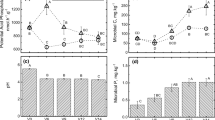
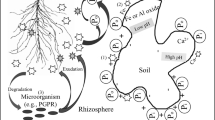
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) is an essential element for crop growth and development. In acid soils, inorganic P (Pi) is immobilised with Fe3+ and Al3+, whereas in calcareous soils, it is fixed with Ca2+. Therefore, P nutrition is not constrained by soil P content per se but by its bioavailability to plants. The large amounts of P fertiliser applied to agricultural land to increase crop P availability can cause eutrophication of non-flowing water bodies. Being a non-renewable resource, P reserves are becoming depleted. Soil P mobilisation is governed by multiple adaptations at the physiological and molecular levels. Below-ground physiological processes including favourable root architecture and morphology, and release of carboxylates, protons and root secretory phosphohydrolases result in significant modification of the rhizosphere microenvironment thereby enhancing P acquisition. Beneficial soil microorganisms work in tandem with plants to mobilise bioavailable soil P. Phosphorus acquisition through rhizosphere modifications is an exciting area of research for plant nutritionists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aski, M. S., Rai, N., Reddy, V. R. P., Gayacharan, Dikshit, H. K., Mishra, G. P., Singh, D., Kumar, A., Pandey, R., Singh, M. P., Pratap, A., Nair, R. M., & Schafleitner, R. (2021). Assessment of root phenotypes in mungbean mini-core collection (MMC) from the World Vegetable Center (AVRDC) Taiwan. PLoS ONE, 16(3), e0247810.
Borah, P., Das, A., Milner, M. J., Ali, A., Bentley, A. R., & Pandey, R. (2018). Long non-coding RNAs as endogenous target mimics and exploration of their role in low nutrient stress tolerance in plants. Genes, 9, 459.
Campos, P., Borie, F., Cornejo, P., Lopez-Raez, J. A., Lopez-Garcia, A., & Seguel, A. (2018). Phosphorus acquisition efficiency related to root traits: Is mycorrhizal symbiosis a key factor to wheat and barley cropping? Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 752.
Campos, P. M. S., Cornejo, P., Rial, C., Borie, F., Varela, R. M., Seguel, A., & Lopez-Raez, J. A. (2019). Phosphate acquisition efficiency in wheat is related to root:shoot ratio, strigolactone levels, and PHO2 regulation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 70(20), 5631–5642.
Carvalhais, L. C., Dennis, P. G., Fedoseyenko, D., Hajirezaei, M.-R., Borriss, R., & von Wiren, N. (2011). Root exudation of sugars, amino acids, and organic acids by maize as affected by nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 3–11.
Chen, Y. L., Dunbabin, V. M., Diggle, A. J., Siddique, K. H. M., & Rengel, Z. (2013). Phosphorus starvation boosts carboxylate secretion in P-deficient genotypes of Lupinus angustifolius with contrasting root structure. Crop and Pasture Science, 64, 588–599.
Ciereszko, I., Zebrowska, E., & Ruminowicz, M. (2011). Acid phosphatases and growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars under diverse phosphorus nutrition. Acta Physiologia Plantarum, 33, 2355–2368.
Cordell, D., & White, S. (2011). Peak phosphorus: Clarifying the key issues of a vigorous debate about long-term phosphorus scarcity. Sustainability, 3, 2027–2049.
Dai, X. Y., Wang, Y. Y., Yang, A., & Zhang, W. H. (2012). OsMYB2P-1, an R2R3 MYB transcription factor, is involved in the regulation of phosphate-starvation responses and root architecture in rice. Plant Physiology, 159, 169–183.
Dechassa, N., & Schenk, M. K. (2004). Exudation of organic anions by roots of cabbage, carrot, and potato as influenced by environmental factors and plant age. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 167, 623–629.
Delhaize, E., Taylor, P., Hocking, P. J., Simpson, R. J., Ryan, P. R., & Richardson, A. E. (2009). Transgenic barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) expressing the wheat aluminium resistance gene (TaALMT1) shows enhanced phosphorus nutrition and grain production when grown on an acid soil. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 7, 391–400.
Deng, S., Lu, L., Li, J., Du, Z., Liu, T., Li, W., Xu, F., Shi, L., Shou, H., & Wang, C. (2020). Purple acid phosphatase 10c encodes a major acid phosphatase that regulates plant growth under phosphate-deficient conditions in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71(14), 4321–4332.
