Abstract
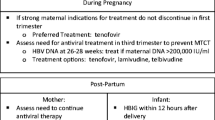
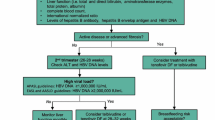
The proper management of pregnant women infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is necessary to prevent maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality and to protect the baby from HBV infection. In the majority of cases, vertical transmission can be prevented with a universal screening program, HBV vaccine immunoprophylaxis, and administration of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIg) for babies born to mothers with HBV. However, in mothers with a high viral load (>200,000 or >1,000,000 IU/ml, depending on the guideline), the chance of immunoprophylaxis failure remains high. The standard recommendation is to give an antiviral agent during the third trimester in these patients. US FDA pregnancy category B agents such as tenofovir and telbivudine are allowed through all trimesters of pregnancy. Breastfeeding for patients who receive antiviral agents can be allowed after a risk–benefit discussion with the patient.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117–71.
World Health Organization. Hepatitis B fact sheet. Geneva: WHO. 2016. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/. Accessed 15 July 2016.
Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30(12):2212–9.
Lavanchy D. Worldwide epidemiology of HBV infection, disease burden, and vaccine prevention. J Clin Virol. 2005;34(Suppl. 1):S1–3.
Jonas MM. Hepatitis B and pregnancy: an underestimated issue. Liver Int. 2009;29(Suppl. 1):133–9.
Stevens CE, Beasley RP, Tsui J, Lee WC. Vertical transmission of hepatitis B antigen in Taiwan. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:771–4.
Chang MH. Natural history of hepatitis B virus infection in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:E16–9.
Tassopoulos NC, Papaevangelou GJ, Sjogren MH, Roumeliotou-Karayannis A, Gerin JL, Purcell RH. Natural history of acute hepatitis B surface antigen-positive hepatitis in Greek adults. Gastroenterology. 1987;92:1844–50.
McMahon BJ, Alward WL, Hall DB, Heyward WL, Bender TR, Francis DP, et al. Acute hepatitis B virus infection: relation to the clinical expression of disease and subsequent development of the carrier state. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:599–603.
Kao JH. Hepatitis B vaccination and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29(6):907–17.
Chang MH, You SL, Chen CJ, Liu CJ, Lee CM, Lin SM, et al. Decreased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B vaccinees: a 20-year follow-up study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:1348–55.
Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(1):261–83.
European Association for the Study of the Liver, et al. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2012;57(1):167–85.
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan HL, Chen CJ, et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 2016;10(1):1–98.
Dragosics B, Ferenci P, Hitchman E, Denk H. Long-term follow-up study of asymptomatic HBsAg-positive voluntary blood donors in Austria: a clinical and histologic evaluation of 242 cases. Hepatology. 1987;7(2):302–6.
Pirutvisuth T. Optimal management of HBV infection during pregnancy. Liver Int. 2013;33(1):188–94.
Pan CQ, Lee HM. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B in pregnancy. Semin Liver Dis. 2013;33(2):138–46.
Sirilert S, Traisrisilp K, Sirivatanapa P, Tongsong T. Pregnancy outcomes among chronic carriers of hepatitis B virus. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2014;126(2):106–10.
Tan J, Surti B, Saab S. Pregnancy and cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2008;14:1081–91.
Shaheen AAM, Myers RP. The outcomes of pregnancy in patients with cirrhosis: a population-based study. Liver Int. 2010;30:275–83.
Russell MA, Craigo SD. Cirrhosis and portal hypertension in pregnancy. Semin Perinatol. 1998;22:156–65.
Britton RC. Pregnancy and esophageal varices. Am J Surg. 1982;143:421–5.
ter Borg MJ, Leemans WF, de Man RA, Janssen HL. Exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection after delivery. J Viral Hepat. 2008;15:37–41.
Lin HH, Chen PJ, Chen DS, Sung JL, Yang KH, Young YC, et al. Postpartum subsidence of hepatitis B viral replication in HBeAg-positive carrier mothers. J Med Virol. 1989;29:1–6.
Dyson JK, Waller J, Turley A, Michael E, Moses S, Valappil M, et al. Hepatitis B in pregnancy. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2014;5:111–7.
Giles M, Visvanathan K, Lewin S, Bowden S, Locarnini S, Spelman T, et al. Clinical and virological predictors of hepatic flares in pregnant women with chronic hepatitis B. Gut. 2015;64:1810–5.
Tan HH, Lui HF, Chow WC. Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in pregnancy. Hepatol Int. 2008;2:370.
Nguyen V, Tan PK, Greenup AJ, Glass A, Davison S, Samarasinghe D, et al. Anti-viral therapy for prevention of perinatal HBV transmission: extending therapy beyond birth does not protect against post-partum flare. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:1225–34.
Chang CY, Aziz N, Poongkunran M, Javaid A, Trinh HN, Lau D, Nguyen MH. Serum alanine aminotransferase and hepatitis B DNA flares in pregnant and postpartum women with chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(10):1410–5.
