Abstract
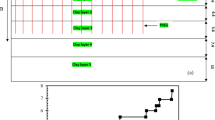
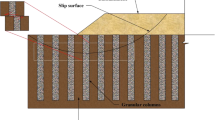
In this study, undrained behavior of a road embankment overlying ordinary and geosynthetic-encased granular columns is evaluated through fully coupled nonlinear stress analysis. In this contribution, the equivalent area methodology is used to convert the strengthened zone into an equivalent area including soft soil and granular columns. Diameter and internal friction angle of granular columns, undrained shear strength of soft soil, encasement stiffness, and encasement length are all varied aiming to compare the performance of embankment in undrained condition. Results show that enlarging columns size from 0.6 to 1.2 m reduces total deformations to half. However, this improvement can be 30% enhanced as granular columns are fully encased. Also, the computed failure mode alters from deep-seated to surficial failure surface as column size, internal friction angle of column filling material, and encasement stiffness increase. Unlike encased columns, embankment on ordinary granular columns in soft soil with threshold cu value of 11.5 kPa fails due to lack of sufficient lateral support from very soft soil. In addition, encasement stiffness is found to be the most critical factor affecting deformations and stability of embankment, among others.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data, codes, and results presented in the paper are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Change history
26 October 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-023-00346-7
Abbreviations
- \(\gamma\) (kN/m3):
-
Soil unit weight
- \({\gamma }_{\mathrm{eq}}\) (kN/m3):
-
Equivalent unit weight
- \({\upphi }{\prime}\)(o):
-
Drained internal angle of friction
- \({\upphi }_{\mathrm{eq}}\)(o):
-
Equivalent internal angle of friction
- c' (kPa):
-
Drained cohesion
- cu (kPa):
-
Clay undrained cohesion
- ceq (kPa):
-
Equivalent cohesion
- ca (-):
-
Apparent cohesion
- E' (kPa):
-
Drained elastic modulus
- Eeq (kPa):
-
Equivalent elastic modulus
- \(\upupsilon\) (-):
-
Poisson’s ratio
- \({\upupsilon }_{\mathrm{eq}}\) (-):
-
Equivalent Poisson’s ratio
- Kp (-):
-
Coefficient of passive earth pressure
- \({\upvarepsilon }_{\mathrm{a}}\) (-):
-
Column axial strain
- H (m):
-
Thickness
- ar (%):
-
Area replacement ratio
- S (m):
-
Columns spacing
- dc (cm):
-
Column diameter
- J (kN/m):
-
Encasement stiffness
- Lc (m):
-
Column length
- Le (m):
-
Encasement length
- OSC:
-
Ordinary stone column
- GEC:
-
Geosynthetic-encased stone column
- LEM:
-
Limit equilibrium method
- FEM:
-
Finite element method
- FDM:
-
Finite difference method
- SF:
-
Safety factor
References
Abusharar, S.W., Han, J.: Two-dimensional deep-seated slope stability analysis of embankments over stone column-improved soft clay. Eng. Geol. 120(1), 103–110 (2011)
Aghili, E., Hosseinpour, I., Chenari, R.J., Ahmadi, H.: Behavior of granular column-improved clay under cyclic shear loading. Transp. Geotech. 31, 100654 (2021)
Alkhorshid, N.R., Araujo, G.L.S., Palmeira, E.M.: Consolidation of soft clay foundation improved by geosynthetic-reinforced granular columns: Numerical evaluation. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng. 13(5), 1173–1181 (2021)
Ashour, S., Ghataora, G., Jefferson, I.: Behaviour of model stone column subjected to cyclic loading. Transp. Geotech. 35, 100777 (2022)
Bahadori, H., Farzalizadeh, R., Barghi, A., Hasheminezhad, A.: A comparative study between gravel and rubber drainage columns for mitigation of liquefaction hazards. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng. 10(5), 924–934 (2018)
Basack, S., Nimbalkar, S.: Load-settlement characteristics of stone column reinforced soft marine clay deposit: combined field and numerical studies. Sustainability 5(9), 7457 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097457
Bathurst, R., Karpurapu, R.: Large-scale triaxial compression testing of geocell-reinforced granular soils. Geotech. Test. J. 16, 296–303 (1993)
Cengiz, C., Guler, E.: Seismic behavior of geosynthetic encased columns and ordinary stone columns. Geotext. Geomembr. 46(1), 40–51 (2018)
Chen, J.F., Li, L.Y., Xue, J.F., Feng, S.Z.: Failure mechanism of geosynthetic-encased stone columns in soft soils under embankment. Geotext. Geomembr. 43(5), 424–431 (2015)
Cooper, M.R., Rose, A.N.: Stone column support for an embankment on deep alluvial soils. Proc. Inst. Civil. Eng-Geotech. Eng. 137(1), 15–25 (1999)
Dawson, E.M., Roth, W.H.: Slope stability analysis with FLAC. In Detournay & Hart (eds.), FLAC and Numerical Modeling in Geomechanics: 3–9. Rotterdam: Balkema (1999)
Deb, K., Chandra, S., Basudhar, P.K.: Response of multilayer geosynthetic-reinforced bed resting on soft soil with stone columns. Comput. Geotech. 35(3), 323–330 (2008)
Deb, K., Behera, A.: Rate of consolidation of stone column–improved ground considering variable permeability and compressibility in smear zone. Int. J. Geomech. 17(6),(2016). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.000083.
