Abstract
Objectives
Studies on the effect of the Nordic diet (ND) on body weight and adiposity indices were conflicting. This study targeted to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) examined the effect of the ND on body weight and composition.
Methods
PubMed, Scopus, ISI web of Science, ProQuest and Google Scholar were searched for the eligible studies up to August 2019. The weighted mean difference (WMD) in body weight and composition indices between the ND and control groups/periods was derived using random-effects model.
Results
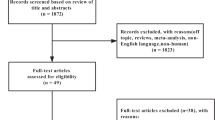
In total, seven studies (n = 774 participants) were included in the present study. Five studies had illustrated the effect of the ND on weight, three on waist circumference (WC), two on body fat, and two on body mass index (BMI). The pooled analysis of eligible trials showed that those adhered to the ND lost 1.83 kg [95% confidence interval (CI) − 2.94, − 0.73, P = 0.001] more weight compared to controls. Qualitative assessment of other anthropometric indices also showed a beneficial effect of this dietary pattern in improving body fat and BMI values; however, these findings are not conclusive because of limited number of studies.
Conclusion
Adherence to the ND significantly improves body weight; however, there is also no certainty that this diet is effective for improving other anthropometric indices. Future studies regarding the effect of the ND on weight and body composition in populations other than Nordic populations are highly recommended.
Level of evidence Level I, systematic reviews and meta-analyses.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ND:
-
Nordic diet
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled clinical trials
- WMD:
-
Weighted mean difference
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- WC:
-
Waist circumference
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- WHO:
-
World health organization
- CVDs:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- DASH:
-
Dietary approaches to stop hypertension
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- PROSPERO:
-
Prospective register of systematic reviews
- SE:
-
Standard error
- SDs:
-
Standard deviations
- PUFAs:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
References
World Health Organization (2016) Fact sheet: obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Accessed 11 Aug 2019
Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, Amarsi Z, Birmingham CL, Anis AH (2009) The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 9:88
Johnston BC, Kanters S, Bandayrel K, Wu P, Naji F, Siemieniuk RA, Ball GD, Busse JW, Thorlund K, Guyatt G, Jansen JP, Mills EJ (2014) Comparison of weight loss among named diet programs in overweight and obese adults: a meta-analysis. JAMA 312:923–933
Ross R, Dagnone D, Jones PJ, Smith H, Paddags A, Hudson R, Janssen I (2000) Reduction in obesity and related comorbid conditions after diet-induced weight loss or exercise-induced weight loss in men. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 133:92–103
Shay CM, Van Horn L, Stamler J, Dyer AR, Brown IJ, Chan Q, Miura K, Zhao L, Okuda N, Daviglus ML, Elliott P, Group I.R (2012) Food and nutrient intakes and their associations with lower BMI in middle-aged US adults: the International Study of Macro-/Micronutrients and Blood Pressure (INTERMAP). Am J Clin Nutr 96:483–491
Mozaffarian D (2017) Foods, obesity, and diabetes-are all calories created equal? Nutr Rev 75:19–31
Sacks FM, Appel LJ, Moore TJ, Obarzanek E, Vollmer WM, Svetkey LP, Bray GA, Vogt TM, Cutler JA, Windhauser MM, Lin PH, Karanja N (1999) A dietary approach to prevent hypertension: a review of the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) Study. Clin Cardiol 22:6–10
Soltani S, Shirani F, Chitsazi MJ, Salehi-Abargouei A (2016) The effect of dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet on weight and body composition in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Obes Rev 17:442–454
Esposito K, Kastorini CM, Panagiotakos DB, Giugliano D (2011) Mediterranean diet and weight loss: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 9:1–12
Poulsen SK, Due A, Jordy AB, Kiens B, Stark KD, Stender S, Holst C, Astrup A, Larsen TM (2014) Health effect of the new nordic diet in adults with increased waist circumference: a 6-mo randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 99:35–45
Mithril C, Dragsted LO, Meyer C, Tetens I, Biltoft-Jensen A, Astrup A (2013) Dietary composition and nutrient content of the New Nordic Diet. Public Health Nutr 16:777–785
Salomo L, Poulsen SK, Rix M, Kamper AL, Larsen TM, Astrup A (2016) The New Nordic diet: phosphorus content and absorption. Eur J Nutr 55:991–996
Akesson A, Andersen LF, Kristjansdottir AG, Roos E, Trolle E, Voutilainen E, Wirfalt E (2013) Health effects associated with foods characteristic of the Nordic diet: a systematic literature review. Food Nutr Res. https://doi.org/10.3402/fnr.v57i0.22790
Adamsson V, Reumark A, Fredriksson IB, Hammarstrom E, Vessby B, Johansson G, Riserus U (2011) Effects of a healthy Nordic diet on cardiovascular risk factors in hypercholesterolaemic subjects: a randomized controlled trial (NORDIET). J Intern Med 269:150–159
