Abstract
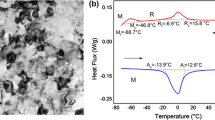
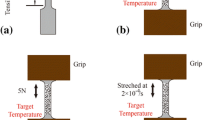
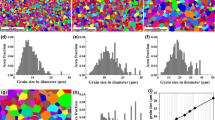
We report recent progress in tailoring the thermal expansion (TE) of nanocrystalline (NC) NiTi by microstructure hierarchical design and control without composition change. Fabrication and characterization methods are outlined and preliminary results of both experiment and mechanism-based modeling are presented to understand and get insight into the unusual TE phenomena. The important roles of the intrinsic thermal expansion anisotropy of B19′ lattice and the suppression of phase transition by the extrinsic fabricated microstructure (cold rolling and annealing, grain size, defects, textures and volume fractions of nanoscaled B2 and B19′ lattices) in the overall macroscopic TE behaviors of the superelastic NC NiTi polycrystal SMAs are emphasized.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kittel C (2004) Introduction to Solid State Physics, 8th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Roy R, Agrawal DK, McKinstry HA (1989) Very low thermal expansion coefficient materials. Annu Rev Mater Sci 19(1):59–81
Chen J, Hu L, Deng J, Xing X (2015) Negative thermal expansion in functional materials: controllable thermal expansion by chemical modifications. Chem Soc Rev 44(11):3522–3567
Lind C (2012) Two decades of negative thermal expansion research: where do we stand? Materials 5(6):1125–1154
van Schilfgaarde M, Abrikosov IA, Johansson B (1999) Origin of the Invar effect in iron–nickel alloys. Nature 400(6739):46–49
Laboratories B, Technologies L, Hill M (2015) Pressure-induced amorphization and negative thermal expansion in ZrW2O8. Science 280:886–888
Kainuma R, Wang JJ, Omori T, Sutou Y, Ishida K (2002) Invar-type effect induced by cold-rolling deformation in shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett 80(23):4348–4350
Sutou Y, Omori T, Wang JJ, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2004) Characteristics of Cu-Al-Mn-based shape memory alloys and their applications. Mater Sci Eng A 378(1):278–282
Monroe JA, Gehring D, Karaman I, Arroyave R, Brown DW, Clausen B (2016) Tailored thermal expansion alloys. Acta Mater 102:333–341
Research Project (Project No. 16209817) on “Negative and zero thermal expansion NiTi alloy by microstructure engineering” (2018–2020) funded by the Research Grant Council of Hong Kong SAR, China
Ahadi A, Matsushita Y, Sawaguchi T, Sun QP, Tsuchiya K (2017) Origin of zero and negative thermal expansion in severely-deformed superelastic NiTi alloy. Acta Mater 124:79–92
Ahadi A, Sun Q (2013) Stress hysteresis and temperature dependence of phase transition stress in nanostructured NiTi-effects of grain size. Appl Phys Lett 103(2):021902
Ahadi A, Sun Q (2014) Effects of grain size on the rate-dependent thermomechanical responses of nanostructured superelastic NiTi. Acta Mater 76:186–197
Sun Q, Aslan A, Li M, Chen M (2014) Effects of grain size on phase transition behavior of nanocrystalline shape memory alloys. Sci China Technol Sci 57(4):671–679
Ahadi A, Sun Q (2015) Stress-induced nanoscale phase transition in superelastic NiTi by in situ X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater 90:272–281
Dadbakhsh S, Speirs M, Kruth JP, Schrooten J, Luyten J, Van Humbeeck J (2014) Effect of SLM parameters on transformation temperatures of shape memory nickel titanium parts. Adv Eng Mater 16(9):1140–1146
Waitz T, Kazykhanov V, Karnthaler HP (2004) Martensitic phase transformations in nanocrystalline NiTi studied by TEM. Acta Mater 52(1):137–147
Simon T, Kröger A, Somsen C, Dlouhy A, Eggeler G (2009) ESOMAT 2009–8th Eur. Symp Martensitic Transform 2030:1–7
Delville R, Malard B, Pilch J, Sittner P, Schryvers D (2011) Transmission electron microscopy investigation of dislocation slip during superelastic cycling of Ni-Ti wires. Int J Plast 27(2):282–297
Tsuchiya K, Inuzuka M, Tomus D, Hosokawa A, Nakayama H, Morii K, Todaka Y, Umemoto M (2006) Martensitic transformation in nanostructured TiNi shape memory alloy formed via severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 438:643–648
Kim YH, Cho GB, Hur SG, Jeong SS, Nam TH (2006) Nanocrystallization of a Ti-50.0 Ni (at.%) alloy by cold working and stress/strain behavior. Mater Sci Eng A 438:531–535
Waitz T, Tsuchiya K, Antretter T, Fischer FD (2009) Phase transformations of nanocrystalline martensitic materials. MRS Bull 34(11):814–821
Delville R, Kasinathan S, Zhang Z, Humbeeck JV, James RD, Schryvers D (2010) Transmission electron microscopy study of phase compatibility in low hysteresis shape memory alloys. Phil Mag 90(1–4):177–195
Tsuchiya K, Hada Y, Koyano T, Nakajima K, Ohnuma M, Koike T, Todaka Y, Umemoto M (2009) Production of TiNi amorphous/nanocrystalline wires with high strength and elastic modulus by severe cold drawing. Scripta Mater 60(9):749–752
Peterlechner M, Waitz T, Karnthaler HP (2008) Nanocrystallization of NiTi shape memory alloys made amorphous by high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater 59(5):566–569
Nakayama H, Tsuchiya K, Umemoto M (2001) Crystal refinement and amorphisation by cold rolling in TiNi shape memory alloys. Scripta Mater 44(8):1781–1785
Yu C, Aoun B, Cui L, Liu Y, Yang H, Jiang X, Cai S, Jiang D, Liu Z, Brown D, Ren Y (2016) Synchrotron high energy X-ray diffraction study of microstructure evolution of severely cold drawn NiTi wire during annealing. Acta Mater 115:35–44
Delville R, Malard B, Pilch J, Sittner P, Schryvers D (2010) Microstructure changes during non-conventional heat treatment of thin Ni–Ti wires by pulsed electric current studied by transmission electron microscopy. Acta Mater 58(13):4503–4515
Prokoshkin S, Brailovski V, Dubinskiy S, Inaekyan K, Kreitcberg A (2016) Gradation of nanostructures in cold-rolled and annealed Ti-Ni shape memory alloys. Shape Mem Superelast 2(1):12–17
Ko WS, Grabowski B, Neugebauer J (2015) Development and application of a Ni-Ti interatomic potential with high predictive accuracy of the martensitic phase transition. Phys Rev B 92(13):134107
Ko WS, Maisel SB, Grabowski B, Jeon JB, Neugebauer J (2017) Atomic scale processes of phase transformations in nanocrystalline NiTi shape-memory alloys. Acta Mater 123:90–101
Yu C, Sun QP, Kang GZ, (2017). Modeling martensite reorientation and the resulting zero and negative thermal expansion of shape memory alloys, unpublished work
Duerig TW, Pelton A, Stöckel D (1999) An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater Sci Eng A 273:149–160
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to the financial support from the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (Project No. 16209817) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 11532010) to the work of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Yu, C. & Kang, G. Negative and Zero Thermal Expansion NiTi Superelastic Shape Memory Alloy by Microstructure Engineering. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 4, 158–164 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0151-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0151-6