Abstract
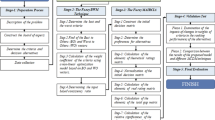
Shared mobility initiatives offer real possibilities to overcome problems such as traffic congestion, air pollution, and natural resource depletion while uniting city residents in a more connected and vibrant atmosphere. This study outlines four innovative and sustainable urban mobility sharing models: electric vehicle \(({{\mathbb{E}}{\mathbb{V}}}),\) autonomous electric vehicle \(({\mathbb{AEV}}),\) electric scooter \(({{\mathbb{E}}{{\mathbb{S}}}}),\) and electric bike \(({{\mathbb{E}}{\mathbb{B}}}),\) all in an effort to promote the ethos of sustainability and shared transportation. By rigorously applying the proposed methodology, we aim to identify optimal transportation solutions that are in harmony with the city’s unique needs and characteristics. Multi-criteria group decision-making is largely dependent on the personal opinions of the experts themselves, which adds an element of subjectivity as well as ambiguity and can influence the preciseness of the outcomes. Pythagorean fuzzy sets manage uncertainty but struggle with subjectivity among experts, while rough sets offer a robust mathematical framework for handling vague and subjective information. The integration of fuzzy and rough methods in Pythagorean fuzzy rough numbers yields a powerful representation of uncertainty that covers the flexibility of fuzzy numbers within adaptive bounding intervals. In multi-criteria decision-making, the Entropy and MARCOS methods have merged as highly effective in evaluating criterion weights and ranking alternative solutions, respectively. Our research aims to advance the field of decision-making by introducing a novel approach that combines Pythagorean fuzzy rough numbers with Entropy and MARCOS methods to create a more comprehensive decision-making model than existing frameworks. We present the Pythagorean fuzzy rough Entropy-MARCOS method (PFR-Entropy-MARCOS) to solve the challenges of a sustainable transportation system in Belgrade, the capital city of Serbia. Through careful application and comparison with other decision-making processes, the method demonstrates remarkable reliability in producing insightful results. This study also involves sensitivity analysis to increase the richness of our findings.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used to support this study.
References
Aguilera-García Á, Gomez J, Sobrino N (2020) Exploring the adoption of moped scooter-sharing systems in Spanish urban areas. Cities 96:102424
Akram Z, Ahmad U (2023) A multi-criteria group decision-making method based on fuzzy rough number for optimal water supply strategy. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08942-y
Akram M, Ashraf M (2023) Multi-criteria group decision-making based on spherical fuzzy rough numbers. Granul Comput 8(6):1267–1298
Akram M, Martino A (2023) Multi-attribute group decision making based on T-spherical fuzzy soft rough average aggregation operators. Granul Comput 8(1):171–207
Akram M, Zahid S (2023) Group decision-making method with Pythagorean fuzzy rough number for the evaluation of best design concept. Granul Comput 8(6):1121–1148
Akram M, Khan A, Luqman A, Senapati T, Pamucar D (2023a) An extended MARCOS method for MCGDM under 2-tuple linguistic q-rung picture fuzzy environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell 120:105892
Akram M, Nawaz HS, Kahraman C (2023b) Rough Pythagorean fuzzy approximations with neighborhood systems and information granulation. Expert Syst Appl 218:119603
Akram M, Ilyas F, Deveci M (2024a) Interval rough integrated SWARA-ELECTRE model: an application to machine tool manufacturing. Expert Syst Appl 238:122067
Akram M, Zahid K, Kahraman C (2024b) A new ELECTRE-based decision-making framework with spherical fuzzy information for the implementation of autonomous vehicles project in Istanbul. Knowl Based Syst 283:111207
Akram M, Zahid S, Deveci M (2024c) Enhanced CRITIC-REGIME method for decision making based on Pythagorean fuzzy rough number. Expert Syst Appl 238:122014
Ali J (2021) A novel score function based CRITIC-MARCOS method with spherical fuzzy information. Comput Appl Math 40(8):280
Alkan Ö, Albayrak ÖK (2020) Ranking of renewable energy sources for regions in Turkey by fuzzy entropy based fuzzy COPRAS and fuzzy MULTIMOORA. Renew Energy 162:712–726
