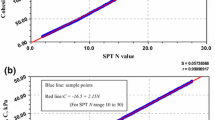
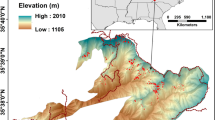
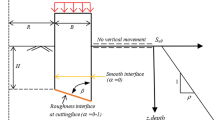
Abstract
Slope stability is the main attribute of geotechnical engineering systems which can be established by calculating factor of safety, FoS. In this context, there are various existing conventional methods which can be used for slope stability analysis. However, in the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the slope stability analysis can be performed using soft computing, SoCom, models which have superior predictive capability in comparison to other methods. SoCom is capable of addressing uncertainty and imprecision and which can be quantified using statistical parameters (viz., R2, RMSE, MAPE, t-stat, etc.). In this context, this review paper mainly focuses on conventional methods viz., Bishop method, Taylor method, Janbu method, Hoek–Brown method, apart from SoCom models viz., SVM, Model Tree, CA, ELM, GRNN, GPR, MARS, MCS, GP, etc. Also, quality assessment parameter like data preprocessing techniques and performance measures have been covered in this paper. Furthermore, merits and limitations of SoCom techniques in comparison to conventional approaches has also been discussed elaborately in this review.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SoCom :
-
Soft computing
- FoS :
-
Factor of safety
- β :
-
Reliability index
- CA:
-
Cubist Algorithm
- MARS:
-
Multivariate adaptive regression splines
- ELM:
-
Extreme learning machines
- GPR:
-
Gaussian process regression
- GRNN:
-
Generalized regression neural networks
- MCS:
-
Monte-Carlo simulation
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- GP:
-
Genetic Programming
- FN:
-
Functional network
- sd :
-
Standard deviation
- AAE :
-
Average absolute error
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- Adj R 2 :
-
Adjusted coefficient determination
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- NS:
-
Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency
- VAF:
-
Variance account factor
- MAE:
-
Maximum absolute error
- MBE:
-
Mean bias error
- WMAE:
-
Weighted mean absolute error
- MAPE:
-
Mean absolute percentage error
- NMBE:
-
Normalized mean bias error
- RPD:
-
Relative percent difference
- LMI:
-
Legate and McCabe’s Index
- U 95 :
-
Uncertainty at 95% confidence level
- α, β :
-
Slope angle
- c :
-
Cohesion
- ϕ :
-
Angle of internal friction
- γ :
-
Unit weight
- τ :
-
Shear stress
References
Al-karni AA, Al-shamrani MA (2000) Study of the effect of soil anisotropy on slope stability using method of slices. Comput Geotech 26:83–103
Armstrong JS, Collopy F (1992) Error measures for generalizing about forecasting methods: empirical comparisons. Int J Forecast 8:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-2070(92)90008-W
ASTM International (1966) Testing Techniques For Rock Mechanics - American Society for Testing and Materials—Google Books. The Society, 1966
Baker R (2004) Nonlinear mohr envelopes based on triaxial data. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng 130:498–506. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(2004)130:5(498)
Bardhan A, Gokceoglu C, Burman A et al (2021) Efficient computational techniques for predicting the California bearing ratio of soil in soaked conditions. Eng Geol 291:106239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106239
Behar O, Khellaf A, Mohammedi K (2015) Comparison of solar radiation models and their validation under Algerian climate—the case of direct irradiance. Energy Convers Manag 98:236–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.03.067
Bieniawski ZT (1989) Engineering rock mass classifications: a complete manual for engineers and geologists in mining, civil, and petroleum engineering. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Bishop AW (1955) The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes. Geotechnique 5:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1955.5.1.7
Boser BE, Vapnik VN, Guyon IM (1992) Training Algorithm Margin for Optimal Classifiers. Perception 144–152
Bui XN, Nguyen H, Choi Y et al (2020) Prediction of slope failure in open-pit mines using a novel hybrid artificial intelligence model based on decision tree and evolution algorithm. Sci Rep 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66904-y
Chen L, Zhang W, Gao X, Wang L, Li Z, Böhlke T, Perego U (2020) Design charts for reliability assessment of rock bedding slopes stability against bi-planar sliding: SRLEM and BPNN approaches. Georisk. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2020.1815215
Dijkstra TA, Dixon N (2010) Climate change and slope stability in the UK: challenges and approaches. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 43:371–385. https://doi.org/10.1144/1470-9236/09-036
Dyson AP, Tolooiyan A (2019) Prediction and classification for finite element slope stability analysis by random field comparison. Comput Geotech 109:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.01.026
Etemad-Shahidi A, Bali M (2012) Stability of rubble-mound breakwater using H50 wave height parameter. Coast Eng 59:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2011.07.002
Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann Stat. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176347963
Goh ATC, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhang W, Xiao Y (2017) Evaluating stability of underground entry-type excavations using multivariate adaptive regression splines and logistic regression. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 70:148–154
Goh ATC, Zhang WG, Zhang YM, Xiao Y, Xiang YZ (2018) Determination of EPB tunnel-related maximum surface settlement: a multivariate adaptive regression splines approach. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:489–500
Gueymard C (2014) A review of validation methodologies and statistical performance indicators for modeled solar radiation data: towards a better bankability of solar projects. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:1024–1034
Hassan MA, Ismail MAM, Shaalan HH (2022) Numerical modeling for the effect of soil type on stability of embankment. Civ Eng J 7:41–57. https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-SP2021-07-04
Hoek E, Brown ET (1997) Practical estimates of rock mass strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34:1165–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80069-X
Hoek E, Marinos P, Benissi M (1998) Applicability of the geological strength index (GSI) classification for very weak and sheared rock masses. The case of the Athens Schist Formation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 57:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100640050031
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems. Univ Michigan Press Ann Arbor Mich. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-006-9026-6
Janbu N (1973) Slope stability computations. John Wiley Sons, Hoboken
Javankhoshdel S, Bathurst RJ (2014) Simplified probabilistic slope stability design charts for cohesive and cohesive-frictional (c-ø) soils. Can Geotech J 1045:1033–1045
Jung NC, Popescu I, Kelderman P et al (2010) Application of model trees and other machine learning techniques for algal growth prediction in yongdam reservoir, Republic of Korea. J Hydroinformatics 12:262–274. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2009.004
Kadar I (2017) The examination of different soil parameters’ coefficient of variation values and types of distributions. issmge.org
Kainthola A, Verma D, Thareja R, Singh TN (2013) A review on numerical slope stability analysis. Int J Sci Eng Technol Res 2:1315–1320
Kardani N, Bardhan A, Kim D et al (2021) Modelling the energy performance of residential buildings using advanced computational frameworks based on RVM, GMDH, ANFIS-BBO and ANFIS-IPSO. J Build Eng 35:102105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.102105
Keshtegar B, Kisi O (2017) M5 model tree and Monte Carlo simulation for efficient structural reliability analysis. Appl Math Model 48:899–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.02.047
Kong D, Luo Q, Zhang W et al (2022) Reliability analysis approach for railway embankment slopes using response surface method based Monte Carlo simulation. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02168-9
Koza JR (1994) Genetic programming as a means for programming computers by natural selection. Stat Comput 4:87–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175355
Koza J (1992) Genetic programming: on the programming of computers by means of natural selection
Kuhn M, Weston S, Keefer C, Coulter N (2016) Cubist Models For Regression. R Packag Vignette R Packag version 00 18
Kumar M, Bardhan A, Samui P et al (2021) Reliability analysis of pile foundation using soft computing techniques: a comparative study. Processes 9:486. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030486
Kung GT, Juang CH, Hsiao EC, Hashash YM (2007) Simplified model for wall deflection and ground-surface settlement caused by braced excavation in clays. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng 133:731–747. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:6(731)
LeBlanc M, Tibshirani R (1994) Adaptive principal surfaces. J Am Stat Assoc 89:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1994.10476445
Legates DR, Mccabe GJ (2013) A refined index of model performance: a rejoinder. Int J Climatol 33:1053–1056. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3487
Li YX, Yang XL (2019) Soil-slope stability considering effect of soil-strength nonlinearity. Int J Geomech 19:04018201. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0001355
Lin Y, Zhou K, Li J (2018) Prediction of slope stability using four supervised learning methods. IEEE Access 6:31169–31179. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2843787
Liu Z, Shao J, Xu W et al (2014) An extreme learning machine approach for slope stability evaluation and prediction. Nat Hazards 73:787–804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1106-7
Liu Q, Liu Y, Peng J et al (2018) Linking GRNN and neighborhood selection algorithm to assess land suitability in low-slope hilly areas. Ecol Indic 93:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.008
Liu LL, Zhang P, Zhang SH et al (2022) Efficient evaluation of run-out distance of slope failure under excavation. Eng Geol 306:106751. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGGEO.2022.106751