Uusitupa M, Hermansen K, Savolainen MJ, Schwab U, Kolehmainen M, Brader L, Mortensen LS, Cloetens L, Johansson-Persson A, Oumlnning G, Landin-Olsson M, Herzig KH, Hukkanen J, Rosqvist F, Iggman D, Paananen J, Pulkki KJ, Siloaho M, Dragsted L, Barri T, Overvad K, Knudsen KEB, Hedemann MS, Arner P, Dahlman I, Borge GIA, Baardseth P, Ulven SM, Gunnarsdottir I, Jonsdottir S, Thorsdottir I, Oresic M, Poutanen KS, Riserus U, Aringkesson B (2013) Effects of an isocaloric healthy Nordic diet on insulin sensitivity, lipid profile and inflammation markers in metabolic syndrome—a randomized study (SYSDIET). J Intern Med 274:52–66
Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Mohammadi M, Salehi-Abargouei A (2019) The effect of healthy Nordic diet on cardio-metabolic markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Eur J Nutr 58:2159–2174
Zimorovat A, Mohammadi M, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Salehi-Abargouei A (2019) The healthy Nordic diet for blood glucose control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Acta Diabetol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01369-8
Sakhaei R, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Mohammadi M, Salehi-Abargouei A (2019) The healthy Nordic dietary pattern has no effect on inflammatory markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Nutrition 58:140–148
Fritzen AM, Lundsgaard AM, Jordy AB, Poulsen SK, Stender S, Pilegaard H, Astrup A, Larsen TM, Wojtaszewski JF, Richter EA, Kiens B (2015) New Nordic diet-induced weight loss is accompanied by changes in metabolism and ampk signaling in adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:3509–3519
De Mello VDF, Schwab U, Kolehmainen M, Koenig W, Siloaho M, Poutanen K, Mykkänen H, Uusitupa M (2011) A diet high in fatty fish, bilberries and wholegrain products improves markers of endothelial function and inflammation in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism in a randomised controlled trial: the sysdimet study. Diabetologia 54:2755–2767
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Mohammadi M, Salehi-Abargouei A, Ramezani Jolfaie N (2017) Effects of Nordic diet on weight and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis on controlled clinical trials. PROSPERO [internet]. CRD42017054860. https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=54860. Accessed 11 Aug 2019
Higgins JPT, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/. Accessed 11 Aug 2019
Fritzen AM, Lundsgaard AM, Jordy AB, Poulsen SK, Stender S, Pilegaard H, Astrup A, Larsen TM, Wojtaszewski JFP, Richter EA, Kiens B (2015) New nordic diet-induced weight loss is accompanied by changes in metabolism and AMPK signaling in adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:3509–3519
Poulsen S, Frost S, Rasmussen L, Astrup A, Larsen T (2011) Weight loss after 12 weeks with new Nordic diet vs. Average Danish diet provided ad libitum—a randomized controlled trial using the shop model. Ann Nutr Metab 58:289
Kolehmainen M, Ulven SM, Paananen J, De Mello V, Schwab U, Carlberg C, Myhrstad M, Pihlajamäki J, Dungner E, Sjöolin E, Gunnarsdottir I, Cloetens L, Landin-Olsson M, Akesson B, Rosqvist F, Hukkanen J, Herzig KH, Dragsted LO, Savolainen MJ, Brader L, Hermansen K, Risérus U, Thorsdottir I, Poutanen KS, Uusitupa M, Arner P, Dahlman I (2015) Healthy Nordic diet downregulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation in subcutaneous adipose tissue in individuals with features of the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 101:228–239
Lankinen M, Kolehmainen M, Jaaskelainen T, Paananen J, Joukamo L, Kangas AJ, Soininen P, Poutanen K, Mykkanen H, Gylling H, Oresic M, Jauhiainen M, Ala-Korpela M, Uusitupa M, Schwab U (2014) Effects of whole grain, fish and bilberries on serum metabolic profile and lipid transfer protein activities: a randomized trial (Sysdimet). Plos One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090352
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Rover C, Knapp G, Friede T (2015) Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman approach and its modification for random-effects meta-analysis with few studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 15:99
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Egger M, Smith GD, Altman D (2008) Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. Wiley, Hoboken
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Andersson J, Mellberg C, Otten J, Ryberg M, Rinnström D, Larsson C, Lindahl B, Hauksson J, Johansson B, Olsson T (2016) Left ventricular remodelling changes without concomitant loss of myocardial fat after long-term dietary intervention. Int J Cardiol 216:92–96
Blomquist C, Alvehus M, Buren J, Ryberg M, Larsson C, Lindahl B, Mellberg C, Soderstrom I, Chorell E, Olsson T (2017) Attenuated low-grade inflammation following long-term dietary intervention in postmenopausal women with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 25:892–900
Boraxbekk CJ, Stomby A, Ryberg M, Lindahl B, Larsson C, Nyberg L, Olsson T (2015) Diet-induced weight loss alters functional brain responses during an episodic memory task. Obes Facts 8:261–272