Devaiah, B. N., Karthikeyan, A. S., & Raghothama, K. G. (2007a). WRKY75 transcription factor is a modulator of phosphate acquisition and root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 143, 1789–1801.
Devaiah, B. N., Nagaranjan, V. K., & Raghothama, K. G. (2007b). Phosphate homeostasis and root development in Arabidopsis are synchronized by the zinc finger transcription factor ZAT6. Plant Physiology, 145, 147–159.
Dong, D., Peng, X., & Yan, X. (2004). Organic acid exudation induced by phosphorus deficiency and/or aluminium toxicity in two contrasting soybean genotypes. Physiologia Plantarum, 122, 190–199.
Emami, S., Alikhani, H. A., Pourbabaei, A. A., Etesami, H., Zadeh, B. M., & Sarmadian, F. (2018). Improved growth and nutrient acquisition of wheat genotypes in phosphorus deficient soils by plant growth-promoting rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 64(6), 719–727.
FAO. (2017). http://faostat3.fao.org/browse/Q/QC/E.
Fess, T. L., Kotcon, J. B., & Benedito, V. A. (2011). Crop breeding for low input agriculture: A sustainable response to feed a growing world population. Sustainability, 3, 1742–1772.
Franco-Zorrilla, J. M., Valli, A., Todesco, M., Mateos, I., Puga, M. I., Rubio-Somoza, I., Leyva, A., Weigel, D., Garcia, J. A., & Paz-Ares, J. (2007). Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nature Genetics, 39, 1033–1037.
Furukawa, J., Yamaji, N., Wang, H., Mitani, N., Murata, Y., Sato, K., Katsuhara, M., Takeda, K., & Ma, J. F. (2007). An aluminum-activated citrate transporter in barley. Plant Cell Physiology, 48(8), 1081–1091.
Gahoonia, T. S., Ali, R., Malhotra, R. S., Jahoor, A., & Rahman, M. M. (2007). Variation in root morphological and physiological traits and nutrient uptake of chickpea genotypes. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 30, 829–841.
Gahoonia, T. S., & Nielsen, N. E. (2003). Phosphorus (P) uptake and growth of a root hairless barley mutant (bald root barley, brb) and wild type in low and high P soils. Plant, Cell and Environment, 26, 1759–1766.
Gamuyao, R., Chin, J. H., Pariasca-Tanaka, J., Pesaresi, P., Catausan, S., Dalid, C., Slamet-Loedin, I., Tecson-Mendoza, E. M., Wissuwa, M., & Heuer, S. (2012). The protein kinase Pstol1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorus deficiency. Nature, 488, 535–539.
Gaume, A., Machler, F., Leon, D., Narro, L., & Frossard, E. (2001). Low-P tolerance by maize (Zea mays) genotypes: Significance of root growth, and organic acids and acid phosphatase root exudation. Plant and Soil, 228, 253–264.
Gonzalez-Munoz, E., Avendano-Vazquez, A.-O., Montes, R. A. C., de Folter, S., Andres-Hernandez, L., Abreu-Goodger, C., & Sawers, R. J. H. (2015). The maize (Zea mays ssp. mays var. B73) genome encodes 33 members of the purple acid phosphatase family. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 341.
Gregory, A. L., Hurley, B. A., Tran, H. T., Valentine, A. J., She, Y., Knowles, V. L., & Plaxton, W. C. (2009). In vivo regulatory phosphorylation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase AtPPC1 in phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochemical Journal, 420, 57–65.
Grun, A., Buchner, P., Broadley, M. R., & Hawkesford, M. J. (2018). Identification and expression profiling of Pht1 phosphate transporters in wheat in controlled environments and in the field. Plant Biology, 20, 374–389.
Gunes, A., & Inal, A. (2008). Phosphorus efficiency in sunflower cultivars and its relationships with phosphorus, calcium, iron, zinc and manganese nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 32(7), 1201–1218.
Guo, W., Zhang, L., Zhao, J., Liao, H., Zhuang, C., & Yan, X. (2008). Identification of temporally and spatially phosphate-starvation responsive genes in Glycine max. Plant Science, 175, 574–584.
Guo, W., Zhao, J., Li, X., Qin, L., Yan, X., & Liao, H. (2011). A soybean β-expansin gene GmEXPB2 intrinsically involved in root system architecture responses to abiotic stresses. The Plant Journal, 66, 541–552.
Guppy, C. N., Menzies, N. W., Moody, P. W., & Blamey, F. P. C. (2005). Competitive sorption reactions between phosphorus and organic matter in soil: A review. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 43, 180–201.