Atanassov KT (1983) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. In: Proceedings of the VII ITKR session, Sofia, Bulgaria (Deposed in Central Sci.-Techn. Library of Bulg. Acad. of Sci., 1697/84) (in Bulgaria)
Awasthi A, Chauhan SS (2012) A hybrid approach integrating affinity diagram, AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS for sustainable city logistics planning. Appl Math Model 36(2):573–584
Awasthi A, Adetiloye T, Crainic TG (2016) Collaboration partner selection for city logistics planning under municipal freight regulations. Appl Math Model 40(1):510–525
Badi I, Pamučar D (2020) Supplier selection for steelmaking company by using combined Grey-MARCOS methods. Decis Mak: Appl Manag Eng 3(2):37–48
Bao Q, Yuxin Z, Yuxiao W, Feng Y (2020) Can entropy weight method correctly reflect the distinction of water quality indices? Water Resour Manag 34:3667–3674
Bellman RE, Zadeh LA (1970) Decision-making in a fuzzy environment. Manag Sci 17:141–164
Biswas R (1994a) On rough sets and fuzzy rough sets. Bull Pol Acad Sci Math 42:345–349
Biswas R (1994b) On rough fuzzy sets. Bull Pol Acad Sci Math 42:352–355
Brandstätter G, Gambella C, Leitner M, Malaguti E, Masini F, Puchinger J, Ruthmair M, Vigo D (2016) Overview of optimization problems in electric car-sharing system design and management. In: Dawid H, Doerner K, Feichtinger G, Kort P, Seidl A (eds) Dynamic perspectives on managerial decision making. Dynamic modeling and econometrics in economics and finance, vol 22. Springer, Cham, pp 441–471
Buldeo Rai H, Verlinde S, Merckx J, Macharis C (2017) Crowd logistics: an opportunity for more sustainable urban freight transport? Eur Transp Res Rev 9:39
Chakraborty S, Chattopadhyay R, Chakraborty S (2020) An integrated D-MARCOS method for supplier selection in an iron and steel industry. Decis Mak: Appl Manag Eng 3(2):49–69
Chen SM, Jian WS (2017) Fuzzy forecasting based on two-factors second-order fuzzy-trend logical relationship groups, similarity measures and PSO techniques. Inf Sci 391:65–79
Chen SM, Wang JY (1995) Document retrieval using knowledge-based fuzzy information retrieval techniques. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25(5):793–803
Chen SM, Wang NY (2010) Fuzzy forecasting based on fuzzy-trend logical relationship groups. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 40(5):1343–1358
Chen C, Zhang H (2023) Evaluation of green development level of Mianyang agriculture, based on the entropy weight method. Sustainability 15(9):7589
Chen SM, Ko YK, Chang YC, Pan JS (2009) Weighted fuzzy interpolative reasoning based on weighted increment transformation and weighted ratio transformation techniques. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17(6):1412–27
Chen SM, Zou XY, Gunawan GC (2019) Fuzzy time series forecasting based on proportions of intervals and particle swarm optimization techniques. Inf Sci 500:127–139
Cieśla M, Sobota A, Jacyna M (2020) Multi-criteria decision making process in metropolitan transport means selection based on the sharing mobility idea. Sustainability 12(17):7231
Cunha-Zeri G, Guidolini JF, Branco EA, Ometto JP (2022) How sustainable is the nitrogen management in Brazil? A sustainability assessment using the Entropy Weight Method. J Environ Manag 316:115330
Daraio C, Diana M, Di Costa F, Leporelli C, Matteucci G, Nastasi A (2016) Efficiency and effectiveness in the urban public transport sector: a critical review with directions for future research. Eur J Oper Res 248(1):1–20
Deveci M, Canitez F, Gökaşar I (2018) WASPAS and TOPSIS based interval type-2 fuzzy MCDM method for a selection of a car sharing station. Sustain Cities Soc 41:777–791
Dos Santos BM, Godoy LP, Campos LM (2019) Performance evaluation of green suppliers using entropy-TOPSIS-F. J Clean Prod 207:498–509
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17:191–209
Duc Trung D (2022) Multi-criteria decision making under the MARCOS method and the weighting methods: applied to milling, grinding and turning processes. Manuf Rev 9:3
Ecer F, Pamucar D (2021) MARCOS technique under intuitionistic fuzzy environment for determining the COVID-19 pandemic performance of insurance companies in terms of healthcare services. Appl Soft Comput 104:107199
Fan J, Yuanyuan L, Xingyuan W (2019) An extended MABAC method for multi-criteria group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy rough numbers. Expert Syst Appl 127:241–255
