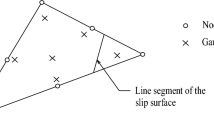
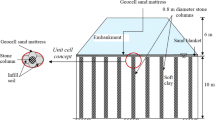
Abstract
Compacted granular columns are commonly used to support embankments over soft soils. Using a reinforcement layer under the embankment causes the total stress to be further transferred to the column rather than soft soil, thus reducing total deformations of the subsoil. In this paper two dimensional (2D) numerical analysis was used to study the influence of stone columns and basal geosynthetic on deformations and stability of an embankment over soft deposit by means of Plaxis 2D finite element code. Unit cell to plane strain conversion approach was applied to transform columns into equivalent walls thus allowing to simulate a full embankment over a group of columns. Comprehensive parametric analysis was then performed to investigate the role of different critical parameters on embankment behavior. Results showed that the use of stone columns yielded the total deformations of the subsoil to significantly reduce, while its influence was less remarkable as a high stiffness geogrid was placed under the embankment. It was also found that the stone column length was the most influential parameter on the embankment total deformations, so that increasing columns length from 0.25Hs to 0.75Hs reduced the vertical and horizontal deformations by about two and five times, respectively. In addition, the use of a high stiffness basal geogrid caused the stability of the embankment to remarkably improve as the value of safety factor at the end of construction increased from 1.25 to about 1.9.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2bc :
-
Thickness of equivalent shear wall (m)
- 2B:
-
Influence thickness of equivalent shear wall (m)
- c⌧ :
-
Cohesion (kPa)
- E s :
-
Elastic modulus of soft soil (kN/m2)
- E c :
-
Elastic modulus of stone column material (kN/m2)
- e :
-
Void ratio (dimensionless)
- H e :
-
Height of embankment (m)
- H s :
-
Thickness of soft soil (m)
- k h :
-
Horizontal soil permeability (m/s)
- k v :
-
Vertical soil permeability (m/s)
- R :
-
Influence radius of one stone column (m)
- r c :
-
Stone column radius (m)
- S :
-
Center to center spacing beyween stone columns (m)
- J :
-
Stiffness of geogrid (kN/m)
- φ s :
-
Angle of shearing resistance of soft soil (degree)
- φ c :
-
Angle of shearing resistance of stone column (degree)
- γ :
-
Unit weight of soil (kN/m3)
- υ :
-
Poisson’s ratio (dimensionless)
- L :
-
Length (m)
- ψ :
-
Dilation angle (degree)
References
Abusharar SW, Han J (2011) Two-dimensional deep-seated slope stability analysis of embankments over stone column-improved soft clay. Engineering Geology 120(1–4):103–110, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.04.002
Al-Bared MAM, Harahap ISH, Marto A, Abad SVANK, Ali MOA (2019) Undrained shear strength and microstructural characterization of treated soft soil with recycled materials. Geomechanics and Engineering 18(4):427–437, DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2019.18.4.427
Al-Bared MAM, Marto A (2017) A review on the geotechnical and engineering characteristics of marine clay and the modern methods of improvements. Malaysian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences 13(4):825–831, DOI: https://doi.org/10.11113/mjfas.v13n4.921
Alfaro MC, Balasubramaniam AS, Bergado D, Chai JC (1994) Improvement techniques of soft ground in subsiding and lowland environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Almeida MSS, Hosseinpour I, Lima B (2019) Field studies of stone columns and geosynthetic-encased columns. From research to applied geotechnics: Invited lectures of the XVI Pan-American conference on soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering (XVI PCSMGE), November 17–20, Cancun, Mexico, 166
Almeida M, Riccio M, Hosseinpour I, Alexiew D (2018) Geosynthetic encased columns for soft soil improvement. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Barksdale RD, Bachus RC (1983) Design and construction of stone columns, vol. I. Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center, McLean, VA, USA
Basack S, Indraratna B, Rujikiatkamjorn C (2016) Analysis of the behaviour of stone column stabilized soft ground supporting transport infrastructure. Procedia Engineering 143:347–354, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.044
Brinkgreve RBJ, Vermeer PA (2012) PLAXIS: Finite element code for soil and rock analyses: version 8.5. Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Cengiz C, Kilic IE, Guler E (2019) On the shear failure mode of granular column embedded unit cells subjected to static and cyclic shear loads. Geotextiles and Geomembranes 47(2):193–202, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.12.011
Debnath P, Dey AK (2017) Bearing capacity of geogrid reinforced sand over encased stone columns in soft clay. Geotextiles and Geomembranes 45(6):653–664, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2017.08.006
Elsawy MBD (2013) Behaviour of soft ground improved by conventional and geogrid-encased stone columns, based on FEM study. Geosynthetics International 20(4):276–285, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/gein.13.00017
Golait YS, Padade AH (2017) Analytical and experimental studies on cemented stone columns for soft clay ground improvement. International Journal of Geomechanics 17(4):4016100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000779
Greenwood DA (1970) Mechanical improvement of soils below ground surface. Proceedings of ground engineering conference, Institute of Civil Engineering, London, UK
Han J (2015a) Principles and practice of ground improvement. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, USA
Han J (2015b) Recent research and development of ground column technologies. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Ground Improvement 168(4):246–264, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/grim.13.00016
Hatami K, Bathurst RJ (2005) Development and verification of a numerical model for the analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced soil segmental walls under working stress conditions. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 42(4):1066–1085, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/t05-040