Ghorbani, A., Hosseinpour, I., Shormage, M.: Deformation and stability analysis of embankment over stone column-strengthened soft ground. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 25(2), 404–416 (2021)
Greenwood, D.A.: Mechanical improvement of soils below ground surface. Conf. Ground. Eng. Inst. Civil. Eng. Lond. Pap. II, 11–22 (1970)
Grizi, A., Al-Ani, W., Wanatowski, D.: Numerical analysis of the settlement behavior of soft soil improved with stone columns. Appl. Sci. 12(11), 5293 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115293
Han, J.: Recent research and development of ground column technologies. Proc. Inst. Civil. Eng-Ground. Improv. 168(4), 246–264 (2015)
Henkel, D.J., Gilbert, G.D.: The effect measured of the rubber membrane on the triaxial compression strength of clay samples. Géotechnique 3(1), 20–29 (1952)
Hosseinpour, I., Almeida, M.S.S., Riccio, M.: Ground improvement of soft soil by geotextile-encased columns. Proc. Inst. Civil. Eng-Ground. Improv. 169(4), 297–305 (2016)
Hosseinpour, I., Ghorbani, A., Zarei, J., Mohapatra, S.R.: Experimental study on the behavior of granular column-treated soft clay under shear loading. Geomech. Geoeng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/17486025.2021.2015977
Indraratna, B., Basack, S., Rujikiatkamjorn, C.: Numerical solution of stone column improved soft soil considering arching, clogging and smear effects. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 139(3), 377–394 (2013)
Jasim, O.H., Tonaroğlu, M.: Using geogrid encased granular columns for embankment’s slope protection: 3D-finite difference analysis. Appl. Sci. 13(4), 2448 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042448
Jayapal, J., Rajagopal, K.: Slope stability analysis of embankment resting on granular columns using FEM. In: Latha Gali, M., P., R.R. (eds) Geotechnical Characterization and Modelling. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 85. Springer, Singapore (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6086-6_25.
Kadhim, S., Parsons, R.L., Han, J.: Stability analysis of embankments supported by geosynthetic encased stone columns. IFCEE: 2318–2327 (2015).
Khabbazian, M., Kaliakin, V., Meehan, C.: Numerical study of the effect of geosynthetic encasement on the behaviour of granular columns. Geosynth. Int. 17, 132–143 (2010)
King, D.J., Bouazza, A., Gniel, J.R., Rowe, R.K., Bui, H.H.: Serviceability design for geosynthetic reinforced column supported embankments. Geotext. Geomembr. 45(4), 261–279 (2017)
Marandi, S.M., Anvar, M., Bahrami, M.: Uncertainty analysis of safety factor of embankment built on stone column improved soft soil using fuzzy logic α-cut technique. Comput. Geotech. 75, 135–144 (2016)
Mirrashed, A., Hosseinpour, I., Mirmoradi, S.H., Ahmadi, H.: Influence of granular columns on the behavior of reinforced-soil wall on layered soft foundation. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotechnol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-022-00241-7
Mohapatra, S.R., Rajagopal, K.: Undrained stability analysis of embankments supported on geosynthetic encased granular columns. Geosynth. Int. 24(5), 465–479 (2017)
Murugesan, S., Rajagopal, K.: Model tests on geosynthetic-encased stone columns. Geosynth. Int. 14(6), 346–354 (2007)
Nimbalkar, S., Karakouzian, M., Bharadwaj, S., Xie, Z., Krause, N.: Field installation effects of stone columns on load settlement characteristics of reinforced soft ground. Int. J. Geomech. 22(4),(2022). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002321.
Pandy, B.K., Rajesh, S., Chandra, S.: Time-dependent behavior of embankment resting on soft clay reinforced with encased stone columns. Transp. Geotech. 36, 100809 (2022)
Priebe, H.J.: The design of vibro replacement. Ground Eng. 28(10), 31–37 (1995)
Thakur, A., Rawat, S., Gupta, A.K.: Experimental study of ground improvement by using encased stone columns Innov. Infrastruct. Solutions. 6(1),(2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-020-00383-y.
Yoo, C.: Settlement behavior of embankment on geosynthetic-encased stone column installed soft ground – A numerical investigation. Geotext. Geomembr. 46(6), 484–492 (2015)
Zhang, Z., Han, J., Ye, G.: Numerical investigation on factors for deep-seated slope stability of stone column-supported embankments over soft clay. Eng. Geol. 168, 104–113 (2014)
Zhang, L., Peng, B., Xu, Z., Zhou, S.: Shear performance of geosynthetic-encased stone column based on 3D-DEM simulation. Comput. Geotech. 151, 104952 (2022)
Zheng, G., Yu, X., Zhou, H., Wang, S., Zhao, J., He, X., Yang, X.: Stability analysis of stone column supported and geosynthetic-reinforced embankments on soft ground. Geotext. Geomembr. 48(3), 349–356 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
It is declared that all the authors whose names are presented in the paper have successfully contributed to this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinpour, I., Rezvani, R. & Ebrahimzade, S. Undrained Stability Analysis of Embankment on Ordinary and Encased-Granular Columns in Soft Clay. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotech. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-023-00339-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-023-00339-6