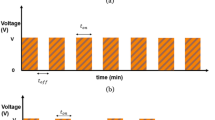
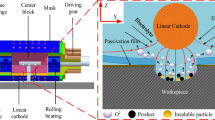
Abstract
High quality micro mould tools are critical for ensuring defect-free production of micro injection moulded products. The demoulding stage of the micro injection moulding can adversely affect the surface integrity due to friction, adhesion and thermal stresses between the metallic mould and polymeric replicated part. In the present work, we propose the use of precision electropolishing (EP) as a shaping and polishing process to control the draft angle and fillet radius of micro features in order to ease demoulding. Typical defects that occur in replicated polymer parts include cracks, burrs and distorted features. A nickel mould having multiple linear ridges and star shape patterns was designed for the present investigation to have characteristic dimensions ranging from 10 μm to 150 μm and with various aspect ratios to study the effect of electropolishing on modifying the shape of micro features and surface morphology. A transient 2D computational analysis has been conducted to anticipate the effect of shaping on the Ni mould after electrochemical polishing with non-uniform material removal rates, based on the distribution of current density. The experimental results indicate that after shaping using EP, the draft angle of star-patterns and linear patterns can be effectively increased by approximately \(3.6^\circ\), while the fillet radius increases by up to 5.0 μm. By controlling the electropolishing process, the surface roughness can be maintained under 50 nm. This work uses a green and environmental friendly nickel sulfamate electrolyte which can be effective for shaping of nickel micro features without causing any surface deposition.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H, Zhang H, Guan T et al (2021) Prototyping and production of polymeric microfluidic chip. Adv Microfluid Nanofluid. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.96355
Abdulhameed A, Halim MM, Halin IA (2023) Simulation and experimental validation of the interplay between dielectrophoretic and electroosmotic behavior of conductive and insulator particles for nanofabrication and lab-on-chip applications. Colloid Surface A 663:131065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.131065
Davis R, Singh A, Jackson MJ et al (2022) A comprehensive review on metallic implant biomaterials and their subtractive manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 120(3/4):1473–1530
Wang X, Li C, Zhang Y et al (2022) Influence of texture shape and arrangement on nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 119(1/2):631–646
Wang Y, Weng C, Deng Z et al (2023) Fabrication and performance of nickel-based composite mold inserts for micro-injection molding. Appl Surf Sci 615:156417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156417
Li J, Ma H, Liu W et al (2023) Effects of cavity thickness and mold surface roughness on the polymer flow during micro injection molding. Polymers 15(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020326
Moazzez B, O’Brien SM, Merschrod SEF (2013) Improved adhesion of gold thin films evaporated on polymer resin: applications for sensing surfaces and MEMS. Sensors 13(6):7021–7032
Chen J, Yang J, Zhou M et al (2021) Self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiols on nickel insert: characterization of friction and analysis on demolding quality in microinjection molding. Micromachines 12(6):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060636
Peixoto C, Valentim PT, Sousa PC et al (2022) Injection molding of high-precision optical lenses: a review. Precis Eng 76:29–51
Zhang N, Zhang H, Stallard C et al (2018) Replication integrity of micro features using variotherm and vacuum assisted microinjection moulding. CIRP J Manuf Sci Tec 23:20–38
Liarte E, Zambrano V, Gracia LA et al (2022) Demoulding process assessment of elastomers in micro-textured moulds. Open Res Europe 1:120. https://doi.org/10.12688/openreseurope.13716.2
Zariatin DL, Kiswanto G, Ko T (2017) Investigation of the micro-milling process of thin-wall features of aluminum alloy 1100. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 93:2625–2637
Raza S, Nadda R, Nirala C (2023) Real-time data acquisition and discharge pulse analysis in controlled RC circuit based micro-EDM. microsyst Technol 29(3):359–376
Arruebo M, Fernández-Pacheco R, Ibarra MR et al (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2(3):22–32
Schoenherr M, Ruehl H, Guenther T et al (2023) Adhesion-induced demolding forces of hard coated microstructures measured with a novel injection molding tool. Polymers 15(5):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051285
Jong WR, Li TC, Chen YW et al (2017) Automatic recognition and construction of draft angle for injection mold design. Journal of Software Engineering and Applications (JSEA) 10(1):78–93
Łosiewicz B (2015) Electrodeposition mechanism of composite coatings. Solid State Phenom 228:65–78
Obilor AF, Pacella M, Wilson A et al (2022) Micro-texturing of polymer surfaces using lasers: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 120(1/2):103–135
Lee H, Yi A, Choi J et al (2022) Texturing of polydimethylsiloxane surface for anti-reflective films with super-hydrophobicity in solar cell application. Appl Surf Sci 584:152625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152625
Ji JW, Khan MA, Zhan ZJ et al (2022) Electrochemical polishing of tungsten: an investigation of critical spatial frequency and ultimate roughness. J Electrochem Soc 169(4):043509. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac63fa
