Abstract
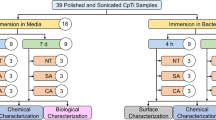
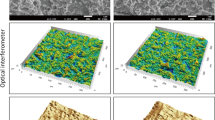
Peri-implantitis is one of the major clinical conditions associated with dental implant failure. Adhesion of bacterial biofilm is considered as the primary etiological factor for this condition. A commonly used therapeutic method for surgical removal of adhered biofilm is mechanical debridement, which may cause detrimental effects on the implant surface. Post-treatment, implants are expected to re-osseointegrate with bone tissue, providing mechanical stability. However, it is important to understand that both bacterial adhesion and detoxification procedures can affect the titanium surface, which is vital for growth of bone-forming cells, osteoblasts. The goal of this study was to evaluate the synergistic effect of bacterial adhesion and detoxification treatment method on subsequent bone cell growth on implant surface. Polished titanium specimens underwent bacterial contamination and debridement/detoxification treatment with acidic and neutral chemicals to model a treatment for a peri-implantitis-infected dental implant. Subsequently, bone cell activity and surface morphology were evaluated using standard cell viability/differentiation assays, scanning electron and optical microscopies, respectively. The synergistic activity of bacterial contamination and detoxification with acidic chemicals generally lowered cell viability and proliferation rates. This suggested higher toxicity of titanium surfaces imparted by detoxification methods on osteoblasts. Electrochemical testing corroborated visual signs of corrosion attack and revealed that immersion-treated specimens had higher corrosion resistance than their corresponding rubbing-treated counterparts, excluding saline. Overall, surface damage induced by detoxification methods must be considered when selecting the most appropriate therapy to increase the probability of re-osseointegration of titanium substrates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dental Implants Facts and Figures. American Academy of Implant Dentistry. http://www.aaid.com/about/Press_Room/Dental_Implants_FAQ.html. Published 2017
Mellado-Valero A, Buitrago-Vera P, Solá-Ruiz MF, Ferrer-García JC (2013) Decontamination of dental implant surface in peri-implantitis treatment: a literature review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. doi:10.4317/medoral.19420
Pier-Francesco A, Adams RJ, Waters MGJ, Williams DW (2006) Titanium surface modification and its effect on the adherence of Porphyromonas gingivalis: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(6):633–637. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01274.x
Elias CN (2011) Factors affecting the success of dental implants. INTECH. doi:10.5772/18746
Ozkurt Z (2011) Zirconia dental implants: a literature review. Oral Implantol 3(37):367–376. http://www.joionline.org/doi/abs/10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-09-00079?code=aaid-premdev
Luo L, Jiang ZY, Bin Wei D, He XF (2014) Surface modification of titanium and its alloys for biomedical application. Adv Mater Res 887–888:1115–1120. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.887-888.1115
Esposito M, Thomsen P, Ericson LE, Sennerby L, Lekholm U (2000) Histopathologic observations on late oral implant failures. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2(1):18–32. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8208.2000.tb00103.x
Santos MCLG (2002) MIGCSRP. Early dental implant failure: a review of the literature. Braz J Oral Sci 1(3):103–111
Sakka S, Baroudi K, Nassani MZ (2012) Factors associated with early and late failure of dental implants. J Investig Clin Dent 3(4):258–261. doi:10.1111/j.2041-1626.2012.00162.x
Rodrigues DC, Sridhar S, Gindri IM et al (2016) Spectroscopic and microscopic investigation of the effects of bacteria on dental implant surfaces. RSC Adv 6(54):48283–48293. doi:10.1039/C6RA07760A
Jovanovic SA (1993) The management of peri-implant breakdown around functioning osseointegrated dental implants. J Periodontol 64((11 Suppl)):1176–1183. doi:10.1902/jop.1993.64.11s.1176
Pontoriero R, Carnevale DG (2001) Surgical crown lengthening: a 12-month clinical wound healing study. Periodontology 72(7):841–848. http://www.joponline.org/doi/abs/10.1902/jop.2001.72.7.841
