Abstract
Purpose
Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) predisposes to endocrine disorders, manifesting as a metabolic phenotype that affects the entire adipose-musculoskeletal unit (AMS). The present cross-sectional study aimed to investigate differences in irisin and adiponectin concentrations between people living with HIV and healthy controls, as well as to explore potential correlations between the levels of the aforementioned adipokines and markers of calcium homeostasis.
Methods
46 HIV-infected individuals and 39 healthy controls (all men) were included in the study. Anthropometric data, adipokine levels, 25-hydroxyvitamin D [(25(OH)D)] and parathyroid hormone (PTH) concentrations were evaluated in the two groups. Correlations for the relationship between adiponectin, irisin, and PTH levels were examined. The results were adjusted for several confounders, including 25(OH)D levels, anthropometry, physical activity, bone mineral density, testosterone levels, and exposure to ultraviolet B radiation.
Results
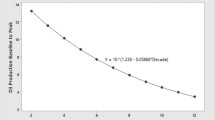
Mean adiponectin concentrations were significantly lower in the HIV group compared to the control group: 5868 ± 3668 vs 9068 ± 4277 ng/mL, p = 0.011. The same was applicable to irisin concentrations: 8.31 ± 8.17 (HIV) vs 29.27 ± 27.23 (controls) ng/mL, p = 0.013. A statistically significant and negative correlation was observed between irisin and PTH in the control group (r = – 0.591; p = 0.033). In contrast, no significant correlation was observed between PTH and irisin in the HIV group (p = 0.898).
Conclusion
Our results are the first to suggest a possible down regulation of the inverse relationship between PTH and irisin in HIV patients and to highlight that AMS dyshomeostasis could be involved in the development of skeletal and adipose HIV-related morbidities.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Li F, Li Y, Duan Y, Hu CA, Tang Y, Yin Y (2017) Myokines and adipokines: Involvement in the crosstalk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 33:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.10.003
Chen W, Wang L, You W, Shan T (2021) Myokines mediate the cross talk between skeletal muscle and other organs. J Cell Physiol 236:2393–2412. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30033
Leal LG, Lopes MA, Batista ML Jr (2018) Physical exercise-induced myokines and muscle-adipose tissue crosstalk: a review of current knowledge and the implications for health and metabolic diseases. Front Physiol 9:1307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01307
Karras SN, Koufakis T, Adamidou L, Dimakopoulos G, Karalazou P, Thisiadou K, Makedou K, Zebekakis P, Kotsa K (2022) Implementation of Christian Orthodox fasting improves plasma adiponectin concentrations compared with time-restricted eating in overweight premenopausal women. Int J Food Sci Nutr 73:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2021.1941803
Krause MP, Milne KJ, Hawke TJ (2019) Adiponectin-consideration for its role in skeletal muscle health. Int J Mol Sci 20:1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071528
Nawrocki AR, Scherer PE (2004) The delicate balance between fat and muscle: adipokines in metabolic disease and musculoskeletal inflammation. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2004.03.003
Waseem R, Shamsi A, Mohammad T, Hassan MI, Kazim SN, Chaudhary AA, Rudayni HA, Al-Zharani M, Ahmad F, Islam A (2022) FNDC5/irisin: physiology and pathophysiology. Molecules 27:1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031118
Maak S, Norheim F, Drevon CA, Erickson HP (2021) Progress and challenges in the biology of FNDC5 and Irisin. Endocr Rev 42:436–456. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnab003
Cho E, Jeong DY, Kim JG, Lee S (2021) The acute effects of swimming exercise on PGC-1α-FNDC5/irisin-UCP1 expression in male C57BL/6J mice. Metabolites 11:111. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020111
Estell EG, Le PT, Vegting Y, Kim H, Wrann C, Bouxsein ML, Nagano K, Baron R, Spiegelman BM, Rosen CJ (2020) Irisin directly stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Elife 9:e58172. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.58172
Kawao N, Kawaguchi M, Ohira T, Ehara H, Mizukami Y, Takafuji Y, Kaji H (2022) Renal failure suppresses muscle irisin expression, and irisin blunts cortical bone loss in mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13:758–771. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12892
Luo Y, Ma Y, Qiao X, Zeng R, Cheng R, Nie Y, Li S, Shen X, Yang M, Xu CC, Xu L (2020) Irisin ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Climacteric 23:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/13697137.2020.1745768
Colaianni G, Cuscito C, Mongelli T, Pignataro P, Buccoliero C, Liu P, Lu P, Sartini L, Di Comite M, Mori G, Di Benedetto A, Brunetti G, Yuen T, Sun L, Reseland JE, Colucci S, New MI, Zaidi M, Cinti S, Grano M (2015) The myokine irisin increases cortical bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:12157–12162. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1516622112
Freitas P, Carvalho D, Santos AC, Madureira AJ, Martinez E, Pereira J, Sarmento A, Medina JL (2014) Adipokines, hormones related to body composition, and insulin resistance in HIV fat redistribution syndrome. BMC Infect Dis 14:347. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-14-347
Tsiodras S, Mantzoros C (2006) Leptin and adiponectin in the HIV associated metabolic syndrome: physiologic and therapeutic implications. Am J Infect Dis 2:141–152. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajidsp.2006.141.152
Nix LM, Tien PC (2014) Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in HIV. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 11:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-014-0219-7
Biver E (2022) Osteoporosis and HIV Infection. Calcif Tissue Int 110:624–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-022-00946-4
Premaor MO, Compston JE (2020) People living with HIV and fracture risk. Osteoporos Int 31:1633–1644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-020-05350-y
Food Processor Analysis Software. 2018. https://www.esha.com/products/food-processor/. Accessed July 2 2022.