Li M, Chen Y, Luo W et al (2021) Demolding force dependence on mold surface modifications in UV nanoimprint lithography. Microelectron Eng 236:111470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2020.111470
Kim SH, Asay DB, Dugger MT (2007) Nanotribology and MEMS. Nano Today 2(5):22–29
Chang WT, Hwang IS, Chang MT et al (2012) Method of electrochemical etching of tungsten tips with controllable profiles. Rev Sci Instrum 83:083704. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4745394
Chen X, Yuan Q (2023) Capillary adhesion around the shapes optimized by dissolution. Adv Mater Interfaces 10(13):2202380. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202202380
Zaki S, Zhang N, Gilchrist MD (2022) Electropolishing and shaping of micro-scale metallic features. Micromachines 13(3):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030468
Li D, Zhang Y, Liu Y et al (2022) Injection moulding of mechanical micro-manufactured structures for optically encoding plastic surfaces. Opt Mater 123:111822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111822
Zhang H, Zhang N, Fang F (2021) Investigation of mass transfer inside micro structures and its effect on replication accuracy in precision micro electroforming. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 165:103717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2021.103717
Saitta L, Arcadio F, Celano G et al (2023) Design and manufacturing of a surface plasmon resonance sensor based on inkjet 3D printing for simultaneous measurements of refractive index and temperature. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 124(7/8):2261–2278
Zhang N, Liu J, Zhang H et al (2019) 3D printing of metallic microstructured mould using selective laser melting for injection moulding of plastic microfluidic devices. Micromachines 10(9):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090595
Martinho PG, Pouzada AS (2021) Alternative materials in moulding elements of hybrid moulds: structural integrity and tribological aspects. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 113(1):351–363
Shao L, Pan B, Hou R et al (2022) User-friendly microfluidic manufacturing of hydrogel microspheres with sharp needle. Biofabrication 14(2):025017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ac57a5
Bolat G, De la Paz E, Azeredo NF et al (2022) Wearable soft electrochemical microfluidic device integrated with iontophoresis for sweat biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 414(18):5411–5421
Li L, Li H, Kou G et al (2022) Dynamic camouflage characteristics of a thermal infrared film inspired by honeycomb structure. J Bionic Eng 19(2):458–470
Guan B, Pai JH, Cherrill M et al (2022) Injection moulding of micropillar arrays: a comparison of poly (methyl methacrylate) and cyclic olefin copolymer. Microsyst Technol 28:2083–2091
Chu Q, Wu A, Tan T et al (2021) Electropolishing behavior of niobium in choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. Appl Surf Sci 550:149322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149322
Kityk A, Protsenko V, Danilov F et al (2021) Enhancement of the surface characteristics of Ti-based biomedical alloy by electropolishing in environmentally friendly deep eutectic solvent (Ethaline). Colloid Surface A 613:126125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126125
Jeong J, Yoon W, Chung B et al (2021) Fabrication of eco-friendly graphene nanoplatelet electrode for electropolishing and its properties. Appl Sci-basel 11(7):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073224
Kumar R (2019) MEMS based cantilever biosensors for cancer detection using potential bio-markers present in VOCs: a survey. Microsyst Technol 25(9):3253–3267
Pong-Ryol J, Tae-Sok J, Nam-Chol K et al (2016) Laser micro-polishing for metallic surface using UV nano-second pulse laser and CW laser. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 85(9):2367–2375
Yang B, Ai Y (2022) Facile fabrication of CuO nanosheets and in situ transmission electron microscopy/X-ray diffraction heating characterization of microstructure evolution. Phys Status Solidi A 219(6):2100617. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.202100617
Shen H, Liao C, Zhou J et al (2021) Two-step laser based surface treatments of laser metal deposition manufactured Ti6Al4V components. J Manuf Process 64:239–252
Du L, Guo B, Dong Y et al (2022) A wearable omnidirectional inertial switch of security detection for the elderly. Microsyst Technol 28:2011–2021
Zhao Y, Qian S, Zhang Y et al (2021) Experimental study on uniformity of copper layer with microstructure arrays by electroforming. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 114(7):2019–2030
Zaki S, Zhang N, Gilchrist MD (2022) Potentiodynamic polarization behaviour of Ni for shaping and electropolishing of micro-mould tools. In: Proceedings of the 38th international manufacturing conference (IMC38), University College Dublin, Dublin
Paul R, Hackert-Oschätzchen M, Danilov I et al (2019) 3D multiphysics simulation of jet electrochemical machining of intersecting line removals. Procedia CIRP 82:196–201
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Science Foundation Ireland and I-Form (Grant No. 16/RC/3872).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zaki, S., Zhang, N. & Gilchrist, M.D. Microscale shaping and rounding of ridge arrays and star pattern features on nickel mould via electrochemical polishing. Adv. Manuf. 12, 207–226 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-023-00474-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-023-00474-w