Liu ZB, Xu WY, Jin HY, Liu DW (2010) Study on warning criterion for rock slope on left bank of Jinping No.1 Hydropower Station. Shuili Xuebao/Journal Hydraul Eng 41:
Luo Z, Bui XN, Nguyen H, Moayedi H (2021) A novel artificial intelligence technique for analyzing slope stability using PSO-CA model. Eng Comput 37:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00839-5
Mahdiyar A, Hasanipanah M, Armaghani DJ et al (2017) A Monte Carlo technique in safety assessment of slope under seismic condition. Eng Comput 33:807–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0499-1
Manouchehrian A, Gholamnejad J, Sharifzadeh M (2014) Development of a model for analysis of slope stability for circular mode failure using genetic algorithm. Environ Earth Sci 71:1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2531-8
Mehta AK, Kumar D, Singh P, Samui P (2021) Modelling of Seismic Liquefaction Using Classification Techniques. Int J Geotech Earthq Eng 12:12–21. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJGEE.2021010102
Mockus J (2005) The Bayesian approach to global optimization. System modeling and optimization. Kluwer academic publishers, New York, pp 473–481
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Peethambaran B, Kanungo DP, Anbalagan R (2022) Insights to pre- and post-event stability analysis of rainfall-cum-anthropogenically induced recent Laxmanpuri landslide, Uttarakhand, India. Environ Earth Sci 81:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-021-10143-5
Phoon K-K, Zhang W (2022) Future of machine learning in geotechnics. Georisk Assess Manag Risk Eng Syst Geohazards. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2022.2087884
Pinheiro M, Sanches S, Miranda T et al (2015) A new empirical system for rock slope stability analysis in exploitation stage. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 76:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.015
Polat Ö, Yildirim T (2008) Genetic optimization of GRNN for pattern recognition without feature extraction. Expert Syst Appl 34:2444–2448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.04.006
Pouladi N, Møller AB, Tabatabai S, Greve MH (2019) Mapping soil organic matter contents at field level with Cubist, Random Forest and kriging. Geoderma 342:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.02.019
Prasomphan S, Machine SM (2013) Generating prediction map for geostatistical data based on an adaptive neural network using only nearest neighbors. Int J Mach Learn Comput 3:98
Quinlan JR (1993) A case study in machine learning. Proc 16th Aust Comput Sci Conf 2:731–737
Rafiei Renani H, Martin CD (2020) Slope stability analysis using equivalent mohr-coulomb and hoek-brown criteria. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01889-3
Rasmussen CE (2004) Gaussian processes in machine learning. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 63–71
Ray R, Choudhary SS, Roy LB (2022) Reliability analysis of soil slope stability using MARS, GPR and FN soft computing techniques. Model Earth Syst Environ 8:2347–2357. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40808-021-01238-W
Sakellariou MG, Ferentinou MD (2005) A study of slope stability prediction using neural networks. Geotech Geol Eng 23:419–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-004-8680-5
Samui P (2008) Slope stability analysis: a support vector machine approach. Environ Geol 56:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1161-4
Singh P, Kumar D, Samui P (2020) Reliability analysis of rock slope using soft computing techniques. Jordan J Civ Eng 14:27–42
Singh P, Mehta A, Kumar D, Samui P (2019) Rock slope reliability analysis using genetic programming. In: ICGGE. MNNIT Allahabad, ICGGE- 2019, Allahabad, pp 1–7
Specht DF (1991) A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 6:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.97934
Srinivasulu S, Jain A (2006) A comparative analysis of training methods for artificial neural network rainfall-runoff models. Appl Soft Comput J 6:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2005.02.002
Steward T, Sivakugan N, Shukla SK, Das BM (2011) Taylor’s slope stability charts revisited. Int J Geomech 11:348–352. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000093
Stone RJ (1993) Improved statistical procedure for the evaluation of solar radiation estimation models. Sol Energy 51:289–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(93)90124-7
Suman S, Khan SZ, Das SK, Chand SK (2016) Slope stability analysis using artificial intelligence techniques. Nat Hazards 84:727–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2454-2
Taheri A, Tani K (2010) Assessment of the stability of Rock slopes by the slope stability rating classification system. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-009-0050-4
Tang L, Ma Y, Wang L, Zhang W, Zheng L, Wen H (2021) Application of long short-term memory neural network and prophet algorithm in slope displacement prediction. Int J Geoeng Case Hist 6(4):48–66
Taylor D (1937) Stability of earth slopes. J Bost Soc Civ