He T, Jia J. Chronic HBV: which pregnant women should be treated? Liver Int. 2016;36(Suppl. S1):105–8.
Patton H, Tran TT. Management of hepatitis B during pregnancy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:402–9.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry Steering Committee. The Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry interim report. 1 January 1989 through 31 January 2016. http://www.apregistry.com/forms/interim_report.pdf. Accessed 26 Nov 2016.
DegliEsposti S, Shah D. Hepatitis B in pregnancy: challenges and treatment. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2011;40:355–72.
Pan CQ, Duan ZP, Bhamidimarri KR, Zou HB, Liang XF, Li J, et al. An algorithm for risk assessment and intervention of mother to child transmission of hepatitis B virus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10(5):452–9.
Wiseman E, Fraser MA, Holden S, et al. Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus: an Australian experience. Med J Aust. 2009;190:489–92.
Zou H, Chen Y, Duan Z, Zhang H, Pan C. Virologic factors associated with failure to passive-active immunoprophylaxis in infants born to HbsAg positive mothers. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19:e18–25.
Xu DZ, Yan YP, Choi BC, Xu JQ, Men K, Zhang JX, et al. Risk factors and mechanism of transplacental transmission of hepatitis B virus: a case–control study. J Med Virol. 2002;67:20–6.
Wong VC, Lee AK, Ip HM. Transmission of hepatitis B antigens from symptom free carrier mothers to the fetus and the infant. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1980;87:958–65.
Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Stevens CE, Lin CC, Hsieh FJ, Wang KY, et al. Efficacy of hepatitis B immune globulin for prevention of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus carrier state: final report of a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 1983;3(2):135–41.
Schalm SW, Mazel JA, de Gast GC, Heijtink RA, Botman MJ, Banffer JR, et al. Prevention of hepatitis B infection in newborns through mass screening and delayed vaccination of all infants of mothers with hepatitis B surface antigen. Pediatrics. 1989;83(6):1041–8.
Stevens CE, Toy PT, Tong MJ, Taylor PE, Vyas GN, Nair PV, et al. Perinatal hepatitis B virus transmission in the United States. Prevention by passive-active immunization. JAMA. 1985;253(12):1740–5.
Ko TM, Tseng LH, Chang MH, Chen DS, Hsieh FJ, Chuang SM, et al. Amniocentesis in mothers who are hepatitis B virus carriers does not expose the infant to an increased risk of hepatitis B virus infection. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 1994;255:25–30.
Alexander JM, Ramus R, Jackson G, Sercely B, Wendel GD Jr. Risk of hepatitis B transmission after amniocentesis in chronic hepatitis B carriers. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7:283–6.
Towers CV, Asrat T, Rumney P. The presence of hepatitis B surface antigen and deoxyribonucleic acid in amniotic fluid and cord blood. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;184:1514–8.
Yi W, Pan CQ, Hao J, Hu Y, Liu M, Li L, Liang D. Risk of vertical transmission of hepatitis B after amniocentesis in HBs antigen-positive mothers. J Hepatol. 2014;60(3):523–9.
Dionne-Odom J, Tita AT, Silverman NS. # 38: Hepatitis B in pregnancy screening, treatment, and prevention of vertical transmission. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(1):6–14.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Global routine vaccination coverage—2012. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62:858–61.
Wong VC, Ip HM, Reesink HW, Lelie PN, Reerink-Brongers EE, Yeung CY, et al. Prevention of the HBsAg carrier state in newborn infants of mothers who are chronic carriers of HBsAg and HBeAg by administration of hepatitis-B vaccine and hepatitis B immunoglobulin: double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet. 1984;1(8383):921–6.
Lo KJ, Tsai YT, Lee SD, Wu JC, Wu TC, Yang ZL, et al. Combined passive and active immunization for interruption of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan. Hepatogastroenterology. 1985;32(2):65–8.
Chen SC, Toy M, Yeh JM, Wang JD, Resch S. Cost-effectiveness of augmenting universal hepatitis B vaccination with immunoglobin treatment [erratum appears in Pediatrics 2014;133(2):346]. Pediatrics. 2013;131(4):e1135–43. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-1262.
Lolekha S, Warachit B, Hirunyachote A, Bowonkiratikachorn P, West DJ, Poerschke G. Protective efficacy of hepatitis B vaccine without HBIG in infants of HBeAg-positive carrier mothers in Thailand. Vaccine. 2002;20(31–32):3739–43.
Hu Y, Zhang S, Luo C, Liu Q, Zhou YH. Gaps in the prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus between recommendations and routine practices in a highly endemic region: a provincial population-based study in China. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:221.
Huang Y, Li L, Sun X, Lu M, Liu H, Tang G, et al. Screening of pregnant women for hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) and subsequent management, Qiandongnan prefecture, Guizhou, China, 2010. Vaccine. 2013;31(Suppl. 9):S62–5.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Hepatitis B vaccine birthdose practices in a country where hepatitis B is endemic—Laos, December 2011–February 2012. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62(29):587–90.