Papathanasiou G, Georgoudis G, Papandreou M, Spyropoulos P, Georgakopoulos D, Kalfakakou V, Evangelou A (2009) Reliability measures of the short International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Greek young adults. Hellenic J Cardiol 50:283–294
Mitsionis G, Pakos EE, Stafilas KS, Paschos N, Papakostas T, Beris AE (2009) Normative data on hand grip strength in a Greek adult population. Int Orthop 33:713–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0551-x
Scherzer R, Shen W, Heymsfield SB, Lewis CE, Kotler DP, Punyanitya M, Bacchetti P, Shlipak MG, Grunfeld C (2011) Study of fat redistribution and metabolic change in HIV infection (FRAM). Intermuscular adipose tissue and metabolic associations in HIV infection. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.115
Karras SN, Koufakis T, Tsekmekidou X, Antonopoulou V, Zebekakis P, Kotsa K (2020) Increased parathyroid hormone is associated with higher fasting glucose in individuals with normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism and prediabetes: a pilot study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 160:107985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107985
Sajid S, Zariwala MG, Mackenzie R, Turner M, Nell T, Bellary S, Renshaw D (2022) Suppression of anti-inflammatory mediators in metabolic disease may be driven by overwhelming pro-inflammatory drivers. Nutrients 14:2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112360
Wu MV, Bikopoulos G, Hung S, Ceddia RB (2014) Thermogenic capacity is antagonistically regulated in classical brown and white subcutaneous fat depots by high fat diet and endurance training in rats: impact on whole-body energy expenditure. J Biol Chem 289:34129–34140. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.591008
Rendina-Ruedy E, Rosen CJ (2022) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulation of metabolic homeostasis: An old dog teaches us new tricks. Mol Metab. 60:101480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101480
Addy CL, Gavrila A, Tsiodras S, Brodovicz K, Karchmer AW, Mantzoros CS (2003) Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, and fat redistribution in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:627–636. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-020795
Mynarcik DC, McNurlan MA, Steigbigel RT, Fuhrer J, Gelato MC (2000) Association of severe insulin resistance with both loss of limb fat and elevated serum tumor necrosis factor receptor levels in HIV lipodystrophy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 25:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042560-200012010-00004
Ledru E, Christeff N, Patey O, de Truchis P, Melchior JC, Gougeon ML (2000) Alteration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha T-cell homeostasis following potent antiretroviral therapy: contribution to the development of human immunodeficiency virus-associated lipodystrophy syndrome. Blood 95:3191–3198
Jan V, Cervera P, Maachi M, Baudrimont M, Kim M, Vidal H, Girard PM, Levan P, Rozenbaum W, Lombès A, Capeau J, Bastard JP (2004) Altered fat differentiation and adipocytokine expression are inter-related and linked to morphological changes and insulin resistance in HIV-1-infected lipodystrophic patients. Antivir Ther 9:555–564
Kinlaw WB, Marsh B (2004) Adiponectin and HIV-lipodystrophy: taking HAART. Endocrinology 145:484–486. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-1513
Tong Q, Sankalé JL, Hadigan CM, Tan G, Rosenberg ES, Kanki PJ, Grinspoon SK, Hotamisligil GS (2003) Regulation of adiponectin in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: relationship to body composition and metabolic indices. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:1559–1564. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-021600
Vigouroux C, Maachi M, Nguyên TH, Coussieu C, Gharakhanian S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Shimomura I, Rozenbaum W, Capeau J, Bastard JP (2003) Serum adipocytokines are related to lipodystrophy and metabolic disorders in HIV-infected men under antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 17:1503–1511. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002030-200307040-00011
Moreno-Perez O, Reyes-Garcia R, Muñoz-Torres M, Merino E, Boix V, Reus S, Giner L, Alfayate R, Garcia-Fontana B, Sanchez-Paya J, Picó A, Portilla J (2018) High Irisin levels in nondiabetic HIV-infected males are associated with insulin resistance, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and subclinical atherosclerosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 89:414–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13800
