Abstract
Background
Ischemia–reperfusion (IR) causes acute kidney injury (AKI), and ischemia pretreatment may exert protection. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (MKK3), which is involved in the signal transduction pathway in IR-induced injury, is a potential target of miR-21. We aimed to verify the targeting regulation of miR-21 on MKK3 and to explore the effects of miR-21-mediated MKK3 expression changes in AKI.
Methods
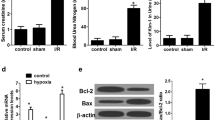
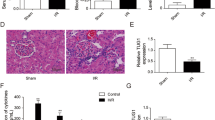
Vectors containing the MKK3 3′UTR and mutated MKK3-3U-M were constructed and co-transfected with nonsense miR, miR-21-5p mimics or inhibitor in HEK293 cells. Gene expressions were detected by dual luciferase reporter assay. The effects of miR-21 on mRNA and protein of MKK3 were investigated in HK-2 cells. Male C57BL/6J mice were treated with ischemic preconditioning (IPC) and IR. Kidney functions were assessed through monitoring serum creatinine (Scr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). Pathological changes were observed and scored with histological samples of kidney. Expression levels of miR-21, MKK3, interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α before and after IPC and IR were examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction and/or immunohistochemistry.
Results
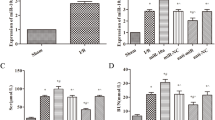
miR-21 regulated the expression of MKK3 via 3′UTR. Following IR, MKK3, IL-6 and TNF-α levels were increased. Scr, BUN and pathological injuries were aggravated, and miR-21 expression was increased. IPC increased miR-21 levels ahead of IR and inhibited the increases in MKK3, IL-6 and TNF-α levels and the aggravation of Scr, BUN and pathological injuries.
Conclusions
miR-21 targets MKK3 in vivo and in vitro, inhibiting the downstream factors IL-6 and TNF-α. Therefore, miR-21 might be involved in protection of IPC against IR of the kidney.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohli HS, Bhat A, Jairam A, Aravindan AN, Sud K, Jha V, Gupta KL, Sakhuja V (2007) Predictors of mortality in acute renal failure in a developing country: a prospective study. Ren Fail 29(4):463–469. doi:10.1080/08860220701260651
Venkatachalam MA, Griffin KA, Lan R, Geng H, Saikumar P, Bidani AK (2010) Acute kidney injury: a springboard for progression in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(5):F1078–F1094. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00017.2010
Molls RR, Savransky V, Liu M, Bevans S, Mehta T, Tuder RM, King LS, Rabb H (2006) Keratinocyte-derived chemokine is an early biomarker of ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290(5):F1187–F1193. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00342.2005
Friedewald JJ, Rabb H (2004) Inflammatory cells in ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int 66(2):486–491. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.761_3.x
Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney ischemic preconditioning. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11(1):43–48
Kim J, Jang HS, Park KM (2010) Reactive oxygen species generated by renal ischemia and reperfusion trigger protection against subsequent renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(1):F158–F166. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00474.2009
Zhang G, He LS, Wong YH, Qian PY (2013) MKK3 was involved in larval settlement of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite through activating the kinase activity of p38MAPK. PLoS One 8(7):e69510. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069510
Ma FY, Tesch GH, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Nikolic-Paterson DJ (2007) MKK3-p38 signaling promotes apoptosis and the early inflammatory response in the obstructed mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293(5):F1556–F1563. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00010.2007
Park KM, Kramers C, Vayssier-Taussat M, Chen A, Bonventre JV (2002) Prevention of kidney ischemia/reperfusion-induced functional injury, MAPK and MAPK kinase activation, and inflammation by remote transient ureteral obstruction. J Biol Chem 277(3):2040–2049. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107525200
Park KM, Chen A, Bonventre JV (2001) Prevention of kidney ischemia/reperfusion-induced functional injury and JNK, p38, and MAPK kinase activation by remote ischemic pretreatment. J Biol Chem 276(15):11870–11876. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007518200
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11(9):597–610. doi:10.1038/nrg2843
Bhatt K, Mi QS, Dong Z (2011) microRNAs in kidneys: biogenesis, regulation, and pathophysiological roles. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300(3):F602–F610. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00727.2010
