Abstract
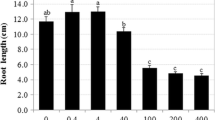
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are pollutants widely distributed in the environment, being the focus of interest due to their toxicity, mutagenicity, and carcinogenicity. Considering that PAHs are accumulated in soil sediments, plant roots are exposed to their toxicity. We evaluated the physiological effects of anthracene on Ri T-DNA-transformed carrot (Daucus carota) roots, mainly related to oxidative stress. In vitro conditions were used, so that external factors covering intrinsic root responses were eliminated. The roots absorbed anthracene from the culture medium and its bioaccumulation induced high H2O2 concentration. Consequently, roots exposed to anthracene showed high antioxidant enzyme activities, indicating oxidative stress. Programmed cell death was observed by chromatin condensation in root tips exposed to anthracene, which could explain growth decrease and development pattern alterations in roots. Here we provide comprehensive information on the responses related to oxidative stress in Ri T-DNA-transformed roots exposed to anthracene.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data obtained in this study can be requested to the corresponding author.
References
Abozeid A, Ying Z et al (2017) Ethylene improves root system development under cadmium stress by modulating superoxide anion concentration in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 8:253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00253
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic press, Cambridge, pp 673–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-091302-2.50032-3
Aranda E, Scervino JM et al (2013) Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus custos in the dissipation of PAHs under root-organ culture conditions. Environ Pollut 181:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.06.034
Babu TS, Akhtar TA et al (2003) Similar stress responses are elicited by copper and ultraviolet radiation in the aquatic plant Lemna gibba: implication of reactive oxygen species as common signals. Plant Cell Physiol 44:1320–1329. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcg160
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Bécard G, Fortin JA (1988) Early events of vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhiza formation on Ri T-DNA transformed roots. New Phytol 108:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1988.tb03698.x
Bi Y, Chen W et al (2009) Production of reactive oxygen species, impairment of photosynthetic function and dynamic changes in mitochondria are early events in cadmium-induced cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Cell 101:629–643. https://doi.org/10.1042/BC20090015
Boldt-Burisch K, Naeth MA et al (2018) Plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizae development in oil sands processing by-products. Sci Environ 621:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.188
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Byron CM, Werner TC (1991) Experiments in synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy for the undergraduate instrumental chemistry course. J Chem Educ 68:433. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed068p433
Christey MC, Braun RH (2005) Production of hairy root cultures and transgenic plants by Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation. Transgenic plants methods and protocols. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-827-7:047
Daudi A, O’Brien JA (2012) Detection of hydrogen peroxide by DAB staining in Arabidopsis leaves. Bio-Protoc 2:1–4. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.263
Debiane D, Garçon G et al (2008) In vitro evaluation of the oxidative stress and genotoxic potentials of anthracene on mycorrhizal chicory roots. Environ Exp Bot 64:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.04.003
Debiane D, Garçon G et al (2009) Mycorrhization alleviates benzo [a] pyrene-induced oxidative stress in an in vitro chicory root model. Phytochemistry 70:1421–1427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.07.002
Demidchik V, Straltsova D et al (2014) Stress induced electrolyte leakage: the role of KC-permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J Exp Bot 65:1259–1270. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru004
Duan Y, Zhang W et al (2010) An endoplasmic reticulum response pathway mediates programmed cell death of root tip induced by water stress in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 186:681–695. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03207.x
Fedorenko AG, Chernikova N et al (2020) Effects of benzo [a] pyrene toxicity on morphology and ultrastructure of Hordeum sativum. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00647-7
Gao S, Sun C, Zhang A (2007) Pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Dev Environ Sci 7:237–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-8177(07)07005-2
Häkkinen ST, Oksman-Caldentey KM (2018) Progress and prospects of hairy root research. Hairy roots. Springer, Singapore, pp 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2562-5_1
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photooxidation in isolated chloroplast. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Houshani M, Salehi-Lisar SY (2020) Agronomic crop responses and tolerance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon toxicity. Agronomic crops. Springer, Singapore, pp 265–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0025-1_15
Huo D, Wu J et al (2018) Macromolecular toxins secreted by botrytis cinerea induce programmed cell death in Arabidopsis leaves. Russ J Plant Physiol 65:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443718040131