Fatima S, Sarwar M, Zafar F (2023) Rough approximations of similarity measures under Pythagorean fuzzy information: a novel approach to decision-making. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09193-7
Ferrero F, Perboli G, Rosano M, Vesco A (2018) Car-sharing services: an annotated review. Sustain Cities Soci 37:501–518
Gao P, Wang X, Wang H, Cheng C (2020) A correction to the entropy weight coefficient method by Shen et al. for accessing urban sustainability [Cities 42 (2015) 186194]. Cities 103:102742
Haseli G, Bonab SR, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Ghoushchi SJ, Deveci M (2024) Fuzzy ZE-numbers framework in group decision-making using the BCM and CoCoSo to address sustainable urban transportation. Inf Sci 653:119809
He Y, Csiszár C (2020) Quality assessment method for mobility as a service. Promet Traffic Transp 32(5):611–624
Horng YJ, Chen SM, Chang YC, Lee CH (2005) A new method for fuzzy information retrieval based on fuzzy hierarchical clustering and fuzzy inference techniques. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 13(2):216–28
Hu Y, Zhang Y, Lamb D, Zhang M, Jia P (2019) Examining and optimizing the BCycle bike-sharing system—a pilot study in Colorado, US. Appl Energy 247:1–12
Ibrahim HA, Qahtan S, Zaidan AA, Deveci M, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mohammed RT, Alamoodi AH (2024) Sustainability in mobility for autonomous vehicles over smart city evaluation; using interval-valued fermatean fuzzy rough set-based decision-making model. Eng Appl Artif Intell 129:107609
Ji Y, Huang GH, Sun W (2015) Risk assessment of hydropower stations through an integrated fuzzy entropy-weight multiple criteria decision making method: a case study of the Xiangxi River. Expert Syst Appl 42(12):5380–5389
Khemiri R, Naija M, Exposito E (2023) Dispatching and rebalancing for ride-sharing autonomous mobility-on-demand systems based on a fuzzy multi-criteria approach. Soft Comput 27(4):2041–2069
Kim K (2015) Can carsharing meet the mobility needs for the low-income neighborhoods? Lessons from carsharing usage patterns in New York City. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 77:249–260
Li W, Kamargianni M (2018) Providing quantified evidence to policy makers for promoting bike-sharing in heavily air-polluted cities: a mode choice model and policy simulation for Taiyuan-China. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 111:277–291
Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang L, Liang L (2020) Regional environmental efficiency in China: an empirical analysis based on entropy weight method and non-parametric models. J Clean Prod 276:124147
Luqman A, Akram M, Alcantud JCR (2021) Digraph and matrix approach for risk evaluations under Pythagorean fuzzy information. Expert Syst Appl 170:114518
Melkonyan A, Gruchmann T, Lohmar F, Bleischwitz R (2022) Decision support for sustainable urban mobility: a case study of the Rhine-Ruhr area. Sustain Cities Soc 80:103806
Nakamura A (1988) Fuzzy rough sets. Note Mult Valued Log Jpn 9(8):1–8
Nanda S, Majumdar S (1992) Fuzzy rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 45:157–160
Pamučar D, Petrović I, Ćirović G (2018) Modification of the best-worst and MABAC methods: a novel approach based on interval-valued fuzzy-rough numbers. Expert Syst Appl 91:89–106
Pamučar D, Ecer F, Deveci M (2021) Assessment of alternative fuel vehicles for sustainable road transportation of United States using integrated fuzzy FUCOM and neutrosophic fuzzy MARCOS methodology. Sci Total Environ 788:147763
Pamučar D, Deveci M, Gokasar I, Popovic M (2022a) Fuzzy Hamacher WASPAAS decision-making model for advantage prioritization of sustainable supply chain of electric ferry implementation in public transportation. Environ Dev Sustain 24:7138–7177
Pamučar D, Simic V, Lazarević D, Dobrodolac M, Deveci M (2022b) Prioritization of sustainable mobility sharing systems using integrated fuzzy DIBR and fuzzy-rough EDAS model. Sustain Cities Soc 82:103910
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Pawlak Z (1985) Rough sets and fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 17:99–102
Pawlak Z (1996) Rough sets, rough relations and rough functions. Fundamenta Informaticae 27(2):103–108