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282(19):14328–14336. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611393200
Lu L, Byrnes K, Han C, Wang Y, Wu T (2014) miR-21 targets 15-PGDH and promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth. Mol Cancer Res 12(6):890–900. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0419
Yang Q, Yang K, Li A (2014) microRNA-21 protects against ischemia-reperfusion and hypoxia-reperfusion-induced cardiocyte apoptosis via the phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt-dependent mechanism. Mol Med Rep 9(6):2213–2220. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2068
Li P, Mao WM, Zheng ZG, Dong ZM, Ling ZQ (2013) Down-regulation of PTEN expression modulated by dysregulated miR-21 contributes to the progression of esophageal cancer. Dig Dis Sci 58(12):3483–3493. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2854-z
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W, Xuming M (2014) MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci 53(2):242–250. doi:10.1007/s12031-014-0293-8
Ye X, Zhang HM, Qiu Y, Hanson PJ, Hemida MG, Wei W, Hoodless PA, Chu F, Yang D (2014) Coxsackievirus-induced miR-21 disrupts cardiomyocyte interactions via the downregulation of intercalated disk components. PLoS Pathog 10(4):e1004070. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004070
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27(15):2128–2136. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210856
Liu F, Lou YL, Wu J, Ruan QF, Xie A, Guo F, Cui SP, Deng ZF, Wang Y (2012) Upregulation of microRNA-210 regulates renal angiogenesis mediated by activation of VEGF signaling pathway under ischemia/perfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Blood Press Res 35(3):182–191. doi:10.1159/000331054
Godwin JG, Ge X, Stephan K, Jurisch A, Tullius SG, Iacomini J (2010) Identification of a microRNA signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(32):14339–14344. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912701107
Xu G, Zhang Y, Wei J, Jia W, Ge Z, Zhang Z, Liu X (2013) MicroRNA-21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell proliferation through repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase 3. BMC Cancer 13:469. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-469
Rabb H, Daniels F, O’Donnell M, Haq M, Saba SR, Keane W, Tang WW (2000) Pathophysiological role of T lymphocytes in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279(3):F525–F531
Kruger J, Rehmsmeier M (2006) RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res 34 (Web Server issue):W451–454. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl243
Kaucsar T, Revesz C, Godo M et al (2013) Activation of the miR-17 family and miR-21 during murine kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nucleic Acid Ther 23(5):344–354. doi:10.1089/nat.2013.0438
Yin C, Salloum FN, Kukreja RC (2009) A novel role of microRNA in late preconditioning: upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and heat shock protein 70. Circ Res 104(5):572–575. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.193250
Cheng Y, Zhu P, Yang J, Liu X, Dong S, Wang X, Chun B, Zhuang J, Zhang C (2010) Ischaemic preconditioning-regulated miR-21 protects heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis through its target PDCD4. Cardiovasc Res 87(3):431–439. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq082
Xu X, Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Usa K, Mladinov D, Liu H, Fang Y, Ding X, Liang M (2012) Delayed ischemic preconditioning contributes to renal protection by upregulation of miR-21. Kidney Int 82(11):1167–1175. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.241
Tu Y, Wan L, Fan Y, Wang K, Bu L, Huang T, Cheng Z, Shen B (2013) Ischemic postconditioning-mediated miRNA-21 protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via PTEN/Akt pathway. PLoS One 8(10):e75872. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075872
Wang Y, Ji HX, Zheng JN, Pei DS, Hu SQ, Qiu SL (2009) Protective effect of selenite on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting ASK1-MKK3-p38 signal pathway. Redox Rep 14(6):243–250. doi:10.1179/135100009X12525712409896
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2015JJ4029), Key Program of Science and Technology Agency of Hunan Province in China (2014SK2008) and “225” Project Funding of High-level medical personnel of Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of our hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Deng, X., Kang, Z. et al. Elevation of miR-21, through targeting MKK3, may be involved in ischemia pretreatment protection from ischemia–reperfusion induced kidney injury. J Nephrol 29, 27–36 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-015-0217-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-015-0217-x