Mombelli A (1993) Microbiology of the dental implant. Adv Dent Res 7(2):202–206. doi:10.1177/08959374930070021201
Mombelli A, Lang NP (1998) The diagnosis and treatment of peri-implantitis evidence for a microbial cause of peri-implant infections. Periodontology 17:63–76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.022
Busscher HJ, Van Der Mei RBHC (1995) Initial microbial adhesion is a determinant for the strength of biofilm adhesion. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128(3):229–234. doi:10.1016/0378-1097(95)00103-C
Manor Y, Oubaid S, Mardinger O, Chaushu G, Nissan J (2009) Characteristics of early versus late implant failure: a retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67(12):2649–2652. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2009.07.050
Scarano A, Piattelli M, Caputi S, Favero GA, Piattelli A (2004) Bacterial adhesion on commercially pure titanium and zirconium oxide disks: an in vivo human study. J Periodontol 75(2):292–296. doi:10.1902/jop.2004.75.2.292
Elter C, Heuer W, Demling A et al (2008) Supra- and subgingival biofilm formation on implant abutments with different surface characteristics. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 23(2):327–334
Burgers R, Gerlach T, Hahnel S, Schwarz F, Handel G, Gosau M (2010) In vivo and in vitro biofilm formation on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implant Res 21(2):156–164. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01815.x
Wadhwani C, Rapoport D, La Rosa S, Hess T, Kretschmar S (2012) Radiographic detection and characteristic patterns of residual excess cement associated with cement-retained implant restorations: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 107(3):151–157. doi:10.1016/S0022-3913(12)60046-8
Valderrama P, Wilson TG (2013) Detoxification of implant surfaces affected by peri-implant disease: an overview of surgical methods. Int J Dent. doi:10.1155/2013/740680
Mouhyi J, Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Albrektsson T (2012) The peri-implantitis: implant surfaces, microstructure, and physicochemical aspects. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14(2):170–183. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00244.x
Subramani K, Wismeijer D (2012) Decontamination of titanium implant surface and re-osseointegration to treat peri-implantitis: a literature review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 27(5):1043–1054
Finnegan M, Linley E, Denyer SP, McDonnell G, Simons C, Maillard JY (2010) Mode of action of hydrogen peroxide and other oxidizing agents: differences between liquid and gas forms. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(10):2108–2115. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq308
Gosau M, Hahnel S, Schwarz F, Gerlach T, Reichert TE, Bürgers R (2010) Effect of six different peri-implantitis disinfection methods on in vivo human oral biofilm. Clin Oral Implants Res 21(8):866–872. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01908.x
de Waal YCM, Raghoebar GM, Meijer HJA, Winkel EG, van Winkelhoff AJ (2015) Implant decontamination with 2% chlorhexidine during surgical peri-implantitis treatment: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 26(9):1015–1023. doi:10.1111/clr.12419
Sridhar S, Wilson TG, Palmer KL et al (2015) In vitro investigation of the effect of oral bacteria in the surface oxidation of dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 17:e562–e575. doi:10.1111/cid.12285
Wheelis SE, Gindri IM, Valderrama P, Wilson TG, Huang J, Rodrigues DC (2016) Effects of decontamination solutions on the surface of titanium: investigation of surface morphology, composition, and roughness. Clin Oral Implants Res 27(3):329–340. doi:10.1111/clr.12545
Rodrigues DC, Valderrama P, Wilson TG et al (2013) Titanium corrosion mechanisms in the oral environment: a retrieval study. Materials (Basel) 6(11):5258–5274. doi:10.3390/ma6115258
Cosyn J, van Aelst L, Collaert B, Persson GR, de Bruyn H (2011) The peri-implant sulcus compared with internal implant and suprastructure components: a microbiological analysis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 13(4):286–295. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00220.x