Hammond, J. P., Broadley, M. R., & White, P. J. (2004). Genetic responses to phosphorus deficiency. Annals of Botany, 94, 323–332.
Haran, S., Logendra, S., Seskar, M., Bratanova, M., & Raskin, I. (2000). Characterization of Arabidopsis acid phosphatase promoter and regulation of acid phosphatase expression. Plant Physiology, 124, 615–626.
Hsieh, L. C., Lin, S. I., Shih, A. C., Chen, J. W., Lin, W. Y., Tseng, C. Y., Li, W. H., & Chiou, T. J. (2009). Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiology, 151, 2120–2132.
Huang, C. Y., Shirley, N., Genc, Y., Shi, B., & Langridge, P. (2011). Phosphate utilisation efficiency correlates with expression of low-affinity phosphate transporters and noncoding RNA, IPS1, in barley. Plant Physiology, 156(3), 1217–1229.
Jiang, H., Qi, P., Wang, T., Wang, M., Chen, M., Chen, N., Pan, L., & Chi, X. (2018). Isolation and characterization of halotolerant phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms from saline soils. 3 Biotech, 8, 461.
Jones, D. L., Dennis, P. G., Owen, A. G., & van Hees, P. A. W. (2003). Organic acid behavior in soils-misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Plant and Soil, 248, 31–41.
Kafle, A., Cope, K. R., Raths, R., Yakha, J. K., Subramanian, S., Bucking, H., & Garcia, K. (2019). Harnessing soil microbes to improve plant phosphate efficiency in cropping systems. Agronomy, 9, 127.
Kaida, R., Serada, S., Norioka, N., Norioka, S., Neumetzler, L., Pauly, M., Sampedro, J., Zarra, I., Hayashi, T., & Kaneko, T. S. (2010). Potential role for purple acid phosphatase in the dephosphorylation of wall proteins in tobacco cells. Plant Physiology, 153, 603–610.
Khorassani, R., Hettwer, U., Ratzinger, A., Steingrobe, B., Karlovsky, P., & Claassen, N. (2011). Citramalic acid and salicylic acid in sugar beet root exudates solubilize soil phosphorus. BMC Plant XI Biology, 11, 121.
Kochian, L. V., Hoekenga, O. A., & Pineros, M. A. (2004). How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminium tolerance and phosphorus efficiency. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55, 459–493.
Krasilnikoff, G., Gahoonia, T., & Neilsen, N. E. (2003). Variation in phosphorus uptake efficiency by genotypes of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) due to differences in root and root hair length and induced rhizosphere processes. Plant and Soil, 251, 83–91.
Lambers, H., Martinoia, E., & Renton, M. (2015). Plant adaptations to severely phosphorus-impoverished soils. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 25, 23–31.
Lambers, H., Shane, M. W., Cramer, M. D., Pearse, S. J., & Veneklaas, E. J. (2006). Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: Matching morphological and physiological traits. Annals of Botany, 98, 693–713.
Li, C., Gui, S., Yang, T., Walk, T., Wang, X., & Liao, H. (2012). Identification of soybean purple acid phosphatase genes and their expression responses to phosphorus availability and symbiosis. Annals of Botany, 109, 275–285.
Li, J., Xie, Y., Dai, A., Liu, L., & Li, Z. (2009). Root and shoot traits responses to phosphorus deficiency and QTL analysis at seedling stage using introgression lines of rice. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 36, 173–183.
Li, S. M., Li, L., Zhang, F. S., & Tang, C. (2004). Acid phosphatase role in chickpea/maize intercropping. Annals of Botany, 94, 297–303.
Liang, C. Y., Chen, Z. J., Yao, Z. F., Tian, J., & Liao, H. (2012). Characterization of two putative protein phosphatase genes and their involvement in phosphorus efficiency in Phaseolus vulgaris. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 54(6), 400–411.
Liang, C., Pineros, M. A., Tian, J., Yao, Z., Sun, L., Liu, J., Shaff, J., Coluccio, A., Kochian, L. V., & Liao, H. (2013). Low pH, aluminium, and phosphorus coordinately regulate malate exudation through GmALMT1 to improve soybean adaptation to acid soils. Plant Physiology, 161, 1347–1361.
Liang, Q., Cheng, X., Mei, M., Yan, X., & Liao, H. (2010). QTL analysis of root traits as related to phosphorus deficiency in soybean. Annals of Botany, 106, 223–234.
