Abstract
Introduction
Hypertension represent the commonest cause of death in 2017. Hypertension is classified into two types which are primary or essential hypertension and secondary hypertension. The perindopril–amlodipine combination showed a significant effect in reduction of the elevated BP and the cardiovascular complications.
Aim
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose single-pill combination of perindopril–amlodipine in hypertensive patients.
Methods
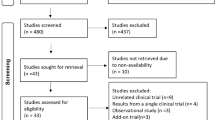
We searched PubMed, Medline, SCOPUS, and Web of Science for relevant clinical trials. Quality appraisal was evaluated according to GRADE and we assessed the risk of bias using Cochrane’s risk of bias tool. We included the following outcomes: systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure, mean blood pressure, heart rate, cough, dizziness, headache, and peripheral edema. We performed the analysis of homogeneous data under the fixed-effects model, while analysis of heterogeneous data was analyzed under the random-effects model. We conducted a meta-regression according to the dose.
Results
We included ten clinical trials. The pooled analysis showed that there was a significant reduction of the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse plessure, mean blood pressure, and heart rate after the the perindopril–amlodipine combination (MD = 18.96 [14.32, 23.60], P < 0.0001), (MD = 11.90 [8.45, 15.35], P < 0.0001), (MD = 8.44 [6.91, 9.97], P = 0.0001), (MD = 13.07 [5.86, 20.29], P = 0.0004), and (MD = 2.93 [0.89, 4.96], P = 0.005), respectively. The results of the meta-regression revealed that the efficacy is increased by increasing the dose (P < 0.001)
Conclusion
The use of the perindopril–amlodipine combination had a significant effect on the reduction of SBP, DBP, mean blood pressure, pulse pressure, and HR.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available to any researcher who contact the corresponding author.
References
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical Pr. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:e127–248.
Erratum: Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Di. Lancet. 2019.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Rosei EA, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Kardiol Pol. 2019;77:71–159.
Oparil S, Acelajado MC, Bakris GL, Berlowitz DR, Cífková R, Dominiczak AF et al. Hypertension. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2018;18014. Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/nrdp201814
Fagard R, Brguljan J, Staessen J, Thijs L, Derom C, Thomis M, et al. Heritability of conventional an ambulatory blood pressures: a study in twins. Hypertension. 1995;26:919–24.
Streeten DHP, Anderson GH. Secondary hypertension. Drugs. 1992;43:805–19.
Hosseinnezhad A, Black RM, Aeddula NR, Adhikari D, Trivedi N. Glucagon-induced pheochromocytoma crisis. Endocr Pract. 2011;17:e51–4.
Biswas S, Dastidar DG, Roy KS, Pal SK, Biswas TK, Ganguly SB. Complications of hypertension as encountered by primary care physician. J Indian Med Assoc. 2003;101:257–9.
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 Evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults. JAMA. 2014;311:507.
Leape L, Berwick D, Clancy C, Conway J, Gluck P, Guest J, et al. Transforming healthcare: a safety imperative. Qual Saf Heal Care. 2009;18:424–8.
Turnbull F. Effects of different blood pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events in individuals with and without diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1410.
Turnbull F, Neal B, Algert C, Chalmers J, Woodward M, MacMahon S, et al. Effects of different blood-pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively-designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet. 2003;362:1527–35.
Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK, Bestwick JP, Wald NJ. Combination therapy versus monotherapy in reducing blood pressure: meta-analysis on 11,000 participants from 42 trials. Am J Med. 2009;122:290–300.
Law MR, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Jordan RE. Value of low dose combination treatment with blood pressure lowering drugs: Analysis of 354 randomised trials. Br Med J. 2003;326:1427.
Dimmitt SB, Stampfer HG. Low drug doses may improve outcomes in chronic disease. Med J Aust. 2009;191:511–3.
Dahlöf B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, Wedel H, Beevers DG, Caulfield M, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-B). Lancet. 2005;366:895–906.
Bangalore S, Kamalakkannan G, Parkar S, Messerli FH. Fixed-dose combinations improve medication compliance: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2007;120:713–9.
Hamrahian SM. Medication non-adherence: a major cause of resistant hypertension. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22:133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-020-01400-3.
Hurst M, Jarvis B. Perindopril: an updated review of its use in hypertension. Drugs. 2001;61:867–96. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200161060-00020.
Fares H, DiNicolantonio JJ, O’Keefe JH, Lavie CJ. Amlodipine in hypertension: a first-line agent with efficacy for improving blood pressure and patient outcomes. Open Heart. 2016;3: e000473. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2016-000473.
Taylor SH. Usefulness of amlodipine for angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1994;73:A28–33.
Gradman AH, Cutler NR, Davis PJ, Robbins JA, Weiss RJ, Wood BC. Combined enalapril and felodipine extended release (ER) for systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79:431–5.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Antes G, Atkins D, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Rev Esp Nutr Humana Diet. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1.
Katz A. Microsoft Excel 2010. Style (DeKalb, IL). 2010.
Clarivate EndNote | Available from: https://endnote.com/.
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2019.
Ojji DB, Mayosi B, Francis V, Badri M, Cornelius V, Smythe W, et al. Comparison of dual therapies for lowering blood pressure in black Africans. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2429–39. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1901113.
