Soc Probab Stat (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41096-023-00172-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41096-023-00172-7