Liao, H., Rubio, G., Yan, X., Cao, A., Brown, K. M., & Lynch, J. P. (2001). Effect of phosphorus availability on basal root shallowness in common bean. Plant and Soil, 232, 69–79.
Liu, J., Magalhaes, J. V., Shaff, J., & Kochian, L. V. (2009). Aluminum-activated citrate and malate transporters from the MATE and ALMT families function independently to confer Arabidopsis aluminum tolerance. The Plant Journal, 57, 389–399.
Liu, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Lu, W., Li, X., & Xiao, K. (2013). TaPht1;4, a high-affinity phosphate transporter gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum), plays an important role in plant phosphate acquisition under phosphorus deprivation. Functional Plant Biology, 40(4), 329–341.
Lopez-Bucio, J., Cruz-Ramirez, A., & Herrera-Estrella, L. (2003). The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6, 280–287.
Lu, L., Qiu, W., Gao, W., Tyerman, S. D., Shou, H., & Wang, C. (2016). OsPAP10c, a novel secreted acid phosphatase in rice, plays an important role in the utilization of external organic phosphorus. Plant, Cell and Environment, 39(10), 2247–2259.
Lung, S., & Lim, B. L. (2006). Assimilation of phytate-phosphorus by the extracellular phytase activity of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) is affected by the availability of soluble phytate. Plant and Soil, 279, 187–199.
Lynch, J. P., & Ho, M. D. (2005). Rhizoeconomics: Carbon costs of phosphorus acquisition. Plant and Soil, 269, 45–56.
Lyu, Y., Tang, H. L., Li, H. G., Zhang, F. S., Rengel, Z., Whalley, W. R., et al. (2016). Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1939.
Magalhaes, J. V., Liu, J., Guimaraes, C. T., Ubiraci, G. P. L., Alves, V. M. C., Wang, T. H., Schaffert, R. E., Hoekenga, O. A., Pineros, M. A., Shaff, J. E., Klein, P. E., Carneiro, N. P., Coelho, C. M., Trick, H. N., & Kochian, L. V. (2007). A gene in the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family confers aluminum tolerance in sorghum. Nature Genetics, 39, 1156–1161.
Magalhaes, P. C., de Souza, T. C., & Cantao, F. R. O. (2011). Early evaluation of root morphology of maize genotypes under phosphorus deficiency. Plant, Soil and Environment, 57, 135–138.
Maron, L. G., Pineros, M. A., Guimaraes, C. T., Magalhaes, J. V., Pleiman, J. K., Mao, C., Shaff, J., Belicuas, S. N. J., & Kochian, L. V. (2010). Two functionally distinct members of the MATE (multi-drug and toxic compound extrusion) family of transporters potentially underlie two major aluminium tolerance QTLs in maize. The Plant Journal, 61(5), 728–740.
Meena, S. K., Pandey, R., Sharma, S., Gayacharan, K. T., Singh, M. P., & Dikshit, H. K. (2021). Physiological basis of combined stress tolerance to low phosphorus and drought in a diverse set of mungbean germplasm. Agronomy—Basel, 11, 99.
Mehra, P., Pandey, B. K., & Giri, J. (2017). Improvement in phosphate acquisition and utilization by a secretory purple acid phosphatase (OsPAP21b) in rice. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 15, 1054–1067.
Miao, J., Sun, J., Liu, D., Li, B., Zhang, A., Li, Z., & Tong, Y. (2009). Characterization of the promoter of phosphate transporter TaPHT1.2 differentially expressed in wheat varieties. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 36(8), 455–466.
Miura, K., Lee, J., Gong, Q., Ma, S., Jin, J. B., Yoo, C. Y., Miura, T., Sato, A., Bohnert, H. J., & Hasegawa, P. M. (2011). SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodelling involves the control of auxin accumulation. Plant Physiology, 155, 1000–1012.
Muller, J., Godde, V., Niehaus, K., & Zorb, C. (2015). Metabolic adaptations of white lupin roots and shoots under phosphorus deficiency. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 1014.
Neumann, G., & Romheld, V. (2012). Rhizosphere chemistry in relation to plant nutrition. In P. Marschner (Ed.), Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants (pp. 347–368). Academic Press.
Nguyen, V. L., Palmer, L., Roessner, U., & Stangoulis, J. (2019). Genotypic variation in the root and shoot metabolite profiles of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) indicate sustained, preferential carbon allocation as a potential mechanism in phosphorus efficiency. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 995.