Mancia G, Asmar R, Amodeo C, Mourad J-J, Taddei S, Gamba MAA, et al. Comparison of single-pill strategies first line in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2015;33:401–11.
Laurent S, Parati G, Chazova I, Sirenko Y, Erglis A, Laucevicius A, et al. Randomized evaluation of a novel, fixed-dose combination of perindopril 3.5 mg/amlodipine 2.5 mg as a first-step treatment in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2015;33:653–62.
Hu D, Sun Y, Liao Y, Huang J, Zhao R, Yang K. Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose perindopril arginine/amlodipine in hypertensive patients not adequately controlled with amlodipine 5 mg or perindopril tert-butylamine 4 mg monotherapy. Cardiology. 2016;134:1–10.
Elliott WJ, Whitmore J, Feldstein JD, Bakris GL. Efficacy and safety of perindopril arginine + amlodipine in hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2015.01.012.
Visco V, Finelli R, Pascale AV, Giannotti R, Fabbricatore D, Ragosa N, et al. Larger blood pressure reduction by fixed-dose compared to free dose combination therapy of ACE inhibitor and calcium antagonist in hypertensive patients. Transl Med. 2017;16:17–23.
Sobngwi E, Mfeukeu-Kuate L, Kouam M, Tankeu AT, Nganou-Gnindjio CN, Hamadou B, et al. Short-term effects of perindopril-amlodipine vs perindopril-indapamide on blood pressure control in sub-Saharan type 2 diabetic individuals newly diagnosed for hypertension: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21:1002–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13557.
Redon J, Pichler G. Comparative study of the efficacy of olmesartan/amlodipine vs. perindopril/amlodipine in peripheral blood pressure after missed dose in type 2 diabetes. J Hypertens. 2016;34:359–67.
Ramirez AJ, Sanchez MJ, Sanchez RA. Diabetic patients with essential hypertension treated with amlodipine. J Hypertens. 2019;37:636–42.
Poulter NR, Dolan E, Gupta AK, O’Brien E, Whitehouse A, Sever PS. Efficacy and safety of incremental dosing of a new single-pill formulation of perindopril and amlodipine in the management of hypertension. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2019;19:313–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40256-018-00314-4.
Jamerson KA, Nwose O, Jean-Louis L, Schofield L, Purkayastha D, Baron M. Initial angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/calcium channel blocker combination therapy achieves superior blood pressure control compared with calcium channel blocker monotherapy in patients with stage 2 hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:495–501.
Philipp T, Glazer RD, Wernsing M, Yen J. Initial combination therapy with amlodipine/valsartan compared with monotherapy in the treatment of hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2011;5:417–24.
Chrysant SG, Melino M, Karki S, Lee J, Heyrman R. The combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine besylate in controlling high blood pressure: COACH, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 8-week factorial efficacy and safety study. Clin Ther. 2008;30:587–604.
Littlejohn TW, Majul CR, Olvera R, Seeber M, Kobe M, Guthrie R, et al. Results of treatment with telmisartan-amlodipine in hypertensive patients. J Clin Hypertens. 2009;11:207–13.
Brown MJ, McInnes GT, Papst CC, Zhang J, MacDonald TM. Aliskiren and the calcium channel blocker amlodipine combination as an initial treatment strategy for hypertension control (ACCELERATE): a randomised, parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2011;377:312–20.
Packard KA, Wurdeman RL, Arouni AJ. ACE inhibitor-induced bronchial reactivity in patients with respiratory dysfunction. Ann Pharmacother. 2002;36:1058–67.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2159–219.
Hackam DG, Khan NA, Hemmelgarn BR, Rabkin SW, Touyz RM, Campbell NRC, et al. The 2010 Canadian hypertension education program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 2—therapy. Can J Cardiol. 2010;26:249–58.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, et al. Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–52. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2.
Sofy AA, Abdelsattar AT, Mohammed OM, Shareef MA, Alamodi AA, Nso N, et al. Amlodipine compared with benidipine in the management of hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2020;27:527–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-020-00412-y.
Habboush S, Sofy AA, Masoud AT, Cherfaoui O, Farhat AM, Abdelsattar AT, et al. Efficacy of single-pill, triple antihypertensive therapy in patients with uncontrolled hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2022;29:245–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-022-00511-y.
Mourad J-J, Waeber B, Zannad F, Laville M, Duru G, Andrjak M. Comparison of different therapeutic strategies in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2004;22:2379–86.
Correction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:2125. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735109711013246
van Vark LC, Bertrand M, Akkerhuis KM, Brugts JJ, Fox K, Mourad J-J, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors reduce mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors involving 158 998 patients. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2088–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehs075.
Schünemann HJ, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, et al. Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, et al., editors. Cochrane Handb. Syst. Rev. Interv. Boca Raton: Wiley; 2019. p. 375–402.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that there are no confict of interest.
Ethical Approval
No ethical approvals were required for this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mostafa, S., Shabana, H., Khalil, F. et al. Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Dual Therapy Perindopril/Amlodipine in the Management of Hypertension. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 29, 565–576 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-022-00544-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-022-00544-3