Wang J, Zhu Q, Zhang X. Effect delivery mode on maternal-infant transmission of hepatitis B virus by immunoprophylaxis. Chin Med J. 2002;115:1510–2.
Yang J, Zeng X, Men Y, Zhao L. Elective caesarean section versus vaginal delivery for preventing mother to child transmission of hepatitis B virus—a systematic review. Virol J. 2008;5:100.
Zou H, Chen Y, Duan Z, Zhang H, Pan C. A retrospective study for clinical outcome of caesarean section on perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus in infants born to HBeAg positive mothers with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Hepatology. 2010;52(Suppl(1)):441A.
Pan CQ, Zou HB, Chen Y, Zhang X, Zhang H, Li J, Duan Z. Cesarean section reduces perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection from hepatitis B surface antigen-positive women to their infants. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11(10):1349–55.
Luo ZB, Li LJ, Ruan B. Impact of the implementation of a vaccination strategy on hepatitis B virus infections in China over a 20-year period. Int J Infect Dis. 2012;16:e82–8.
Lee C, Gong Y, Brok J, Boxall EH, Gluud C. Effect of hepatitis B immunization in newborn infants of mothers positive for hepatitis B surface antigen: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2006;332:328–36.
van Zonneveld M, van Nunen AB, Niesters HG, de Man RA, Schalm SW, Janssen HL, et al. Lamivudine treatment during pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat. 2003;10:294–7.
Xu WM, Cui YT, Wang L, Yang H, Liang ZQ, Li XM, et al. Lamivudine in late pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Viral Hepat. 2009;16(2):94–103.
Han L, Zhang H-W, Xie J-X, Zhang Q, Wang HY, Cao GW, et al. A meta-analysis of lamivudine for interruption of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4321–33.
Han GR, Cao MK, Zhao W, Jiang HX, Wang CM, Bai SF, et al. A prospective and open-label study for the efficacy and safety of telbivudine in pregnancy for the prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2011;55(6):1215–21.
Zhang H, Pan CQ, Pang Q, Tian R, Yan M, Liu X. Telbivudine or lamivudine use in late pregnancy safely reduces perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus in real-life practice. Hepatology. 2014;60(2):468–76.
Wu Q, Huang H, Sun X, Pan M, He Y, Tan S, et al. Telbivudine prevents vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus from women with high viral loads: a prospective long-term study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(6):1170–6.
Chen HL, Lee CN, Chang CH, Ni YH, Shyu MK, Chen SM, et al.; Taiwan Study Group for the Prevention of Mother-to-Infant Transmission of HBV (PreMIT Study); Taiwan Study Group for the Prevention of Mother-to-Infant Transmission of HBV PreMIT Study. Efficacy of maternal tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in interrupting mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 2015;62(2):375–86.
Pan CQ, Duan Z, Dai E, Zhang S, Han G, Wang Y, et al.; China Study Group for the Mother-to-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B. Tenofovir to prevent hepatitis B transmission in mothers with high viral load. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(24):2324–34.
Greenup AJ, Tan PK, Nguyen V, Glass A, Davison S, Chatterjee U, et al. Efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol. 2014;61(3):502–7.
Fan L, Owusu-Edusei K Jr, Schillie SF, Murphy TV. Cost-effectiveness of testing hepatitis B-positive pregnant women for hepatitis B e antigen or viral load. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(5):929–37.
Hung HF, Chen HH. Cost-effectiveness analysis of prophylactic lamivudine use in preventing vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. Pharmacoeconomics. 2011;29(12):1063–73.
Wang W, Wang J, Dang S, Zhuang G. Cost-effectiveness of antiviral therapy during late pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. PeerJ. 2016;24(4):e1709.
Hill JB, Sheffield JS, Kim MJ, Alexander JM, Sercely B, Wendel GD. Risk of hepatitis B transmission in breast-fed infants of chronic hepatitis B carriers. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:1049–52.
Shi Z, Yang Y, Wang H, Ma L, Schreiber A, Li X, et al. Breastfeeding of newborns by mothers carrying hepatitis B virus: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2011;165(9):837–46.
World Health Organization. Hepatitis B and breastfeeding. No. 22. Geneva: WHO; 1996. http://www.who.int/child_adolescent_health/documents/pdfs/hepatitis_b_and_breastfeeding.pdf. Accessed 27 Nov 2016.
Benaboud S, Pruvost A, Coffie PA, Ekouévi DK, Urien S, Arrivé E, et al. Concentrations of tenofovir and emtricitabine in breast milk of HIV-1-infected women in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, in the ANRS12109 TEmAA Study, step 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:1315–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Naichaya Chamroonkul has no conflicts of interest. Teerha Piratvisuth has received research grants from Geliad, MSD, and BMS and consulting fees or speakers’ honoraria from Geliad, MSD, BMS, Roche, GSK, Novatis, and Bayers.
Funding
No sources of funding were used to support the writing of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamroonkul, N., Piratvisuth, T. Hepatitis B During Pregnancy in Endemic Areas: Screening, Treatment, and Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission. Pediatr Drugs 19, 173–181 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-017-0229-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-017-0229-1