Puška A, Stojanovic I, Maksimovic A, Osmanovic N (2020) Project management software evaluation by using the measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS) method. Oper Res Eng Sci: Theory Appl 3(1):89–102
Qu M, Yu S, Yu M (2017) An improved approach to evaluate car sharing options. Ecol Indic 72:686–702
Santos G (2017) Road transport and CO2 emissions: what are the challenges? Transp Policy 59:71–74
Sarwar M (2023) Improved assessment model for health-care waste management based on dual 2-tuple linguistic rough number clouds. Eng Appl Artif Intell 123:106255
Sarwar M, Akram M (2023) Certain hybrid rough models with type-2 soft information. J Mult Valued Log Soft Comput 40:433–467
Sarwar M, Akram M, Liu P (2021) An integrated rough ELECTRE II approach for risk evaluation and effects analysis in automatic manufacturing process. Artif Intell Rev 54:4449–4481
Sarwar M, Ali G, Shahzadi S (2023a) Dual interval rough integrated cloud COPRAS method: a novel hybrid assessment model for remanufacturing system selection. Soft Comput 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09327-x
Sarwar M, Zafar F, Akram M (2023b) Novel group decision making approach based on the rough soft approximations of graphs and hypergraphs. J Appl Math Comput 69:2795–2830
Sarwar M, Gulzar W, Ashraf S (2023c) Improved risk assessment model based on rough integrated clouds and ELECTRE-II method: an application to intelligent manufacturing process. Granul Comput 8(6):1533–1560
Shemshadi A, Shirazi H, Toreihi M, Tarokh MJ (2011) A fuzzy VIKOR method for supplier selection based on entropy measure for objective weighting. Expert Syst Appl 38:12160–12167
Simić V, Lazarević D, Dobrodolac M (2021) Picture fuzzy WASPAS method for selecting last-mile delivery mode: a case study of Belgrade. Eur Transp Res Rev 13(1):1–22
Stanković M, Stević Ž, Das DK, Subotić M, Pamučar D (2020) A new fuzzy MARCOS method for road traffic risk analysis. Mathematics 8(3):457
Stević Ž, Pamučar D, Puška A, Chatterjee P (2020) Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS). Comput Ind Eng 140:106231
Tian ZP, Wang JQ, Wang J, Zhang HY (2018) A multi-phase QFD-based hybrid fuzzy MCDM approach for performance evaluation: a case of smart bike-sharing programs in Changsha. J Clean Prod 171:1068–1083
Xue Y, Zhang Y, Chen Y (2019) An evaluation framework for the planning of electric car-sharing systems: a combination model of AHP-CBA-VD. Sustainability 11(20):5627
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean fuzzy subsets. In: 2013 joint IFSA world congress and NAFIPS annual meeting (IFSA/NAFIPS), vol 6608375. IEEE, pp 57–61
Yager RR (2013b) Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):958–965
Yannis G, Kopsacheili A, Dragomanovits A, Petraki V (2020) State-of-the-art review on multi-criteria decision-making in the transport sector. J Traffic Transp Eng 7(4):413–431
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf Sci 8:199–249
Zahid K, Akram M (2023) Multi-criteria group decision-making for energy production from municipal solid waste in Iran based on spherical fuzzy sets. Granul Comput 8(6):1299–323
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhong ZW (2008) A rough set enhanced fuzzy approach to quality function deployment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:613–624
Zhi-Hong Z, Yi Y, Jing-Nan S (2006) Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. J Environ Sci 18:1020–1023
Zhu Y, Tian D, Yan F (2020a) Effectiveness of entropy weight method in decision-making. Math Probl Eng 2020:1–5
Zhu GN, Hu J, Ren H (2020b) A fuzzy rough number-based AHP-TOPSIS for design concept evaluation under uncertain environments. Appl Soft Comput 91:106228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Akram: concept, design, analysis, writing, and revision of the manuscript. Sadaf Zahid: concept, design, analysis, writing, and revision of the manuscript. Ahmad N. Al-Kenani: concept, design, analysis, writing, and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, M., Zahid, S. & Al-Kenani, A.N. Multi-criteria group decision-making for evaluating efficient and smart mobility sharing systems using Pythagorean fuzzy rough numbers. Granul. Comput. 9, 50 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-024-00466-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-024-00466-6