Chin MYH, Sandham A, de Vries J, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2007) Biofilm formation on surface characterized micro-implants for skeletal anchorage in orthodontics. Biomaterials 28(11):2032–2040. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.12.014
Mathew MT, Abbey S, Hallab NJ, Hall DJ, Sukotjo C, Wimmer MA (2012) Influence of pH on the tribocorrosion behavior of CpTi in the oral environment: synergistic interactions of wear and corrosion. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater 100 B(6):1662–1671. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.32735
Barão Va, Mathew MT, Assunção WG, Yuan JC, Wimmer Ma, Sukotjo C (2011) The role of lipopolysaccharide on the electrochemical behavior of titanium. J Dent Res 90(5):613–618. doi:10.1177/0022034510396880
Souza JCM, Henriques M, Oliveira R, Teughels W, Celis J-P, Rocha La (2010) Do oral biofilms influence the wear and corrosion behavior of titanium? Biofouling 26(4):471–478. doi:10.1080/08927011003767985
Thierry B, Tabrizian M, Savadogo O, Yahia L (2000) Effects of sterilization processes on NiTi alloy: surface characterization. J Biomed Mater Res 49(1):88–98. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(200001)49:1<88:AID-JBM11>3.0.CO;2-I
Schwarz F, Sculean A, Romanos G et al (2005) Influence of different treatment approaches on the removal of early plaque biofilms and the viability of SAOS2 osteoblasts grown on titanium implants. Clin Oral Investig 9(2):111–117. doi:10.1007/s00784-005-0305-8
Chaturvedi TP (2009) An overview of the corrosion aspect of dental implants (titanium and its alloys). Indian J Dent Res 20(1):91–98. doi:10.4103/0970-9290.49068
Mabilleau G, Bourdon S, Joly-Guillou ML, Filmon R, Baslé MF, Chappard D (2006) Influence of fluoride, hydrogen peroxide and lactic acid on the corrosion resistance of commercially pure titanium. Acta Biomater 2(1):121–129. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2005.09.004
Anil S, Anand PS, Alghamdi H, Jansen Ja (2011) Dental implant surface enhancement and osseointegration. Implant Dent A Rapidly Evol Pract. doi:10.5772/16475
Albrektsson T, Hansson HA, Ivarsson B (1985) Interface analysis of titanium and zirconium bone implants. Biomaterials 6(2):97–101. doi:10.1016/0142-9612(85)90070-5
Pontoriero R, Tonelli MP, Carnevale G, Mombelli A, Nyman SR, Lang NP (1994) Experimentally induced peri-implant mucositis. A clinical study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 5(4):254–259. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0501.1994.050409.x
Takasaki AA, Aoki A, Mizutani K, Kikuchi S, Oda S, Ishikawa I (2007) Er:YAG laser therapy for peri-implant infection: a histological study. Lasers Med Sci 22(3):143–157. doi:10.1007/s10103-006-0430-x
Heydenrijk K, Meijer HJA, van der Reijden WA, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A, Stegenga B (2002) Microbiota around root-form endosseous implants: a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 17(6):829–838
Leonhardt A, Adolfsson B, Lekholm U, Wikstrom M, Dahlen G (1993) A longitudinal microbiological study on osseointegrated titanium implants in partially edentulous patients. Clin Oral Implant Res 4(3):113–120. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0501.1993.040301.x
Shibli JA, Martins MC, Lotufo RF, Marcantonio E Jr (2003) Microbiologic and radiographic analysis of ligature-induced peri-implantitis with different dental implant surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant 18(3):383–390
Hensten-Pettersen A, Helgeland K (1981) Sensitivity of different human cell line in the biologic evaluation of dental resin-based restorative materials. Scand J Dent Res 89(1):102–107
Costa CADS, Hebling J, Hanks CT (2000) Current status of pulp capping with dentin adhesive systems: a review. Dent Mater 16(3):188–197. doi:10.1016/S0109-5641(00)00008-7
Ribeiro DA, Marques MESD (2006) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of glass ionomer cements on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17:495–500
Grivet M, Morrier JJ, Souchier C, Barsotti O (1999) Automatic enumeration of adherent streptococci or actinomyces on dental alloy by fluorescence image analysis. J Microbiol Methods 38(1–2):33–42. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00074-3
