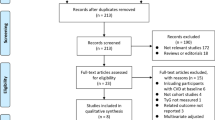
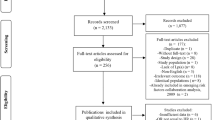
Abstract
Background
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) has increasingly been reported as linked to cardiovascular (CV) events; however, reported results have been inconsistent, and no meta-analysis has been undertaken to quantitatively assess this association.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases for cohort articles published up to December 1, 2020. Fixed or random-effects models were used to estimate the summary relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of CV events in relation to IGF-1. Restricted cubic splines were used to model the dose–response association.
Results
We identified 11 articles (thirteen cohort studies) covering a total of 22,995 participants and 3040 CV events in this meta-analysis. The risk of overall CV events reduced by 16% from the highest to the lowest IGF-1 levels (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.72–0.95), while the occurrence of CV events reduced by 28% (RR 0.72, 95% CI 0.56–0.92), but not for CV deaths, however (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.65–1.55). We also found linear associations between IGF-1 levels and CV events. With each per 45 μg/mL IGF-1 increase, the pooled RRs were 0.91 (95% CI 0.86–0.96), 0.91 (95% CI 0.85–0.97) and 0.91 (95% CI 0.84–0.98) for overall CV events, for the occurrence of CV events, and for CV deaths, respectively.
Conclusions
Our findings based on cohort studies support the contention that any increase in IGF-1 is helpful in reducing the overall risk of CV events. As an important biomarker for assessing the likelihood of CV events, IGF-1 appears to offer a promising prognostic approach for aiding prevention.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death .Accessed Dec 2020.
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO et al (2020) Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol 76(25):2982–3021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
NCD Countdown 2030 collaborators (2020). NCD Countdown 2030: pathways to achieving Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4. Lancet (London, England), 396(10255):918–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31761-X
Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE (1978) The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem 253(8):2769–2776
Berelowitz M, Szabo M, Frohman LA, Firestone S, Chu L, Hintz RL (1981) Somatomedin-C mediates growth hormone negative feedback by effects on both the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Science 212(4500):1279–1281. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6262917
Schutte AE, Conti E, Mels CM et al (2016) Attenuated IGF-1 predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a black population: a five-year prospective study. Eur J Prev Cardiol 23(16):1690–1699. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487316661436
Sun J, Axelsson J, Machowska A et al (2016) Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease and mortality risk in patients with advanced CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(7):1163–1172. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.10441015
Hinojosa-Amaya JM, Varlamov EV, Yedinak CG et al (2021) Echocardiographic findings in acromegaly: prevalence of concentric left ventricular remodeling in a large single-center cohort. J Endocrinol Invest 44(12):2665–2674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01579-4
Parolin M, Dassie F, Vettor R, Steeds RP, Maffei P (2021) Electrophysiological features in acromegaly: re-thinking the arrhythmic risk? J Endocrinol Invest 44(2):209–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01343-0
Vasan RS, Sullivan LM, D’Agostino RB et al (2003) Serum insulin-like growth factor I and risk for heart failure in elderly individuals without a previous myocardial infarction: the Framingham heart study. Ann Intern Med 139(8):642–648. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-139-8-200310210-00007
Bleumink GS, Rietveld I, Janssen JA et al (2004) Insulin-like growth factor-I gene polymorphism and risk of heart failure (the Rotterdam study). Am J Cardiol 94(3):384–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.04.044
van Bunderen CC, van Nieuwpoort IC, van Schoor NM, Deeg DJ, Lips P, Drent ML (2010) The association of serum insulin-like growth factor-I with mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer in the elderly: a population-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(10):4616–4624. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-0940
Ricketts SL, Rensing KL, Holly JM et al (2011) Prospective study of insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3, genetic variants in the IGF1 and IGFBP3 genes and risk of coronary artery disease. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2(3):261–285
Friedrich N, Haring R, Nauck M et al (2009) Mortality and serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein 3 concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(5):1732–1739. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-2138
Jing Z, Hou X, Wang Y et al (2015) Association between insulin-like growth factor-1 and cardiovascular disease risk: evidence from a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol 198:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.114
Kaplan RC, McGinn AP, Pollak MN et al (2007) Association of total insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), and IGFBP-3 levels with incident coronary events and ischemic stroke. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(4):1319–1325. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-1631
Saber H, Himali JJ, Beiser AS et al (2017) Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and the risk of ischemic stroke: the Framingham study. Stroke 48(7):1760–1765. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.116.016563