Trombeta JCDS, Prestes J, Nascimento DDC, Tibana RA, Pereira GB, Lima TDR, Fraga GA, Vieira-Junior RC, Voltarelli FA (2017) New insights into the effects of irisin levels in HIV-infected subjects: correlation with adiposity, fat-free mass, and strength parameters. Arch Endocrinol Metab 61:382–390. https://doi.org/10.1590/2359-3997000000270
Palermo A, Sanesi L, Colaianni G, Tabacco G, Naciu AM, Cesareo R, Pedone C, Lelli D, Brunetti G, Mori G, Colucci S, Manfrini S, Napoli N, Grano M (2019) A novel interplay between irisin and PTH: from basic studies to clinical evidence in hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104:3088–3096. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-02216
Anastasilakis AD, Polyzos SA, Makras P, Gkiomisi A, Bisbinas I, Katsarou A, Filippaios A, Mantzoros CS (2014) Circulating irisin is associated with osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with low bone mass but is not affected by either teriparatide or denosumab treatment for 3 months. Osteoporos Int 25:1633–1642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2673-x
He L, He WY, Yang WL, Zhang AH (2018) Lower serum irisin levels are associated with increased vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res 43:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487689
Colaianni G, Sanesi L, Storlino G, Brunetti G, Colucci S, Grano M (2019) Irisin and bone: from preclinical studies to the evaluation of its circulating levels in different populations of human subjects. Cells 8:451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050451
Ahmad IH, Mohamed Mostafa ER, Mohammed SA, Shipl W, Soliman AA, Said M (2023) Correlations between serum testosterone and irisin levels in a sample of Egyptian men with metabolic syndrome; (case-control study). Arch Physiol Biochem 129:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2020.1808018
Assyov Y, Gateva A, Karamfilova V, Gatev T, Nedeva I, Velikova T, Kamenov ZA (2020) Impact of testosterone treatment on circulating irisin in men with late-onset hypogonadism and metabolic syndrome. Aging Male 23:1381–1387. https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2020.1770721
Rochira V, Zirilli L, Orlando G, Santi D, Brigante G, Diazzi C, Carli F, Carani C, Guaraldi G (2011) Premature decline of serum total testosterone in HIV-infected men in the HAART-era. PLoS ONE 6:e28512. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028512
De Vincentis S, Decaroli MC, Fanelli F, Diazzi C, Mezzullo M, Tartaro G, Tagliavini S, De Santis MC, Roli L, Milic J, Trenti T, Pagotto U, Guaraldi G, Rochira V (2022) Primary, secondary and compensated male biochemical hypogonadism in people living with HIV (PLWH): relevance of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) measurement and comparison between liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and chemiluminescent immunoassay for sex steroids assay. Aging Male 25:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2022.2039116
De Vincentis S, Decaroli MC, Fanelli F, Diazzi C, Mezzullo M, Morini F, Bertani D, Milic J, Carli F, Cuomo G, Santi D, Tartaro G, Tagliavini S, De Santis MC, Roli L, Trenti T, Pagotto U, Guaraldi G, Rochira V (2021) Health status is related to testosterone, estrone and body fat: moving to functional hypogonadism in adult men with HIV. Eur J Endocrinol 184:107–122. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-20-0855
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNK conceptualized and designed the study. SNK, EZ, PM, EM, PK, KT, KM collected all data. GD performed the statistical analysis. SNK, TK, GD and KK analyzed and interpreted the results. OT, PZ, and SM contributed to the clinical management of the patients involved. SNK, TK, and GD performed the literature review and drafted the first version of the manuscript. All authors have read and critically reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical standard
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the AHEPA University Hospital (approval number 25224/2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karras, S.N., Koufakis, T., Dimakopoulos, G. et al. Down regulation of the inverse relationship between parathyroid hormone and irisin in male vitamin D-sufficient HIV patients. J Endocrinol Invest 46, 2563–2571 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02112-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02112-5