Abstract
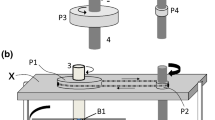
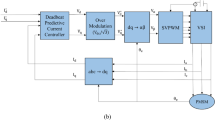
This work proposes a systematic procedure for the dynamic modeling of linear permanent magnet synchronous motors comprising the parameter determination and the development of a numerical co-simulation setup combining mechanical, electrical, and magnetic analysis. A theoretical model is obtained based on the equivalence between the rotary and linear machines, and its parameters are determined through numerical analysis and verified by experimental tests on a prototype of a slotless tubular electromagnetic actuator with a double quasi-Halbach array of permanent magnets. A co-simulation environment using the finite element model of the actuator is developed to demonstrate that this tool can also be used for the dynamic analysis of linear machines. The validation of the analytical and co-simulation models is carried out with experimental tests performed on the prototype under three different open-loop voltage excitation signals in the synchronous reference frame: step, sinusoidal, and triangular wave. The proposed modeling, parameter determination procedure, and co-simulation setup can be seen as reliable tools for the analysis of the machine dynamic performance and future control design without the need for a prototype.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boff, B. H. B., Zanatta, A. P., Dorrell, D. G., & Eckert, P. R. (2017). Influence of end effects on direct-and quadrature-axis inductances in linear electromagnetic actuators. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 53(11), 1–7.
Boff, B. H. B., Tavares, R. B., Flores Filho, A. F., & Eckert, P. R. (2019). Analysis of end pole sizing effects in linear permanent magnet synchronous actuators with quasi-halbach arrays. In 2019 12th international symposium on linear drives for industry applications (LDIA). IEEE.
Ebersberger, S., & Piepenbreier, B. (2012). Identification of differential inductances of permanent magnet synchronous machines using test current signal injection. In International symposium on power electronics power electronics, electrical drives: Automation and motion. IEEE.
Eckert, P., Flores Filho, A., Perondi, E., Ferri, J., & Goltz, E. (2016). Design methodology of a dual-halbach array linear actuator with thermal-electromagnetic coupling. Sensors, 16(3), 360.
Eckert, P. R., Flores Filho, A. F., Perondi, E. A., & Dorrell, D. G. (2018). Dual quasi-halbach linear tubular actuator with coreless moving-coil for semiactive and active suspension. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65(12), 9873–9883.
Fang, S., Lin, H., & Ho, S. (2009). Transient co-simulation of low voltage circuit breaker with permanent magnet actuator. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 45(3), 1242–1245.
Hall, S., Marquez-Fernandez, F. J., & Alakula, M. (2017). Dynamic magnetic model identification of permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 32(4), 1367–1375.
Li, L., Hong, J., Wu, H., Kou, B., & Liu, R. (2011). Direct and quadrature inductances measurement of the permanent magnetic linear synchronous machines. Energy Conversion and Management, 52(5), 2282–2287.
Liang, W., Wang, J., Lu, T., & Fang, W. (2014). A new method for multiple finite-element models in cosimulation with electrical circuit using machine multiloop modeling scheme. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61(12), 6583–6590.
Liu, Z.-H., Wei, H.-L., Li, X.-H., Liu, K., & Zhong, Q.-C. (2018). Global identification of electrical and mechanical parameters in PMSM drive based on dynamic self-learning PSO. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 33(12), 10858–10871.
Pereira, L. A., Perin, M., & Pereira, L. F. A. (2018). A new method to estimate induction machine parameters from the no-load startup transient. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 30(1), 41–53.
Schoonhoven, G., & Uddin, M. N. (2017). Harmonic injection-based adaptive control of IPMSM motor drive for reduced motor current THD. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 53(1), 483–491.
Štumberger, G., Štumberger, B., & Marčič, T. (2019). Magnetically nonlinear dynamic models of synchronous machines and experimental methods for determining their parameters. Energies, 12(18), 3519.
Susperregui, A., Tapia, G., & Tapia, A. (2007). Application of two alternative sliding-mode control approaches to DC servomotor position tracking. IET Electric Power Applications, 1(4), 611.
Tursini, M., Villani, M., Tullio, A. D., Fabri, G., & Collazzo, F. P. (2017). Nonlinear model suitable for the offline cosimulation of fault-tolerant PM motors drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 53(4), 3719–3729.
Vas, P. (1998). Sensorless Vector and Direct Torque Control. Monographs in electrical and electronic engineering. Oxford University Press.
Wang, Z., Chinthavali, M., Campbell, S. L., Wu, T., & Ozpineci, B. (2019). A 50-kW air-cooled SiC inverter with 3-d printing enabled power module packaging structure and genetic algorithm optimized heatsinks. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 55(6), 6256–6265.
Yan, L., Zhang, L., Jiao, Z., Hu, H., Chen, C.-Y., & Chen, I.-M. (2014). Armature reaction field and inductance of coreless moving-coil tubular linear machine. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61(12), 6956–6965.
Zanatta, A. P., Boff, B. H. B., Eckert, P. R., Flores Filho, A. F., & Dorrell, D. G. (2018). Tubular linear permanent magnet synchronous machine applied to semi-active suspension systems. COMPEL, 37(5), 1781–1794.
Zhu, X., Cheng, M., Zhao, W., Liu, C., & Chau, K. (2007). A transient cosimulation approach to performance analysis of hybrid excited doubly salient machine considering indirect field-circuit coupling. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 43(6), 2558–2560.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001; by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul—Brasil (FAPERGS)—Code 17/2551-0000897-9; and by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brasil (CNPq), Grants: GD-142369/2018-7 and PQ-306223/2018-0. Data available on request from the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boff, B.H.B., Flores, J.V., Flores Filho, A.F. et al. Dynamic Modeling of Linear Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Determination of Parameters and Numerical Co-simulation. J Control Autom Electr Syst 32, 1782–1794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-021-00749-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-021-00749-2