Hosseinpour I, Almeida MSS, Riccio M (2017a) Verification of a plane strain model for the analysis of encased granular columns. Journal of Geo Engineering 12(4):137–145, DOI: https://doi.org/10.6310/jog.2017.12(4).1
Hosseinpour I, Almeida MSS, Riccio, M, Baroni M (2017b) Strength and compressibility characteristics of a soft clay subjected to ground treatment. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 35(3):1051–1066, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0161-8
Hosseinpour I, Mirmoradi SH, Barari A, Omidvar M (2010) Numerical evaluation of sample size effect on the stress-strain behavior of geotextile-reinforced sand. Journal of Zhejiang University — Science A 11(8):555–562, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900535
Hosseinpour I, Soriano C, Almeida MSS (2019) A comparative study for the performance of encased granular columns. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 11(2):379–388, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.12.002
Indraratna B, Basack S, Rujikiatkamjorn C (2013) Numerical solution of stone column-improved soft soil considering arching, clogging, and smear effects. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 139(3):377–394, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000789
Indraratna B, Ngo NT, Rujikiatkamjorn C, Sloan SW (2015) Coupled discrete element-finite difference method for analysing the load-deformation behaviour of a single stone column in soft soil. Computers and Geotechnics 63:67–278, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.10.002
Johnson A (2012) Recommendations for design and analysis of earth structures using geosynthetic reinforcements-EBGEO. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, USA
Kadhim ST, Parsons RL, Han J (2018) Three-dimensional numerical analysis of individual geotextile-encased sand columns with surrounding loose sand. Geotextiles and Geomembranes 46(6):836–847, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.08.002
Lima BT, Almeida MSS, Hosseinpour I (2019) Field measured and simulated performance of a stone columns-strengthened soft clay deposit. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 1–10, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2019.1653506
Mahawish A, Bouazza A, Gates WP (2018) Improvement of soft soils using bio-cemented sand columns. Proceedings of China-Europe Conference on Geotechnical Engineering, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 822–825
Márcio de Souza SA, Marques MES (2013) Design and performance of embankments on very soft soils. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Mehrannia N, Nazariafshar J, Kalantary F (2018) Experimental investigation on the bearing capacity of stone columns with granular blankets. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 36(1):209–222, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0317-6
Mitchell JK, Huber TR (1985) Performance of a stone column foundation. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 111(2):205–223, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:2(205)
Mohapatra SR, Rajagopal K (2017) Undrained stability analysis of embankments supported on geosynthetic encased granular columns. Geosynthetics International 24(5):465–479, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/jgein.17.00015
Muzammil SP, Varghese RM, Joseph J (2018) Numerical simulation of the response of geosynthetic encased stone columns under oil storage tank. International Journal of Geosynthetics and Ground Engineering 4(1):4, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-017-0122-6
Najjar SS, Sadek S, Maakaroun T (2010) Effect of sand columns on the undrained load response of soft clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 136(9):1263–1277, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000328
Poorooshasb HB, Meyerhof GG (1997) Analysis of behavior of stone columns and lime columns. Computers and Geotechnics 20(1):47–70, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-352X(96)00013-4
Samanta M, Bhowmik R (2019) 3D numerical analysis of piled raft foundation in stone column improved soft soil. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 13(5):474–483, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2017.1368139
Sharma RK (2019) A numerical study of granular pile anchors subjected to uplift forces in expansive soils using PLAXIS 3D. Indian Geotechnical Journal 49(3):304–313, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-018-0333-3
Tan SA, Oo KK (2005) Stone column FEM modeling — 2D and 3D considerations illustrated by case history. Proceedings of international symposium on tsunami reconstruction with geosynthetics, Asian Center for Soil Improvement and Geosynthetics, December 8–9, Bangkok, Thailand, 157–169
Tan SA, Tjahyono S, Oo KK (2008) Simplified plane-strain modeling of stone-column reinforced ground. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 134(2):185–194, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:2(185)
Tandel YK, Solanki CH, Desai AK (2012) Reinforced stone column: Remedial of ordinary stone column. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology 3(2):340
Vinoth M, Prasad PS, Vittal UKG (2019) Performance analysis of PLAXIS models of stone columns in soft marine clay. Geotechnics for Transportation Infrastructure, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 557–569
Xue J, Liu Z, Chen J (2019) Triaxial compressive behaviour of geotextile encased stone columns. Computers and Geotechnics 108:53–60, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.12.010
Zhao L-S, Zhou W-H, Geng X, Yuen K-V, Fatahi B (2019) A closed-form solution for column-supported embankments with geosynthetic reinforcement. Geotextiles and Geomembranes 47(3):389–401, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2019.01.006
Acknowledgments
Not Applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, A., Hosseinpour, I. & Shormage, M. Deformation and Stability Analysis of Embankment over Stone Column-Strengthened Soft Ground. KSCE J Civ Eng 25, 404–416 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0349-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0349-y