Niu, T. F., Chai, R. S., Jin, G. L., Wang, H., Tang, C. X., & Zhang, Y. S. (2013). Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: A review. Annals of Botany, 112(2), 391–408.
O’Rourke, J. A., Yang, S. S., Miller, S. S., Bucciarelli, B., Liu, J., Rydeen, A., Bozsoki, Z., Udhe-Stone, C., Tu, Z. J., Allan, D., Gronwald, J. W., & Vance, C. P. (2013). An RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis of orthophosphate-deficient white lupin reveals novel insights into phosphorus acclimation in plants. Plant Physiology, 161, 705–724.
Olczak, M., Morawiecka, B., & Wątorek, W. (2003). Plant purple acid phosphatases: Genes, structures and biological function. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 50, 1245–1256.
Pandey, B. K., Mehra, P., Verma, L., Bhadouria, J., & Giri, J. (2017). OsHAD1, a haloacid dehalogenase-like APase, enhances phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiology, 174, 2316–2332.
Pandey, R. (2006). Root-exuded acid phosphatase and 32Pi-uptake kinetics of wheat, rye and triticale under phosphorus starvation. Journal of Nuclear and Agricultural Biology, 35(3 & 4), 168–179.
Pandey, R., Lal, M. K., & Vengavasi, K. (2018). Differential response of hexaploid and tetraploid wheat to interactive effects of elevated [CO2] and low phosphorus. Plant Cell Reports, 37, 1231–1244.
Pandey, R., Meena, S. K., Krishnapriya, V., Ahmad, A., & Kishora, N. (2014). Root carboxylate exudation capacity under phosphorus stress does not improve grain yield in green gram. Plant Cell Reports, 33, 919–928.
Pandey, R., Singh, B., & Nair, T. V. R. (2005). Impact of arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi on phosphorus use efficiency on wheat, rye and triticale. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 28, 1867–1876.
Pandey, R., Singh, B., & Nair, T. V. R. (2006). Effect of arbuscular-mycorrhizal inoculation in low phosphorus soil in relation to P utilization efficiency of wheat genotypes. The Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 76(6), 349–353.
Pandey, R., Zinta, G., AbdElgawad, H., Ahmad, A., Jain, V., & Janssens, I. A. (2015). Physiological and molecular alterations in plants exposed to high [CO2] under phosphorus stress. Biotechnology Advances, 33, 303–316.
Pant, B. D., Buhtz, A., Kehr, J., & Scheible, W. R. (2008). MicroRNA399 is a long-distance signal for the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis. The Plant Journal, 53, 731–738.
Park, K. H., Lee, C. Y., & Son, H. J. (2009). Mechanism of insoluble phosphate solubilization by Pseudomonas fluorescens RAF15 isolated from ginseng rhizosphere and its plant growth-promoting activities. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 49, 222–228.
Parniske, M. (2008). Arbuscular mycorrhiza: The mother of plant root endosymbioses. Nature Reviews in Microbiology, 6, 763–775.
Pearse, S. J., Veneklaas, E. J., Cawthray, G., Bolland, M. D., & Lambers, H. (2007). Carboxylate composition of root exudates does not relate consistently to a crop species’ ability to use phosphorus from aluminium, iron or calcium phosphate sources. New Phytologist, 173, 181–190.
Peret, B., Clement, M., Nussaume, L., & Desnos, T. (2011). Root development adaptation to phosphate starvation: Better safe than sorry. Trends in Plant Science, 16, 442–450.
Perez-Torres, C. A., Lopez-Bucio, J., Cruz-Ramirez, A., Ibarra-Laclette, E., Dharmasiri, S., Estelle, M., & Herrera-Estrella, L. (2008). Phosphate availability alters lateral root development in Arabidopsis by modulating auxin sensitivity via a mechanism involving the TIR1 auxin receptor. The Plant Cell, 20, 3258–3272.
Pii, Y., Mimmo, T., Tomasi, N., Terzano, R., Cesco, S., & Crecchio, C. (2015). Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: Beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 51, 403–415.
Plaxton, W. C., & Tran, H. T. (2011). Metabolic adaptations of phosphate-starved plants. Plant Physiology, 156, 1006–1015.
Qin, L., Guo, Y., Chen, L., Liang, R., Gu, M., Xu, G., Zhao, J., Walk, T., & Liao, H. (2012). Functional characterization of 14 Pht1 family genes in yeast and their expressions in response to nutrient starvation in soybean. PLoS ONE, 7, e47726.