Chorell E, Ryberg M, Larsson C, Sandberg S, Mellberg C, Lindahl B, Antti H, Olsson T (2016) Plasma metabolomic response to postmenopausal weight loss induced by different diets. Metabolomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1013-x
Mellberg C, Sandberg S, Ryberg M, Eriksson M, Brage S, Larsson C, Olsson T, Lindahl B (2014) Long-term effects of a Palaeolithic-type diet in obese postmenopausal women: a 2-year randomized trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 68:350–357
Otten J, Mellberg C, Ryberg M, Sandberg S, Kullberg J, Lindahl B, Larsson C, Hauksson J, Olsson T (2016) Strong and persistent effect on liver fat with a Paleolithic diet during a two-year intervention. Int J Obes (Lond) 40:747–753
Marklund M, Magnusdottir OK, Rosqvist F, Cloetens L, Landberg R, Kolehmainen M, Brader L, Hermansen K, Poutanen KS, Herzig KH, Hukkanen J, Savolainen MJ, Dragsted LO, Schwab U, Paananen J, Uusitupa M, Åkesson B, Thorsdottir I, Risérus U (2014) A dietary biomarker approach captures compliance and cardiometabolic effects of a healthy nordic diet in individuals with metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 144:1642–1649
Myhrstad MCW, de Mello VD, Dahlman I, Kolehmainen M, Paananen J, Rundblad A, Carlberg C, Olstad OK, Pihlajamaki J, Holven KB, Hermansen K, Dragsted LO, Gunnarsdottir I, Cloetens L, Storm MU, Akesson B, Rosqvist F, Hukkanen J, Herzig KH, Riserus U, Thorsdottir I, Poutanen KS, Savolainen MJ, Schwab U, Arner P, Uusitupa M, Ulven SM (2019) Healthy Nordic diet modulates the expression of genes related to mitochondrial function and immune response in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from subjects with metabolic syndrome—a SYSDIET sub-study. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201801405
Huseinovic E, Bertz F, Agelii ML, Johansson EH, Winkvist A, Brekke HK (2016) Effectiveness of a weight loss intervention in postpartum women: results from a randomized controlled trial in primary health care. Am J Clin Nutr 104:362–370
Poulsen SK, Crone C, Astrup A, Larsen TM (2015) Long-term adherence to the New Nordic Diet and the effects on body weight, anthropometry and blood pressure: a 12-month follow-up study. Eur J Nutr 54:67–76
Darwiche G, Höglund P, Roth B, Larsson E, Sjöberg T, Wohlfart B, Steen S, Ohlsson B (2016) An Okinawan-based Nordic diet improves anthropometry, metabolic control, and health-related quality of life in Scandinavian patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot trial. Food Nutr Res. https://doi.org/10.3402/fnr.v60.32594
Li YJ, Roswall N, Strom P, Sandin S, Adami HO, Weiderpass E (2015) Mediterranean and Nordic diet scores and long-term changes in body weight and waist circumference: results from a large cohort study. Br J Nutr 114:2093–2102
Winkvist A, Klingberg S, Nilsson LM, Wennberg M, Renstrom F, Hallmans G, Boman K, Johansson I (2017) Longitudinal 10-year changes in dietary intake and associations with cardio-metabolic risk factors in the Northern Sweden Health and Disease Study. Nutr J 16:20
Slavin JL (2005) Dietary fiber and body weight. Nutrition 21:411–418
Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS (2002) Appel LJ (2002) American heart association. Nutrition C: fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 106:2747–2757
Bender N, Portmann M, Heg Z, Hofmann K, Zwahlen M, Egger M (2014) Fish or n3-PUFA intake and body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 15:657–665
Santesso N, Akl EA, Bianchi M, Mente A, Mustafa R, Heels-Ansdell D, Schunemann HJ (2012) Effects of higher- versus lower-protein diets on health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 66:780–788
Weigle DS, Breen PA, Matthys CC, Callahan HS, Meeuws KE, Burden VR, Purnell JQ (2005) A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr 82:41–48
Willett WC, Sacks F, Trichopoulou A, Drescher G, Ferro-Luzzi A, Helsing E, Trichopoulos D (1995) Mediterranean diet pyramid: a cultural model for healthy eating. Am J Clin Nutr 61:1402S–1406S
van Dooren C, Aiking H (2016) Defining a nutritionally healthy, environmentally friendly, and culturally acceptable Low Lands Diet. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:688–700
Funding
The study was funded by the Nutrition and Food Security research center, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ contributions were as follows: ASA, MM and NRJ conceived and designed the research; MM and NRJ conducted systematic research and study selection; MM and NRJ extracted data; ASA and MM analyzed data; NRJ, MM and ASA wrote the manuscript; and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to report for this study.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was registered and ethically approved by the research council of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences (registration code: IR.SSU.SPH.REC.1397.059).
Informed consent
The informed consent was not applicable for the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani-Jolfaie, N., Mohammadi, M. & Salehi-Abargouei, A. Effects of a healthy Nordic diet on weight loss in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Eat Weight Disord 25, 1141–1150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00773-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00773-x