Idowu O, Semple KT et al (2019) Beyond the obvious: environmental health implications of polar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Int 123:543–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.051
Jha P, Sen R et al (2020) Biotransformation of xenobiotics by hairy roots. Phyto 176:112421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112421
Kolek J, Kozinka V (1992) Physiology of the plant root system. Dev Plants Soil Sci 46:361
Liu H, Weisman D et al (2009) An oxidative stress response to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure is rapid and complex in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 176:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.12.002
Mesa-Marín J, Del-Saz NF et al (2018) PGPR reduces root respiration and oxidative stress enhancing Spartina maritima root growth and heavy metal rhizo accumulation. Front Plant Sci 9:1500. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01500
Møller IM, Jensen PE, Hansson A (2007) Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:459–481. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103946
Morales M, Munné-Bosch S (2019) Malondialdehyde: facts and artifacts. Plant Phys 180:1246–1250. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00405
Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2004) Levels of PAHs in soil and vegetation samples from Tarragona County, Spain. Environ Pollut 132:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.04.003
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Phys 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Paris A, Ledauphin J et al (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fruits and vegetables: origin, analysis, and occurrence. Environ Poll 234:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.028
Plaza-Bonilla D, Cantero-Martínez C et al (2012) Low-cost image analysis method to quantify root surface area. International conference of agricultural engineering. Valencia, Spain, pp 8–12
Qiu Z, Zhu L et al (2019) DNA damage and reactive oxygen species cause cell death in the rice local lesions 1 mutant under high light and high temperature. New Phytol 222:349–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15597
Shen Y, Li J et al (2018) Carotenoid and superoxide dismutase are the most effective antioxidants participating in ROS scavenging in phenanthrene accumulated wheat leaf. Chem 197:513–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.036
Shen Y, Li J et al (2019) Application of carotenoid to alleviate the oxidative stress caused by phenanthrene in wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:3593–3602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3832-y
Singh D, Singh SK et al (2020) Plant growth–promoting bacteria and their role in environmental management. Abatement of Environmental Pollutants, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 161–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818095-2.00008-4
US EPA (2000) Supplementary guidance for conducting health risk assessment of chemical mixtures. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=20533. Accessed 30 July 2020
Verdin A, Sahraoui ALH et al (2006) Effects of anthracene on development of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and contribution of the symbiotic association to pollutant dissipation. Mycorrhiza 16:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-006-0055-8
Wang P, Zhu Y et al (2010) Visualizing localizations and movement of anthracene in Kandelia candel (L.) Druce leaves by fluorescence microscopy. J Coast Res. https://doi.org/10.2112/08-1148.1
Wild E, Dent J et al (2005) Direct observation of organic contaminant uptake, storage, and metabolism within plant roots. Environ Sci Technol 39:3695–3702. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048136a
Xi Y, Liu H et al (2019) Selenium enhances Conyza canadensis phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. J Soils Sediments 19:2823–2835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02274-x
Xu J, Yin H et al (2010) Nitric oxide is associated with long-term zinc tolerance in Solanum nigrum. Plant Phys 154:1319–1334. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.162982
Zhan X, Zhu M et al (2018) Apoplastic and symplastic uptake of phenanthrene in wheat roots. Environ Pollut 233:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.056
Zhang FQ, Wang YS et al (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chem 67:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.007
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT-2019-00073), the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) and Universidad Nacional del Comahue (UNComahue- PIN 04B-216).
Funding
This work was funded by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT-2019-00073), the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) and Universidad Nacional del Comahue (UNComahue- PIN 04B-216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS, NS and EA made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data; RS, JMS, SF and EA drafted the work and revised it critically for important intellectual contribution; JMS approved the version to be published; JMS agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storb, R., Aranda, E., Fracchia, S. et al. Oxidative effects on Ri T-DNA-transformed root of Daucus carota exposed to anthracene. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 34, 83–93 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-021-00231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-021-00231-z