Raghothama, K. G. (1999). Phosphate acquisition. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 50(1), 665–693.
Reddy, V. R, P., Aski, M. S., Mishra, G. P., Dikshit, H. K., Singh, A., Pandey, R, Singh, M. P., Gayacharan, Ramtekey, V., Priti, Rai, N., & Nair R. M. (2020). Genetic variation for root architectural traits in response to phosphorus deficiency in mungbean at the seedling stage. PLoS ONE, 15(6), e0221008.
Ribot, C., Wang, Y., & Poirier, Y. (2008). Expression analyses of three members of the AtPHO1 family reveal differential interactions between signaling pathways involved in phosphate deficiency and the responses to auxin, cytokinin, and abscisic acid. Planta, 227(5), 1025–1036.
Richardson, A. E., Barea, J., McNeill, A. M., & Prigent-Combaret, C. (2009). Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant and Soil, 321, 305–339.
Rodriguez, H., Fraga, R., Gonzalez, T., & Bashan, Y. (2006). Genetics of phosphate solubilization and its potential applications for improving plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant and Soil, 287, 15–21.
Rose, T. J., Hardiputra, B., & Rengel, Z. (2010). Wheat, canola and grain legume access to soil phosphorus fractions differs in soils with contrasting phosphorus dynamics. Plant and Soil, 326, 159–170.
Rose, T. J., Impa, S. M., Rose, M. T., Pariasca, T. J., Mori, A., Heuer, S., Johnson-Beebout, S. E., & Wissuwa, M. (2012). Enhancing phosphorus and zinc acquisition efficiency in rice: A critical review of root traits and their potential utility in rice breeding. Annals of Botany, 112(2), 331–345.
Ryan, P. R., James, R. A., Weligama, C., Delhaize, E., Rattey, A., Lewis, D. C., Bovill, W. D., McDonald, G., Rathjen, T. M., Wang, E., Fettell, N. A., & Richardson, A. E. (2014). Can citrate efflux from roots improve phosphorus uptake by plants? Testing the hypothesis with near-isogenic lines of wheat. Physiologia Plantarum, 151(3), 230–242.
Ryan, P. R., Tyerman, S. D., Sasaki, T., Furuichi, T., Yamamoto, Y., Zhang, W. H., & Delhaize, E. (2011). The identification of aluminium-resistance genes provides opportunities for enhancing crop production on acid soils. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62, 9–20.
Sasaki, T., Yamamoto, Y., Ezaki, B., Katsuhara, M., Ahn, S. J., Ryan, P. R., Delhaize, E., & Matsumoto, H. (2004). A wheat gene encoding an aluminium-activated malate transporter. The Plant Journal, 37, 645–653.
Shane, M. W., Cramer, M. D., Funayama-Noguchi, S., Cawthray, G. R., Millar, A. H., Day, D. A., & Lambers, H. (2004). Developmental physiology of cluster-root carboxylate synthesis and exudation in Harsh Hakea. Expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and the alternative oxidase. Plant Physiology, 135, 549–560.
Sharma, M., Pang, J., Wen, Z., Borda, A. D., Kim, H. S., Liu, Y., Lambers, H., Ryan, M. H., & Siddique, K. H. M. (2021). A significant increase in rhizosheath carboxylates and greater specific root length in response to terminal drought is associated with greater relative phosphorus acquisition in chickpea. Plant and Soil, 460, 51–68.
Shen, H., Chen, J., Wang, Z., Yang, C., Sasaki, T., Yamamoto, Y., Matsumoto, H., & Yan, X. (2007). Root plasma membrane H+-ATPase is involved in the adaptation of soybean to phosphorus starvation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 1353–1362.
Sidhu, S. K., Kaur, K., & Grewal, S. K. (2017). Genotypic variation for phosphorus efficiency of pigeonpea genotypes under varied phosphorus levels. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 6(11), 3633–3647.
Singh, B., & Pandey, R. (2003). Differences in root exudation among phosphorus-starved genotypes of maize and green gram and its relationship with phosphorus uptake. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 26, 2391–2401.
Soumya, P. R. (2020). Study of association between candidate genes and traits governing phosphorus use efficiency in wheat. Ph.D. thesis, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India.
Soumya, P. R., Sharma, S., Meena, M. K., & Pandey, R. (2021). Response of diverse bread wheat genotypes in terms of root architectural traits at seedling stage in response to low phosphorus stress. Plant Physiology Reports, 26(1), 152–161.