Tinoco J, Gomes Correia A, Cortez P, Toll DG (2018) Stability condition identification of rock and soil cutting slopes based on soft computing. J Comput Civ Eng 32:04017088. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000739
Tobutt DC (1982) Monte Carlo simulation methods for slope stability. Comput Geosci 8:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(82)90021-8
Verma D, Kainthola A, Thareja R, Singh TN (2013) Stability analysis of an open cut slope in Wardha valley coal field. J Geol Soc India 81:804–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0105-8
Viscarra Rossel RA, McGlynn RN, McBratney AB (2006) Determining the composition of mineral-organic mixes using UV-vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 137:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.07.004
Wang Y, Witten IH (1997) Induction of model trees for predicting continuous classes. In: Proc. 9th Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn. Poster Pap. 128–137
Wang Z, Liu H, Gao X, Böhlke T, Zhang W (2020) Stability analysis of soil slopes based on strain information. Acta Geotech 15(11):3121–3134
Wang Z, Gu D, Zhang W (2021) A DEM study on influence of excavation schemes on slope stability. J Mt Sci 17:1509–1522
Williams CKI (1998) Prediction with Gaussian processes: from linear regression to linear prediction and beyond. Learning in graphical models. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 599–621
Wong JL, Lee ML, Teo FY, Liew KW (2022) A review of impacts of climate change on slope stability. Lect Notes Civ Eng 178:157–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5501-2_13
Wu C, Hong L, Wang L et al (2022) Prediction of wall deflection induced by braced excavation in spatially variable soils via convolutional neural network, Gondwana Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.g.
Xiang X, Zi-Hang D (2017) Numerical implementation of a modified Mohr-Coulomb model and its application in slope stability analysis. J Mod Transp 25:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40534-017-0123-0
Yuan C, Moayedi H (2020) The performance of six neural-evolutionary classification techniques combined with multi-layer perception in two-layered cohesive slope stability analysis and failure recognition. Eng Comput 36:1705–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00791-4
Yuvaraj P, Ramachandra Murthy A, Iyer NR et al (2013) Multivariate adaptive regression splines model to predict fracture characteristics of high strength and ultra high strength concrete beams. Comput Mater Contin 36:73–97
Zhang WG, Goh ATC (2013) Multivariate adaptive regression splines for analysis of geotechnical engineering systems. Comput Geotech 48:82–95
Zhang WG, Goh ATC (2016) Multivariate adaptive regression splines and neural network models for prediction of pile drivability. Geosci Frontiers 7:45–52
Zhang WG, Phoon KK (2022) Editorial for Advances and applications of deep learning and soft computing in geotechnical underground engineering. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 4:671–673
Zhang T, Cai Q, Han L et al (2017) 3D stability analysis method of concave slope based on the Bishop method. Int J Min Sci Technol 27:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2017.01.020
Zhang W, Zhang R, Wu C et al (2020) State-of-the-art review of soft computing applications in underground excavations. Geosci Front 11:1095–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.12.003
Zhang W, Li H, Li Y, Liu H, Chen Y, Ding X (2021) Application of deep learning algorithms in geotechnical engineering: a short critical review. Artif Intell Rev 54(8):5633–5673
Zhang WG, Li HR, Tang LB, Gu X, Wang LQ, Wang L (2022) Displacement prediction of Jiuxianping landslide using gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01495-8
Zhang W, Li H, Han L, Chen L, Wang L (2022a) Prediction of slope stability using ensemble learning techniques: a case study in Yunyang County, Chongqing, China. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.12.011
Zhang W, Gu X, Tang L, Yin Y, Liu D, Zhang Y (2022b) Application of machine learning, deep learning and optimization algorithms in geoengineering and geoscience: comprehensive review and future challenge. Gondwana Res 109:1–17
Zhang J, Li J (2019) A comparative study between infinite slope model and Bishop’s method for the shallow slope stability evaluation. 25:1503–1520. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2019.1584768
Zhou J, Li E, Yang S et al (2019) Slope stability prediction for circular mode failure using gradient boosting machine approach based on an updated database of case histories. Saf Sci 118:505–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.05.046
Funding
High-end Foreign Experts Recruitment Plan of China, DL2021165001L, Zhang, G20200022005, Wengang Zhang, Chongqing Science and Technology Commission, 2019-0045, Wengang Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Bardhan, A., Han, F. et al. A critical review of conventional and soft computing methods for slope stability analysis. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 9, 1–17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01489-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01489-1