Fürst MM, Salvi GE, Lang NP, Persson GR (2007) Bacterial colonization immediately after installation on oral titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 18(4):501–508. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01381.x
Rodrigues DC, Urban RM, Jacobs JJ, Gilbert JL (2009) In vivo severe corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement of retrieved modular body titanium alloy hip-implants. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater 88(1):206–219. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.31171
Golvano I, Garcia I, Conde A, Tato W, Aginagalde A (2015) Influence of fluoride content and pH on corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviour of Ti13Nb13Zr alloy in oral environment. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 49:186–196. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.05.008
Sato N (1989) Toward a more fundamental understanding of corrosion processes. Corrosion 45(5):354–368. doi:10.5006/1.3582030
Gilbert JL, Buckley CA, Jacobs JJ (1993) In vivo corrosion of modular hip prosthesis components in mixed and similar metal combinations. The effect of crevice, stress, motion, and alloy coupling. J Biomed Mater Res 27(12):1533–1544. doi:10.1002/jbm.820271210
Triplett RG, Frohberg U, Sykaras N, Woody RD (2003) Implant materials, design, and surface topographies: their influence on osseointegration of dental implants. J Long Term Eff Med Implants 13(6):485–501. doi:10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.v13.i6.50
Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR (1986) The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1(1):11–25
Lee T-H, Hu C-C, Lee S-S, Chou M-Y, Chang Y-C (2010) Cytotoxicity of chlorhexidine on human osteoblastic cells is related to intracellular glutathione levels. Int Endod J 43(5):430–435. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01700.x
Schwarz F, John G, Mainusch S, Sahm N, Becker J (2012) Combined surgical therapy of peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface debridement and decontamination. A two-year clinical follow up report. J Clin Periodontol 39(8):789–797. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01867.x
Nalbandian JCN (1982) Direct histological comparison of periodontal wound healing in the beagle dog with and without citric acid conditioning. Periodontology 13:538–549
Crigger M, Bogle GNR (1978) The effect of topical citric acid application on the healing of experimental furcation defects in dogs. Periodontology 13:538–549
Klinge B, Nilveus R, Egelberg J (1985) Effect of periodic tooth displacement on healing of experimental furcation defects in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 12(3):239–246
Wikesjo UME, Selvig KA, Zimmerman G, Nilveus R (1991) Periodontal repair in dogs—healing in experimentally created chronic periodontal defects. J Periodontol 62(4):258–263. doi:10.1902/jop.1991.62.4.258
Alhag M, Renvert S, Polyzois I, Claffey N (2008) Re-osseointegration on rough implant surfaces previously coated with bacterial biofilm: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 19(2):182–187. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01429.x
Kolonidis SG, Renvert S, Hämmerle CHF, Lang NP, Harris D, Claffey N (2003) Osseointegration on implant surfaces previously contaminated with plaque. An experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 14:373–380. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0501.2003.01871.x
Noguti J, De Oliveira F, Peres RC, Renno ACM, Ribeiro DA (2012) The role of fluoride on the process of titanium corrosion in oral cavity. Biometals 25(5):859–862. doi:10.1007/s10534-012-9570-6
Garg H, Bedi G, Garg A (2012) Implant surface modifications: a review. J Clin Diagn Res 6(2):319–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, D., Sridhar, S., Siddiqui, D.A. et al. Detoxification of Titanium Implant Surfaces: Evaluation of Surface Morphology and Bone-Forming Cell Compatibility. J Bio Tribo Corros 3, 50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-017-0111-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-017-0111-2