Tawayara, K., Horie, R., Shinano, T., Wagatsuma, T., Saito, K., & Oikawa, A. (2014). Metabolite profiling of soybean root exudates under phosphorus deficiency. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 60(5), 679–694.
Teng, W., Deng, Y., Chen, X. P., Xu, X. F., Chen, R. Y., Lv, Y., Zhao, Y. Y., Zhao, X. Q., He, X., Li, B., Tong, Y. P., Zhang, F. S., & Li, Z. S. (2013). Characterization of root response to phosphorus supply from morphology to gene analysis in field-grown wheat. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64(5), 1403–1411.
Teng, W., Zhao, Y. Y., Zhao, X. Q., He, X., Ma, W. Y., Deng, Y., Chen, X. P., & Tong, Y. P. (2017). Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of PHT1 phosphate transporters in wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 543.
Tesfaye, M., Temple, S. J., Allan, D. L., Vance, C. P., & Samac, D. A. (2001). Overexpression of malate dehydrogenase in transgenic alfalfa enhances organic acid synthesis and confers tolerance to aluminium. Plant Physiology, 127, 1836–1844.
Thudi, M., Chen, Y., Pang, J., Kalavikatte, D., Bajaj, P., Roorkiwal, M., Chitikineni, A., Ryan, M. H., Lambers, H., Siddique, K. H. M., & Varshney, R. K. (2021). Novel genes and genetic loci associated with root morphological traits, phosphorus-acquisition efficiency and phosphorus-use efficiency in chickpea. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 636973.
Tian, J., & Liao, H. (2015). The role of intracellular and secreted purple acid phosphatases in plant phosphorus scavenging and recycling. Annual Plant Reviews: Phosphorus Metabolism in Plants, 48, 265–288.
Tiessen, H. (2008). Phosphorus in the global environment. In P. J. White & J. P. Hammond (Eds.), Ecophysiology of plant-phosphorus interactions (pp. 1–8). Springer.
Tovkach, A., Ryan, P. R., Richardson, A. E., Lewis, D. C., Rathjen, T. M., Ramesh, S., Tyerman, S. D., & Delhaize, E. (2013). Transposon-mediated alteration of TaMATE1B expression in wheat confers constitutive citrate efflux from root apices. Plant Physiology, 161(2), 880–892.
Uhde-Stone, C., Gilbert, G., Jonhson, J. M. F., Litjens, R., Zinn, K. E., Temple, S. J., Vance, C. P., & Allan, D. L. (2003). Acclimation of white lupin to phosphorus deficiency involves enhanced expression of genes related to organic acid metabolism. Plant and Soil, 248, 99–116.
Veljanovski, V., Vanderbeld, B., Knowles, V. L., Snedden, W. A., & Plaxton, W. C. (2006). Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP26, a vacuolar purple acid phosphatase up-regulated in phosphate-deprived Arabidopsis suspension cells and seedlings. Plant Physiology, 142(3), 1282–1293.
Veneklaas, E. J., Stevens, J., Cawthray, G. R., Turner, S., Grigg, A. M., & Lambers, H. (2003). Chickpea and white lupin rhizosphere carboxylates vary with soil properties and enhance phosphorus uptake. Plant and Soil, 248, 187–197.
Vengavasi, K., & Pandey, R. (2016). Root exudation index as a physiological marker for efficient phosphorus acquisition in soybean: An effective tool for plant breeding. Crop and Pasture Science, 67, 1096–1109.
Vengavasi, K., Pandey, R., Abraham, G., & Yadav, R. K. (2017). Comparative analysis of soybean root proteome reveals molecular basis of differential carboxylate efflux under low phosphorus stress. Genes, 8, 341.
Wan, W., Qin, Y., Wu, H., Zuo, W., He, H., Tan, J., Wang, Y., & He, D. (2020). Isolation and characterization of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria with multiple phosphorus sources utilizing capability and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 752.
Wang, L., & Shen, J. (2019). Root/Rhizosphere management for improving phosphorus use efficiency and crop productivity. Better Crops, 103(1), 36–39.
Wang, X., Tang, C., Guppy, C. N., & Sale, P. W. G. (2008). Phosphorus acquisition characteristics of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) under P deficient conditions. Plant and Soil, 312, 117–128.
Wang, Y., Krogstad, T., Clarke, N., Ogaard, A. F., & Clarke, J. L. (2017). Impact of phosphorus on rhizosphere organic anions of wheat at different growth stages under field conditions. AoB PLANTS, 9, plx008. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plx008.