Kaplan RC, Strizich G, Aneke-Nash C et al (2017) Insulinlike growth factor binding protein-1 and ghrelin predict health outcomes among older adults: cardiovascular health study cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102(1):267–278. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-2779
Ruidavets JB, Luc G, Machez E et al (2011) Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 in preventing acute coronary syndromes: the PRIME study. Atherosclerosis 218(2):464–469
Juul A, Scheike T, Davidsen M, Gyllenborg J, Jørgensen T (2002) Low serum insulin-like growth factor I is associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease: a population-based case-control study. Circulation 106(8):939–944. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000027563.44593.cc
Saydah S, Graubard B, Ballard-Barbash R, Berrigan D (2007) Insulin-like growth factors and subsequent risk of mortality in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 166(5):518–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwm124
Schneider HJ, Wallaschofski H, Völzke H et al (2012) Incremental effects of endocrine and metabolic biomarkers and abdominal obesity on cardiovascular mortality prediction. PLoS ONE 7(3):e33084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033084
Laughlin GA, Barrett-Connor E, Criqui MH, Kritz-Silverstein D (2004) The prospective association of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-1 levels with all cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in older adults: the Rancho Bernardo study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(1):114–120. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-030967
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25(9):603–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Ohlsson C, Mohan S, Sjogren K et al (2009) The role of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocr Rev 30(5):494–535. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0010
Orsini N, Li R, Wolk A, Khudyakov P, Spiegelman D (2012) Meta-analysis for linear and nonlinear dose-response relations: examples, an evaluation of approximations, and software. Am J Epidemiol 175(1):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwr265
Saber H, Himali JJ, Beiser A, et al. High serum insulin-like growth factor 1 is associated with lower risk of ischemic stroke: The framingham heart study. Stroke Conference: American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. 2015;46(1).
Hamling J, Lee P, Weitkunat R, Ambühl M (2008) Facilitating meta-analyses by deriving relative effect and precision estimates for alternative comparisons from a set of estimates presented by exposure level or disease category. Stat Med 27(7):954–970. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3013
Bekkering GE, Harris RJ, Thomas S et al (2008) How much of the data published in observational studies of the association between diet and prostate or bladder cancer is usable for meta-analysis? Am J Epidemiol 167(9):1017–1026. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwn005
Greenland S (1995) Dose-response and trend analysis in epidemiology: alternatives to categorical analysis. Epidemiology 6(4):356–365. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001648-199507000-00005
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Liu X, Zhang D, Liu Y et al (2017) Dose-response association between physical activity and incident hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Hypertension 69(5):813–820. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.116.08994 (Dallas, Tex : 1979)
Cai Z, Fan X (2020) A comparison of fixed-effects and random-effects models for multivariate meta-analysis using an SEM approach. Multivariate Behav Res 55(6):839–854. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2019.1689348
Allison PD. Fixed Effects Regression Models. SAGE. 2006
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Saber H, Himali JJ, Beiser AS et al (2017) Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and the risk of ischemic stroke. Stroke 48(7):1760–1765
Obradovic M, Zafirovic S, Soskic S et al (2019) Effects of IGF-1 on the cardiovascular system. Curr Pharm Des 25(35):3715–3725. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666191106091507
Higashi Y, Gautam S, Delafontaine P, Sukhanov S (2019) IGF-1 and cardiovascular disease. Growth Horm IGF Res 45:6–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ghir.2019.01.002
Johnsen SP, Hundborg HH, Sørensen HT et al (2005) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, -II, and IGF binding protein-3 and risk of ischemic stroke. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(11):5937–5941. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-2088
De Lorenzo A, Moreira AS, Souza EG, Oliveira GM (2016) Insulin-like growth factor-1 in early-onset coronary artery disease: insights into the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol 202:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.032
Junnila RK, List EO, Berryman DE, Murrey JW, Kopchick JJ (2013) The GH/IGF-1 axis in ageing and longevity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9(6):366–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2013.67
Perkel D, Naghi J, Agarwal M et al (2012) The potential effects of IGF-1 and GH on patients with chronic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 17(1):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1177/1074248411402078
Kaklamani VG, Linos A, Kaklamani E, Markaki I, Mantzoros C (1999) Age, sex, and smoking are predictors of circulating insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3. J Clin Oncol 17(3):813–817. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.1999.17.3.813
Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Wilhelmsen L, Lappas G et al (1994) Serum insulin-like growth factor I in a random population sample of men and women: relation to age, sex, smoking habits, coffee consumption and physical activity, blood pressure and concentrations of plasma lipids, fibrinogen, parathyroid hormone and osteocalcin. Clin Endocrinol 41(3):351–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.1994.tb02556.x
Foncea R, Andersson M, Ketterman A et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I rapidly activates multiple signal transduction pathways in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 272(31):19115–19124. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.31.19115
Okura Y, Brink M, Zahid AA, Anwar A, Delafontaine P (2001) Decreased expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerotic plaque. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33(10):1777–1789. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.2001.1441
Patel VA, Zhang QJ, Siddle K et al (2001) Defect in insulin-like growth factor-1 survival mechanism in atherosclerotic plaque-derived vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by reduced surface binding and signaling. Circ Res 88(9):895–902. https://doi.org/10.1161/hh0901.090305
Walsh MF, Barazi M, Pete G, Muniyappa R, Dunbar JC, Sowers JR (1996) Insulin-like growth factor I diminishes in vivo and in vitro vascular contractility: role of vascular nitric oxide. Endocrinology 137(5):1798–1803. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.137.5.8612517
Troncoso R, Ibarra C, Vicencio JM, Jaimovich E, Lavandero S (2014) New insights into IGF-1 signaling in the heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25(3):128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2013.12.002
Arcopinto M, Bobbio E, Bossone E et al (2013) The GH/IGF-1 axis in chronic heart failure. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 13(1):76–91. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530311313010010
Castellano G, Affuso F, Conza PD, Fazio S (2009) The GH/IGF-1 axis and heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rev 5(3):203–215. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340309788970306
Chennaoui M, Léger D, Gomez-Merino D (2020) Sleep and the GH/IGF-1 axis: consequences and countermeasures of sleep loss/disorders. Sleep Med Rev 49:101223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2019.101223
Saccà L, Cittadini A, Fazio S (1994) Growth hormone and the heart. Endocr Rev 15(5):555–573. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv-15-5-555
Rosén T, Bengtsson BA (1990) Premature mortality due to cardiovascular disease in hypopituitarism. Lancet 336(8710):285–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(90)91812-o
Gravholt CH, Viuff MH, Brun S, Stochholm K, Andersen NH (2019) Turner syndrome: mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Endocrinol 15(10):601–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0224-4
Oldfield EH, Jane JA Jr, Thorner MO, Pledger CL, Sheehan JP, Vance ML (2017) Correlation between GH and IGF-1 during treatment for acromegaly. J Neurosurg 126(6):1959–1966. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.Jns161123
Bruch C, Herrmann B, Schmermund A, Bartel T, Mann K, Erbel R (2002) Impact of disease activity on left ventricular performance in patients with acromegaly. Am Heart J 144(3):538–543. https://doi.org/10.1067/mhj.2002.123572
Wright AD, Hill DM, Lowy C, Fraser TR (1970) Mortality in acromegaly. Q J Med 39(153):1–16
Friehs I, Stamm C, Cao-Danh H, McGowan FX, del Nido PJ (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves postischemic recovery in hypertrophied hearts. Ann Thorac Surg 72(5):1650–1656. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-4975(01)03098-3
Li B, Setoguchi M, Wang X et al (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-1 attenuates the detrimental impact of nonocclusive coronary artery constriction on the heart. Circ Res 84(9):1007–1019. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.84.9.1007
Anwar A (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-α regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 expression in vascular smooth muscle. Circulation 105(10):1220–1225
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge all the authors and Prof. Dongsheng Hu for methodological advice and help to modify the meta-analysis. All authors have read and approved the submission of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 81402752 and 81673260), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant no. 2019A1515011183), the Science and Technology Development Foundation of Shenzhen (Grant no. JCYJ20190808145805515), and the SZU medical young scientists’ program (Grant no. 71201-000001). The investigators are grateful to the dedicated participants and all research staff involved in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL substantially contributed to the design and drafting of the study and the analysis and interpretation of the data. TL wrote the manuscript. YZ, XY, YF, YL, YW, MZ, XL, HH, JZ, LY, YL, XS, PQ, CC, and DH revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Tianze Li, Yang Zhao, Xingjin Yang, Yifei Feng, Yang Li, Yuying Wu, Ming Zhang, Xi Li, Huifang Hu, Jinli Zhang, Lijun Yuan, Yu Liu, Xizhuo Sun, Pei Qin, Chuanqi Chen, and Dongsheng Hu declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Ethical approval
This study dealt with published data only, no ethical approval was needed.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Zhao, Y., Yang, X. et al. Association between insulin-like growth factor-1 and cardiovascular events: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of cohort studies. J Endocrinol Invest 45, 2221–2231 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-022-01819-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-022-01819-1