Wang, Y., & Lambers, H. (2020). Root-released organic anions in response to low phosphorus availability: Recent progress, challenges and future perspectives. Plant and Soil, 447, 135–156.
Wang, Y., Xu, H., Kou, J., Shi, L., Zhang, C., & Xu, F. (2013). Dual effects of transgenic Brassica napus overexpressing CS gene on tolerances to aluminium toxicity and phosphorus deficiency. Plant and Soil, 362, 231–246.
Wang, Z., Li, Q., Ge, X., Yang, C. L., Luo, X. L., Zhang, A. H., Xiao, J. L., Tian, Y. C., Xia, G. X., Chen, X. Y., Li, F. G., & Wu, J. H. (2015). The mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase 1 gene GhmMDH1 is involved in plant and root growth under phosphorus deficiency conditions in cotton. Scientific Reports, 5, 10343.
Wasaki, J., Yamamura, T., Shinano, T., & Osaki, M. (2003). Secreted acid phosphatase is expressed in cluster roots of lupin in response to phosphorus deficiency. Plant and Soil, 248, 129–136.
White, P. J. (2012). Ion uptake mechanisms of individual cells and roots: Short-distance transport. In P. Marschner (Ed.), Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants (pp. 7–47). Academic Press.
Wongkaew, A., Srinives, P., & Nakasathien, S. (2013). Isolation and characterization of purple acid phosphatase gene during seedling development in mungbean. Biologia Plantarum, 57(2), 267–273.
Wu, A., Fang, Y., Liu, S., Wang, H., Xu, B., Zhang, S., Deng, X., Palta, J. A., Siddique, K. H. M., & Chen, Y. (2021). Root morphology and rhizosheath acid phosphatase activity in legume and graminoid species respond differently to low phosphorus supply. Rhizosphere, 19, 100391.
Yan, X., Liao, H., Beebe, S. E., Blair, M. W., & Lynch, J. P. (2004). QTL mapping for root hair and acid exudation traits and their relationship to phosphorus uptake in common bean. Plant and Soil, 265, 17–29.
Ye, D., Zhang, X., Li, T., Xu, J., & Chen, G. (2017). Phosphorus-acquisition characteristics and rhizosphere properties of wild barley in relation to genotypic differences as dependent on soil phosphorus availability. Plant and Soil, 423, 503–516.
Yokosho, K., Yamaji, N., Ueno, D., Mitani, N., & Ma, J. F. (2009). OsFRDL1 is a citrate transporter required for efficient translocation of iron in rice. Plant Physiology, 149, 297–305.
Yun, S. J., & Kaeppler, S. M. (2001). Induction of maize acid phosphatase activities under phosphorus starvation. Plant and Soil, 237, 109–115.
Zebrowska, E., Milewska, M., & Ciereszko, I. (2017). Mechanisms of oat (Avena sativa L.) acclimation to phosphate deficiency. Peer Journal, 5, e3989.
Zeng, H., Wang, G., Hu, X., Wang, H., Du, L., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Role of microRNAs in plant responses to nutrient stress. Plant and Soil, 374, 1005–1021.
Zhang, D., Cheng, H., Geng, L., Kan, G., Cui, S., Meng, Q., Gai, J., & Yu, D. (2009). Detection of quantitative trait loci for phosphorus deficiency tolerance at soybean seedling stage. Euphytica, 167, 313–322.
Zhao, J., Fu, J., Liao, H., He, Y., Nian, H., Hu, Y., Qiu, L., Dong, Y., & Yan, X. (2004). Characterization of root architecture in an applied core collection for phosphorus efficiency of soybean germplasm. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49, 1611–1620.
Ziegler, J., Schmidt, S., Chutia, R., Muller, J., Bottcher, C., Strehmel, N., et al. (2016). Non-targeted profiling of semi-polar metabolites in Arabidopsis root exudates uncovers a role for coumarin secretion and lignification during the local response to phosphate starvation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67, 1421–1432.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Extra Mural Research Division [Grant Number 38(1354)/13/EMR-II] of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, India, to RP. Rothamsted Research receives grant-aided support from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) through the Designing Future Wheat programme [BB/P016855/1] to MJH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vengavasi, K., Pandey, R., Soumya, P.R. et al. Below-ground physiological processes enhancing phosphorus acquisition in plants. Plant Physiol. Rep. 26, 600–613 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-021-00627-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-021-00627-8